Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00190) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Rifapentine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
RIFAPENTINE; Rifapentina; Rifapentinum; Cyclopentylrifampicin; Rifamycin AF/ACPP; Antibiotic DL 473IT; KTC 1; 61379-65-5; MDL 473; DRG-0283; DL 473; R-773; R 77-3; 3-(N-(4-Cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)formimidoyl)rifamycin; 3-(4-Cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)iminomethylrifamycin SV; 3-(((4-Cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)imino)methyl)rifamycin; Rifapentin,(S); NCGC00167431-01; ZINC169621228; NCGC00167431-03; AN-15578; RPE
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
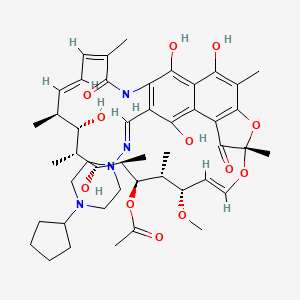
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Target | DNA-directed RNA polymerase (RNAP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C47H64N4O12
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@H]1/C=C/C=C(\\C(=O)NC2=C(C(=C3C(=C2O)C(=C(C4=C3C(=O)[C@](O4)(O/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)C)O)O)/C=N/N5CCN(CC5)C6CCCC6)/C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C47H64N4O12/c1-24-13-12-14-25(2)46(59)49-37-32(23-48-51-20-18-50(19-21-51)31-15-10-11-16-31)41(56)34-35(42(37)57)40(55)29(6)44-36(34)45(58)47(8,63-44)61-22-17-33(60-9)26(3)43(62-30(7)52)28(5)39(54)27(4)38(24)53/h12-14,17,22-24,26-28,31,33,38-39,43,53-57H,10-11,15-16,18-21H2,1-9H3,(H,49,59)/b13-12+,22-17+,25-14-,48-23+/t24-,26+,27+,28+,33-,38-,39+,43+,47-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WDZCUPBHRAEYDL-GZAUEHORSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Protein TetT (TETT) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain TG1 | 562 | ||
| Streptococcus agalactiae strain B130 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus anginosus strain MG16 | 1328 | |||
| Streptococcus anginosus strain MG23 | 1328 | |||
| Streptococcus anginosus strain MG32 | 1328 | |||
| Streptococcus bovis strain D135 | 1335 | |||
| Streptococcus bovis strain D295 | 1335 | |||
| Streptococcus equisimilis strain C94 | 119602 | |||
| Streptococcus equisimilis strain C95 | 119602 | |||
| Streptococcus equisimilis strain C96 | 119602 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain A498 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus sp. strain G59 | 1306 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The gene tet(T) was isolated from Streptococcus pyogenes A498, and the nucleotide sequence that was necessary and sufficient for the expression of tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli was determined. The deduced Tet(T) protein consists of 651 amino acids. A phylogenetic analysis revealed that Tet T represents a novel branching order among the Tet determinants so far described. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expressiom | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 1773 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These results support the model that the roles of OmpA as a porin protein overexpressing in mycobacteria can increase the hydrophilic ability of the cell wall which can facilitate the streptomycin uptakes and increase the mycobacteria's sensitivity to aminoglycosides. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A473T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q465R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L466S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q468K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D471Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A477T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I527M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S529L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.L466S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.S529L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.I527M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.S529L+p.Q465R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H481N+p.A473T+p.A477T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta (RPOB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D471Y+p.S486L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain T109 | 1280 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T112 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T113 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T115 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T118 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T124 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T161 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T166 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T20 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T211 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T212 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T236 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23aac | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T23bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T248 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T249 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T25 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T250 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T262 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T264 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T295 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T296 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T297 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T36 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T382 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38aa | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T38bb | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T397 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T398 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T399 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T4 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T400 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T401 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T402 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T403 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T404 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T46 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T59 | 1280 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus strain T66 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Twelve mutational changes at 10 positions were identified, with 473Ala-Thr representing a new mutation site. New amino acid substitutions, 465Gln-Arg, 466Leu-Ser, 468Gln-Lys, and 477Ala-Thr in cluster I and 527Ile-Met and 529Ser-Leu in cluster II, were described, thereby emphasizing the high variability of these amino acid positions. Codon 481 was mutated on 32 separate occasions, which indicates a central role of this amino acid. All in vivo isolates that demonstrated two or three amino acid changes exhibited high-level resistance. Interestingly enough, all of these isolates showed the mutational change 481His-Asn, which is capable of conferring low-level resistance on its own, thereby indicating a two-step resistance mechanism in vivo to high-level resistance within these isolates. High-level resistance in vivo, however, was not demonstrated to occur through multiple mutations alone. The single amino acid substitution 468Gln-Lys also causes high-level resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
