Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol03009)
| Name |
Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 5 (ENTPD5)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ENTPD5; CD39L4; PCPH
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ENTPD5
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr14:73,958,010-74,019,399[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MATSWGTVFFMLVVSCVCSAVSHRNQQTWFEGIFLSSMCPINVSASTLYGIMFDAGSTGT
RIHVYTFVQKMPGQLPILEGEVFDSVKPGLSAFVDQPKQGAETVQGLLEVAKDSIPRSHW KKTPVVLKATAGLRLLPEHKAKALLFEVKEIFRKSPFLVPKGSVSIMDGSDEGILAWVTV NFLTGQLHGHRQETVGTLDLGGASTQITFLPQFEKTLEQTPRGYLTSFEMFNSTYKLYTH SYLGFGLKAARLATLGALETEGTDGHTFRSACLPRWLEAEWIFGGVKYQYGGNQEGEVGF EPCYAEVLRVVRGKLHQPEEVQRGSFYAFSYYYDRAVDTDMIDYEKGGILKVEDFERKAR EVCDNLENFTSGSPFLCMDLSYITALLKDGFGFADSTVLQLTKKVNNIETGWALGATFHL LQSLGISH Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Hydrolyzes nucleoside diphosphates with a preference for GDP, IDP and UDP compared to ADP and CDP. In the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, hydrolyzes UDP that acts as an end-product feedback inhibitor of the UDP-Glc:glycoprotein glucosyltransferases. UMP can be transported back by an UDP-sugar antiporter to the cytosol