Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00219) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Dapsone
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aczone; Atrisone; Avlosulfon; Avlosulfone; Avlosulphone; Avsulfor; Croysulfone; Croysulphone; DADPS; DDS; Dapson; Dapsona; Dapsonum; Diaminodifenilsulfona; Diaminodiphenylsulfone; Diaphenylsulfon; Diaphenylsulfone; Diaphenylsulphon; Diaphenylsulphone; Diphenasone; Diphone; Disulone; Dubronax; Dubronaz; Dumitone; Eporal; Novophone; Protogen; Sulfadione; Sulfona; Sulfonyldianiline; Sulphadione; Sulphonyldianiline; Tarimyl; Udolac; Araldite HT; D SS; Diaminodifenilsulfona [Spanish]; Diaminodiphenyl sulfone;Fatol Brand of Dapsone; Metabolite C; Orsade Brand of Dapsone; Sulfone ucb; Sumicure S; Araldite HT 976; F 1358; HT 976; HY 976; Hardener HT 976; W R 448; WR 448; ALBB-005917; AZT + Dapsone cominbation; Aczone (TN); DDS (pharmaceutical); DDS, diaphenylsulfone; DDS, pharmaceutical; DSS (VAN); Dapsoderm-X; Dapson-Fatol; Dapsona [INN-Spanish]; Dapsone (USP); Dapsone [USAN:BAN]; Dapsonum [INN-Latin];Diamino-diphenyl sulphone; Diaphenylsulfone (JAN); IN-201; Mex-America Brand of Dapsone; P-Aminophenyl sulfone; Sulfanona-mae; Sulfon-mere; Sulfona-MAE; Sulphon-mere; Bis(4-aminophenyl) sulfone; Bis(4-aminophenyl)sulfone; Bis(4-aminophenyl)sulphone; Bis(p-aminophenyl) sulfone; Bis(p-aminophenyl)sulphone; Di(4-aminophenyl) sulfone; Di(4-aminophenyl)sulfone; Di(4-aminophenyl)sulphone; Di(p-aminophenyl) sulfone; Di(p-aminophenyl)sulphone; P,p-Diaminodiphenyl sulphone; P,p-Sulfonylbisbenzamine; P,p-Sulfonylbisbenzenamine; P,p-Sulphonylbisbenzamine; P,p-Sulphonylbisbenzenamine; P,p-Sulphonyldianiline; N, N'-Diphenyl sulfondiamide; N,N'-Diphenyl sulfondiamide; P, p'-Sulfonyldianiline; P,p'-Diaminodiphenyl sulfone; P,p'-sulfonyldianiline; Diamino-4,4'-diphenyl sulfone; Diamino-4,4'-diphenyl sulphone; Sulfone, 4,4'-Diaminophenyl; (4-sulfanilylphenyl)amine; 1,1'-Sulfonylbis(4-aminobenzene); 1,1'-Sulfonylbis[4-aminobenzene]; 1,1'-Sulphonylbis(4-aminobenzene); 4,4' Diaminophenyl Sulfone; 4,4'-Dapsone; 4,4'-Diaminodiphenyl sulfone; 4,4'-Diaminodiphenyl suphone; 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylsulfone; 4,4'-Sulfonylbisaniline; 4,4'-Sulfonylbisbenzamine; 4,4'-Sulfonylbisbenzenamine; 4,4'-Sulfonyldianiline;4,4'-Sulfonyldianiline (Dapsone); 4,4'-Sulphonylbisbenzamine; 4,4'-Sulphonylbisbenzenamine; 4,4'-Sulphonyldianiline; 4,4'-diaminophenyl sulfone; 4,4-Diaminodifenylsulfon; 4,4-Diaminodifenylsulfon [Czech]; 4,4-Sulfonyldianiline; 4-(4-aminophenyl)sulfonylaniline; 4-Aminop henyl sulfone; 4-Aminophenyl sulfone; 4-Aminophenylsulfone; 4-[(4-aminobenzene)sulfonyl]aniline; 4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]aniline
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
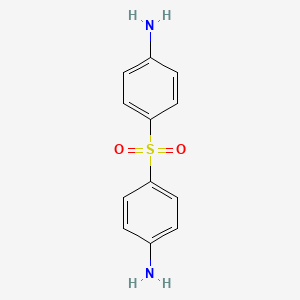
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Pneumocystis carinii Dihydropteroate synthase (PC DHPS) | FOL1_PNECA | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C12H12N2O2S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1N)S(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C12H12N2O2S/c13-9-1-5-11(6-2-9)17(15,16)12-7-3-10(14)4-8-12/h1-8H,13-14H2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MQJKPEGWNLWLTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T53A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium leprae isolates | 1769 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Footpad granuloma from M. leprae-infected nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and single-stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mouse footpad assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations genes reported in this study have been demonstrated to be responsible for drug resistance by mouse footpad assay. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P55R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium leprae isolates | 1769 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Footpad granuloma from M. leprae-infected nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and single-stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mouse footpad assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations genes reported in this study have been demonstrated to be responsible for drug resistance by mouse footpad assay. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase/DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (DHFR/RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | folP p.P55L+poB p.S531L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium leprae isolates | 1769 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Footpad granuloma from M. leprae-infected nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and single-stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mouse footpad assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations genes reported in this study have been demonstrated to be responsible for drug resistance by mouse footpad assay. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase/DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (DHFR/RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | folP p.P55S+rpoB p.S531L+rpoB p.V547I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium leprae isolates | 1769 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Footpad granuloma from M. leprae-infected nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and single-stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mouse footpad assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations genes reported in this study have been demonstrated to be responsible for drug resistance by mouse footpad assay. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase/DNA gyrase subunit A/DNA gyrase subunit B (DHFR/GYRA/GYRB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | folP p.P55L+gyrA p.A91V+gyrB p.A91V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium leprae isolates | 1769 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Footpad granuloma from M. leprae-infected nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and single-stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mouse footpad assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations genes reported in this study have been demonstrated to be responsible for drug resistance by mouse footpad assay. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase/DNA gyrase subunit A/DNA gyrase subunit B (DHFR/GYRA/GYRB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | folP p.P55L+gyrA p.D205N+gyrB p.D205N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium leprae isolates | 1769 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Footpad granuloma from M. leprae-infected nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and single-stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mouse footpad assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations genes reported in this study have been demonstrated to be responsible for drug resistance by mouse footpad assay. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
