Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00040) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Thioguanine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
6-thioguanine; Lanvis; THG; Tabloid; ThioguaninGSK; Tioguanin; Tioguanina; Tioguanine; Tioguaninum; Glaxo Wellcome Brand of Thioguanine; Glaxo Wellcome Brand of Tioguanine; GlaxoSmithKline Brand of Thioguanine; GlaxoSmithKline Brand of Tioguanine; Thioguanin GSK; Thioguanine Hemihydrate; Thioguanine Monosodium Salt; Thioguanine Tabloid; Tioguanina Wellcome; Tioguanine GlaxoSmithKline Brand; Wellcome Brand of Thioguanine; BW 5071; DX4; LT00455187; Wellcome U3B; Lanvis (TN); Thioguanin-GSK; Thioguanine [USAN:BAN]; Tioguanina[INN-Spanish]; Tioguanine (INN); Tioguaninum [INN-Latin]; Purine antimetabolite: antimetabolite: inhibits nucleic acid replication; Guanine, thio-(VAN); 2 Amino 6 Purinethiol; 2-Amino 6MP; 2-Amino-1,7-dihydro-6H-purin-6-thion; 2-Amino-1,7-dihydro-6H-purin-6-thion [Czech]; 2-Amino-1,7-dihydro-6H-purine-6-thione; 2-Amino-6-MP; 2-Amino-6-mercaptopurine; 2-Amino-6-merkaptopurin; 2-Amino-6-merkaptopurin [Czech]; 2-Amino-6-purinethiol; 2-Amino-9H-purine-6-thiol; 2-Aminopurin-6-thiol; 2-Aminopurin-6-thiol [Czech]; 2-Aminopurine-6(1H)-thione; 2-Aminopurine-6-thiol; 2-Thioguanine; 2-amino-3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione; 6 Thioguanine; 6-Mercapto-2-aminopurine; 6-Mercaptoguanine; 6-TG; 6-Thioguanine; 6-Thioguanine (6-TG); 6-Thioguanine, Thioguanine; Thioguanine (Guanine analog)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
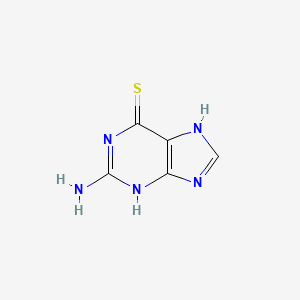
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C5H5N5S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1=NC2=C(N1)C(=S)N=C(N2)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C5H5N5S/c6-5-9-3-2(4(11)10-5)7-1-8-3/h1H,(H4,6,7,8,9,10,11)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WYWHKKSPHMUBEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase (NT5C2) | [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R238W (c.c712t) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.84 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
R
-
G
0
|
-
S
-
M
-
S
T
T
S
S
W
W
S
S
D
D
R
R
L
L
10
|
Q
Q
N
N
A
A
A
A
D
D
M
M
P
P
A
A
N
N
M
M
20
|
D
D
K
K
H
H
A
A
L
L
K
K
K
K
Y
Y
R
R
R
R
30
|
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
H
H
R
R
V
V
F
F
V
V
N
N
R
R
40
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
E
E
K
K
I
I
K
K
C
C
F
F
50
|
G
G
F
F
D
D
M
M
D
D
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
A
A
V
V
60
|
Y
Y
K
K
S
S
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
S
S
L
L
G
G
70
|
F
F
E
E
L
L
T
T
V
V
E
E
R
R
L
L
V
V
S
S
80
|
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
P
P
Q
Q
E
E
L
L
L
L
S
S
F
F
90
|
A
A
Y
Y
D
D
S
S
T
T
F
F
P
P
T
T
R
R
G
G
100
|
L
L
V
V
F
F
D
D
T
T
L
L
Y
Y
G
G
N
N
L
L
110
|
L
L
K
K
V
V
D
D
A
A
Y
Y
G
G
N
N
L
L
L
L
120
|
V
V
C
C
A
A
H
H
G
G
F
F
N
N
F
F
I
I
R
R
130
|
G
G
P
P
E
E
T
T
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
Y
Y
P
P
N
N
140
|
K
K
F
F
I
I
Q
Q
R
R
D
D
D
D
T
T
E
E
R
R
150
|
F
F
Y
Y
I
I
L
L
N
N
T
T
L
L
F
F
N
N
L
L
160
|
P
P
E
E
T
T
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
A
A
C
C
L
L
V
V
170
|
D
D
F
F
F
F
T
T
N
N
C
C
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
T
T
180
|
S
S
C
C
E
E
T
T
G
G
F
F
K
K
D
D
G
G
D
D
190
|
L
L
F
F
M
M
S
S
Y
Y
R
R
S
S
M
M
F
F
Q
Q
200
|
D
D
V
V
R
R
D
D
A
A
V
V
D
D
W
W
V
V
H
H
210
|
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
S
S
L
L
K
K
E
E
K
K
T
T
V
V
220
|
E
E
N
N
L
L
E
E
K
K
Y
Y
V
V
V
V
K
K
D
D
230
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
P
P
L
L
L
L
L
L
S
S
R
W
M
M
240
|
K
K
E
E
V
V
G
G
K
K
V
V
F
F
L
L
A
A
T
T
250
|