where it is consumed to regenerate UDP-glucose. Therefore, it positively regulates protein reglucosylation by clearing UDP from the ER lumen and by promoting the regeneration of UDP-glucose. Protein reglucosylation is essential to proper glycoprotein folding and quality control in the ER.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia [ICD-11: 2C82.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia [ICD-11: 2C82.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.95E-06 Fold-change: 1.89E-01 Z-score: 5.92E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| PC-3 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Forced expression of the PCPH protein or, in particular, of the mt-PCPH oncoprotein increased the levels of phosphorylated PKCalpha concurrently with those of Ser70-phosphorylated and total Bcl-2 protein, thus promoting cisplatin resistance. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.95E-06; Fold-change: 1.37E+00; Z-score: 1.50E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
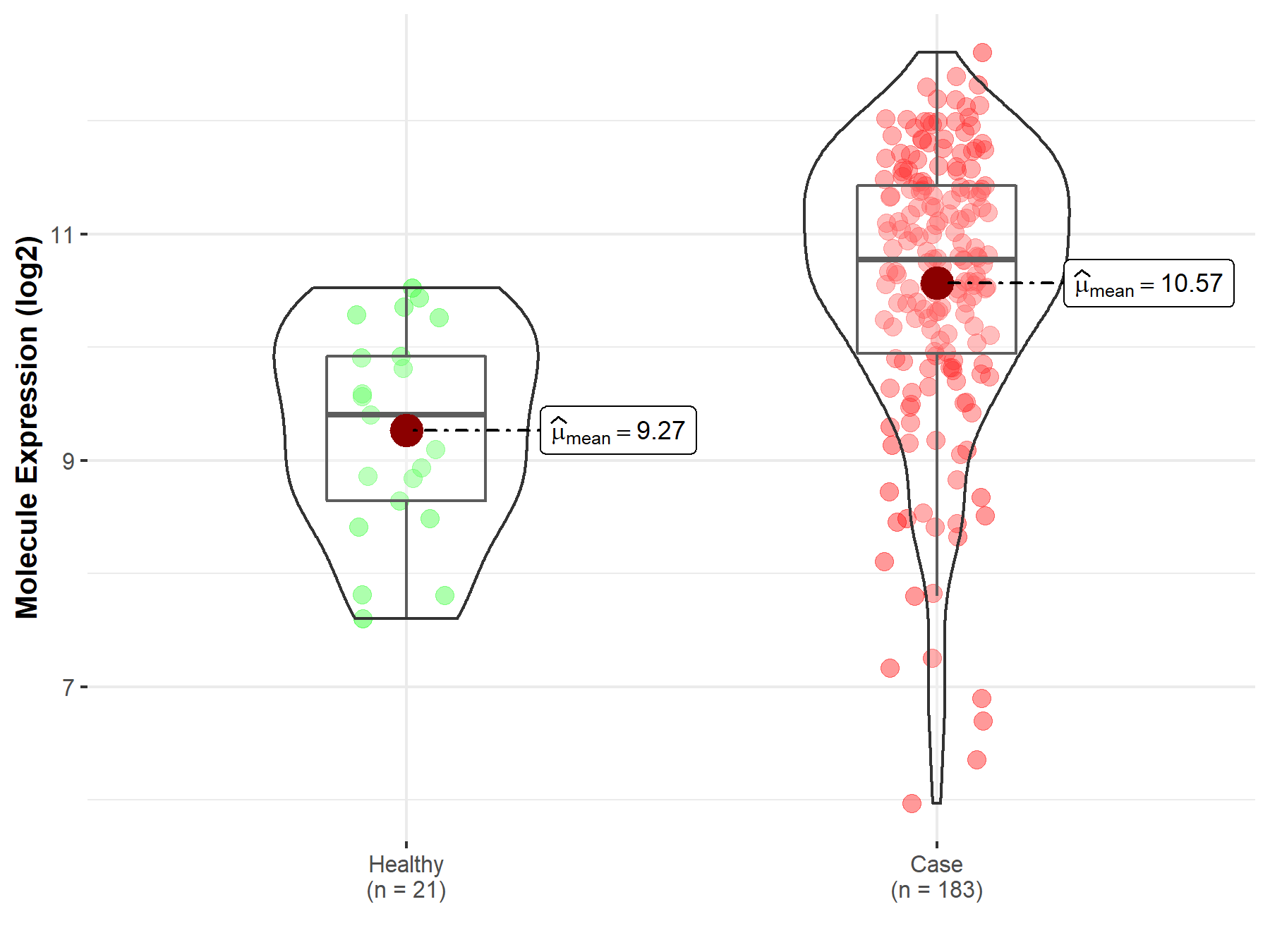
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

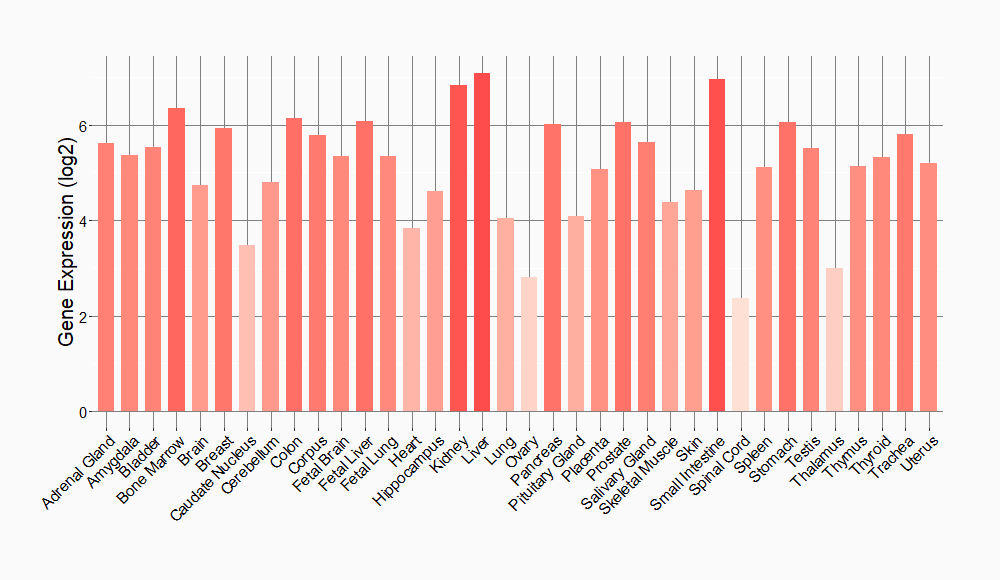
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
