Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00205) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
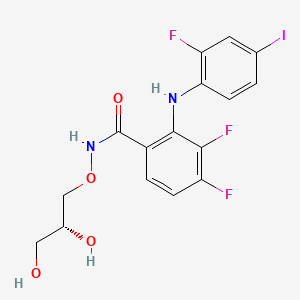
PD-0325901
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PD 0325901; PD 325901; PD0325901; PD325901; PD-325901; S06-0029; N-[((R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl)oxy]-3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]benzamide; N-[(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]-3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodo-phenyl)amino]benzamide; N-{[(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}-3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]benzamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[1]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | MAPK/ERK kinase kinase (MAP3K) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H14F3IN2O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1=CC(=C(C=C1I)F)NC2=C(C=CC(=C2F)F)C(=O)NOC[C@@H](CO)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H14F3IN2O4/c17-11-3-2-10(16(25)22-26-7-9(24)6-23)15(14(11)19)21-13-4-1-8(20)5-12(13)18/h1-5,9,21,23-24H,6-7H2,(H,22,25)/t9-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SUDAHWBOROXANE-SECBINFHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MAPK/ERK kinase 2 (MEK2) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V215E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS/RAF/MEk signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| HCT-116 MEk-R cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V401 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
BrdUrd assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The RAS/RAF/MEk pathway is activated in more than 30% of human cancers, most commonly via mutation in the k-ras oncogene and also via mutations in BRAF. Importantly, in all cases the MEk-resistant cell lines retained their addiction to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPk) pathway, as evidenced by their sensitivity to a selective inhibitor of the ERk1/2 kinases. These data suggest that tumors with acquired MEk inhibitor resistance remain dependent on the MAPk pathway and are therefore sensitive to inhibitors that act downstream of the mutated MEk target. | |||
| Key Molecule: MAPK/ERK kinase 1 (MEK1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F129L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS/RAF/MEk signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| HCT-116 MEk-R cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V401 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
BrdUrd assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The RAS/RAF/MEk pathway is activated in more than 30% of human cancers, most commonly via mutation in the k-ras oncogene and also via mutations in BRAF. Importantly, in all cases the MEk-resistant cell lines retained their addiction to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPk) pathway, as evidenced by their sensitivity to a selective inhibitor of the ERk1/2 kinases. These data suggest that tumors with acquired MEk inhibitor resistance remain dependent on the MAPk pathway and are therefore sensitive to inhibitors that act downstream of the mutated MEk target. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MAPK/ERK kinase 1 (MEK1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L115P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS/RAF/MEk signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| HCT-116 MEk-R cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V401 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
BrdUrd assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The RAS/RAF/MEk pathway is activated in more than 30% of human cancers, most commonly via mutation in the k-ras oncogene and also via mutations in BRAF. Importantly, in all cases the MEk-resistant cell lines retained their addiction to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPk) pathway, as evidenced by their sensitivity to a selective inhibitor of the ERk1/2 kinases. These data suggest that tumors with acquired MEk inhibitor resistance remain dependent on the MAPk pathway and are therefore sensitive to inhibitors that act downstream of the mutated MEk target. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell cycle assay; Tissue microarrays staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase)1/2 inhibitors, including PD0325901, selumetinib, trametinib and TAK-733, selectively antagonized IGF1R signaling-mediated antiestrogen resistance but did not affect cell proliferation under normal growth conditions. RNAseq analysis revealed that MEK inhibitors PD0325901 and selumetinib drastically altered cell cycle progression and cell migration networks under IGF1R signaling-mediated antiestrogen resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