N
N
S
S
D
D
Y
Y
K
K
Y
Y
T
T
D
D
K
K
I
I
260
|
M
M
T
T
Y
Y
L
L
F
F
D
D
F
F
P
P
H
H
G
G
270
|
P
P
K
K
P
P
G
G
S
S
S
S
H
H
R
R
P
P
W
W
280
|
Q
Q
S
S
Y
Y
F
F
D
D
L
L
I
I
L
L
V
V
D
D
290
|
A
A
R
R
K
K
P
P
L
L
F
F
F
F
G
G
E
E
G
G
300
|
T
T
V
V
L
L
R
R
Q
Q
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
T
T
310
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
K
K
I
I
G
G
T
T
Y
Y
T
T
G
G
320
|
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
H
H
G
G
I
I
V
V
Y
Y
S
S
G
G
330
|
G
G
S
S
S
S
D
D
T
T
I
I
C
C
D
D
L
L
L
L
340
|
G
G
A
A
K
K
G
G
K
K
D
D
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
I
I
350
|
G
G
D
D
H
H
I
I
F
F
G
G
D
D
I
I
L
L
K
K
360
|
S
S
K
K
K
K
R
R
Q
Q
G
G
W
W
R
R
T
T
F
F
370
|
L
L
V
V
I
I
P
P
E
E
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
E
E
L
L
380
|
H
H
V
V
W
W
T
T
D
D
K
K
S
S
S
S
L
L
F
F
390
|
E
E
E
E
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
L
L
D
D
I
I
F
F
L
L
400
|
A
A
E
E
L
L
Y
Y
K
K
H
H
L
L
D
D
S
S
S
S
410
|
S
S
N
N
E
E
R
R
P
P
D
D
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
420
|
Q
Q
R
R
R
R
I
I
K
K
K
K
V
V
T
T
H
H
D
D
430
|
M
M
D
D
M
M
C
C
Y
Y
G
G
M
M
M
M
G
G
S
S
440
|
L
L
F
F
R
R
S
S
G
G
S
S
R
R
Q
Q
T
T
L
L
450
|
F
F
A
A
S
S
Q
Q
V
V
M
M
R
R
Y
Y
A
A
D
D
460
|
L
L
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
S
S
F
F
I
I
N
N
L
L
L
L
470
|
Y
Y
Y
Y
P
P
F
F
S
S
Y
Y
L
L
F
F
R
R
A
A
480
|
A
A
H
H
V
V
L
L
M
M
P
P
H
H
E
E
S
S
-
T
490
|
-
V
-
E
-
H
-
T
-
H
-
V
-
D
-
I
-
N
-
E
500
|
-
M
-
E
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
A
-
T
-
R
-
N
-
R
510
|
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
D
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
T
-
D
-
Y
520
|
-
K
-
R
-
H
-
Q
-
L
-
T
-
R
-
S
-
I
-
S
530
|
-
E
-
I
-
K
-
P
-
P
-
N
-
L
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Exome sequencing assay; Transcriptome sequencing assay; Whole genome sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Several of these alterations are known to induce a more stem cell-like state (eg, IkZF1) or confer resistance directly to specific chemotherapy agents such as CREBBP and glucocorticoids and mutations in the 5-nucleotidase gene NT5C2 and nucleoside a.logs. Many relapse-acquired lesions are enriched in specific pathways, including B-cell development (IkZF1), tumor suppression (TP53),34 Ras signaling, chromatin modification (CREBBP, SETD2),17 and drug metabolism (NT5C2). | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase (NT5C2) | [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S445F (c.c1334t) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Exome sequencing assay; Transcriptome sequencing assay; Whole genome sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Several of these alterations are known to induce a more stem cell-like state (eg, IkZF1) or confer resistance directly to specific chemotherapy agents such as CREBBP and glucocorticoids and mutations in the 5-nucleotidase gene NT5C2 and nucleoside a.logs. Many relapse-acquired lesions are enriched in specific pathways, including B-cell development (IkZF1), tumor suppression (TP53),34 Ras signaling, chromatin modification (CREBBP, SETD2),17 and drug metabolism (NT5C2). | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase (NT5C2) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequencing assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recent sequencing studies of T-ALL have confirmed the presence of these mutations as well as novel recurrent mutations in the tumor suppressor CNOT3, ribosomal proteins(RPL5 and RPL10) and in the setting of relapse, the NT5C2 gene, which inactivates nucleoside-analogue chemotherapy drugs. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
