Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol02134)
| Name |
Protocadherin beta-9 (PCDHB9)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Protocadherin beta-9 (PCDH-beta-9) (Protocadherin-3H); PCDHB9; PCDH3H
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PCDHB9
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
Chromosome 5: 141,187,127-141,191,541 forward strand
|
||||
| Sequence |
MKTRGFSFPRQRQVLFLFLFWGVSLAGSGFGRYSVTEETEKGSFVVNLAKDLGLAEGELA
ARGTRVVSDDNKQYLLLDSHTGNLLTNEKLDREKLCGPKEPCMLYFQILMDDPFQIYRAE LRVRDINDHSPVFRHKEMVLKISENTAEGTAFRLERAQDPDEGHNSIQNYTISSNSFFHI KISGSDEGMIYPELVLDKALDREEQEELSLTLTALDGGSPSRSGTSTIRIVVLDVNDNVP QFAQALYETQAPENSPVGSLIVKVSAGDADSGVNAEVSYSFFDASEDILTTFQINPFSGE IFLRELLDYELVNSYKINIQAMDGGGLSARCTVLIKVLDSNDNPPELIISSLSNSVAENS PGIVLAVFKIKDRDSGENGKTICYVQDNLPFFLKPSVDNFYILMTEGALDRESKAEYNIT ITVTDLGTPRLKTEHSITLQVSDVNDNAPAFTQTSYTLFVRENNSPALHIGSVSATDRDS GTNAQVTYSLLPPQDPHLPLASLVSINADNGHLFALRSLDYEALQAFDFRVGASDRGSPA LSSEALVRVLVLDANDNSPFVLYPLQNGSAPCTELVPRAAEPGYLVTKVVAVDGDSGQNA WLSYQLLKATEPGLFGVWAHNGEVRTARLLSERDAAKHRLVVLVKDNGEPPRSATATLHV LLVDGFSQPYLPLPEAAPAQAQADLLTVYLVVALASVSSLFLLSVLLFVAVRLCRRSRAA SVGRCSVPEGPFPGHLVDVSGTGTLFQSYQYEVCLTGGSETGEFKFLKPITPHLPPHRGG KEIEENSTLPNSFGFNY Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Potential calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. May be involved in the establishment and maintenance of specific neuronal connections in the brain.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bicalutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.81E-02 Fold-change: 7.01E-02 Z-score: 2.42E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | LN229 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0393 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Bicalutamide has been widely used as a first-line treatment for PCa. Although patients initially show a favorable response to bicalutamide treatment, PCa eventually acquires bicalutamide resistance. Several factors have been shown to be involved in bicalutamide resistance. However, the mechanism of bicalutamide resistance is not fully understood. In this study, the knockdown of protocadherin B9 reduced nuclear AR translocation and bicalutamide resistance in androgen-dependent LNCaP cells in the presence of DHT. The overexpression of protocadherin B9 had no effect on bicalutamide resistance in androgen-independent DU145 cells. These results further indicate that protocadherin B9 is involved in bicalutamide resistance through the modulation of AR signaling. Taken together, our findings suggest that protocadherin B9 targeted therapy could be more effective therapy than bicalutamide alone for patients with PCa. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.81E-02; Fold-change: -1.09E-01; Z-score: -3.39E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
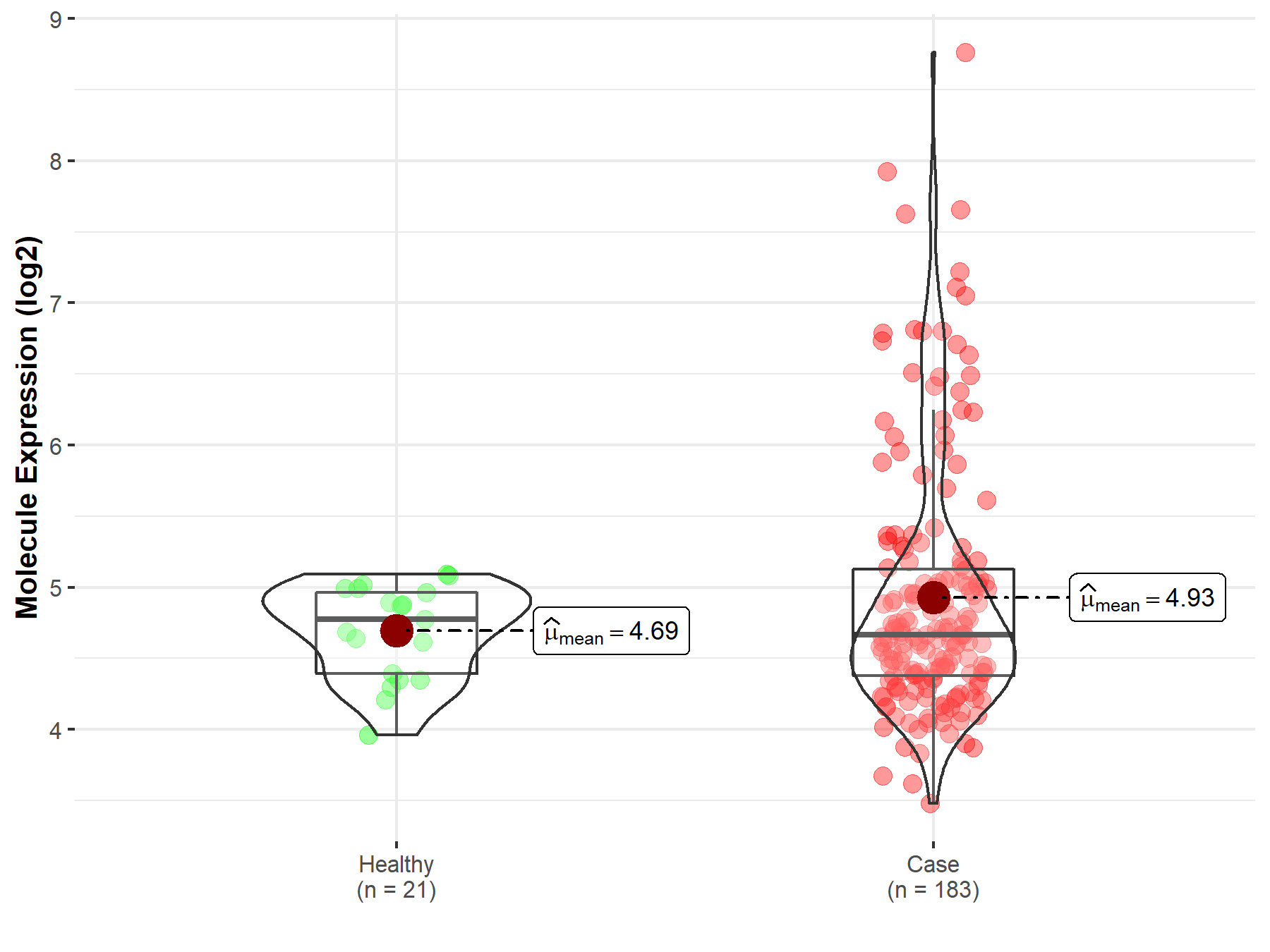
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
