Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01983)
| Name |
Leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
LRRK2; PARK8
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
LRRK2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr12:40,196,744-40,369,285[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MASGSCQGCEEDEETLKKLIVRLNNVQEGKQIETLVQILEDLLVFTYSERASKLFQGKNI
HVPLLIVLDSYMRVASVQQVGWSLLCKLIEVCPGTMQSLMGPQDVGNDWEVLGVHQLILK MLTVHNASVNLSVIGLKTLDLLLTSGKITLLILDEESDIFMLIFDAMHSFPANDEVQKLG CKALHVLFERVSEEQLTEFVENKDYMILLSALTNFKDEEEIVLHVLHCLHSLAIPCNNVE VLMSGNVRCYNIVVEAMKAFPMSERIQEVSCCLLHRLTLGNFFNILVLNEVHEFVVKAVQ QYPENAALQISALSCLALLTETIFLNQDLEEKNENQENDDEGEEDKLFWLEACYKALTWH RKNKHVQEAACWALNNLLMYQNSLHEKIGDEDGHFPAHREVMLSMLMHSSSKEVFQASAN ALSTLLEQNVNFRKILLSKGIHLNVLELMQKHIHSPEVAESGCKMLNHLFEGSNTSLDIM AAVVPKILTVMKRHETSLPVQLEALRAILHFIVPGMPEESREDTEFHHKLNMVKKQCFKN DIHKLVLAALNRFIGNPGIQKCGLKVISSIVHFPDALEMLSLEGAMDSVLHTLQMYPDDQ EIQCLGLSLIGYLITKKNVFIGTGHLLAKILVSSLYRFKDVAEIQTKGFQTILAILKLSA SFSKLLVHHSFDLVIFHQMSSNIMEQKDQQFLNLCCKCFAKVAMDDYLKNVMLERACDQN NSIMVECLLLLGADANQAKEGSSLICQVCEKESSPKLVELLLNSGSREQDVRKALTISIG KGDSQIISLLLRRLALDVANNSICLGGFCIGKVEPSWLGPLFPDKTSNLRKQTNIASTLA RMVIRYQMKSAVEEGTASGSDGNFSEDVLSKFDEWTFIPDSSMDSVFAQSDDLDSEGSEG SFLVKKKSNSISVGEFYRDAVLQRCSPNLQRHSNSLGPIFDHEDLLKRKRKILSSDDSLR SSKLQSHMRHSDSISSLASEREYITSLDLSANELRDIDALSQKCCISVHLEHLEKLELHQ NALTSFPQQLCETLKSLTHLDLHSNKFTSFPSYLLKMSCIANLDVSRNDIGPSVVLDPTV KCPTLKQFNLSYNQLSFVPENLTDVVEKLEQLILEGNKISGICSPLRLKELKILNLSKNH ISSLSENFLEACPKVESFSARMNFLAAMPFLPPSMTILKLSQNKFSCIPEAILNLPHLRS LDMSSNDIQYLPGPAHWKSLNLRELLFSHNQISILDLSEKAYLWSRVEKLHLSHNKLKEI PPEIGCLENLTSLDVSYNLELRSFPNEMGKLSKIWDLPLDELHLNFDFKHIGCKAKDIIR FLQQRLKKAVPYNRMKLMIVGNTGSGKTTLLQQLMKTKKSDLGMQSATVGIDVKDWPIQI RDKRKRDLVLNVWDFAGREEFYSTHPHFMTQRALYLAVYDLSKGQAEVDAMKPWLFNIKA RASSSPVILVGTHLDVSDEKQRKACMSKITKELLNKRGFPAIRDYHFVNATEESDALAKL RKTIINESLNFKIRDQLVVGQLIPDCYVELEKIILSERKNVPIEFPVIDRKRLLQLVREN QLQLDENELPHAVHFLNESGVLLHFQDPALQLSDLYFVEPKWLCKIMAQILTVKVEGCPK HPKGIISRRDVEKFLSKKRKFPKNYMSQYFKLLEKFQIALPIGEEYLLVPSSLSDHRPVI ELPHCENSEIIIRLYEMPYFPMGFWSRLINRLLEISPYMLSGRERALRPNRMYWRQGIYL NWSPEAYCLVGSEVLDNHPESFLKITVPSCRKGCILLGQVVDHIDSLMEEWFPGLLEIDI CGEGETLLKKWALYSFNDGEEHQKILLDDLMKKAEEGDLLVNPDQPRLTIPISQIAPDLI LADLPRNIMLNNDELEFEQAPEFLLGDGSFGSVYRAAYEGEEVAVKIFNKHTSLRLLRQE LVVLCHLHHPSLISLLAAGIRPRMLVMELASKGSLDRLLQQDKASLTRTLQHRIALHVAD GLRYLHSAMIIYRDLKPHNVLLFTLYPNAAIIAKIADYGIAQYCCRMGIKTSEGTPGFRA PEVARGNVIYNQQADVYSFGLLLYDILTTGGRIVEGLKFPNEFDELEIQGKLPDPVKEYG CAPWPMVEKLIKQCLKENPQERPTSAQVFDILNSAELVCLTRRILLPKNVIVECMVATHH NSRNASIWLGCGHTDRGQLSFLDLNTEGYTSEEVADSRILCLALVHLPVEKESWIVSGTQ SGTLLVINTEDGKKRHTLEKMTDSVTCLYCNSFSKQSKQKNFLLVGTADGKLAIFEDKTV KLKGAAPLKILNIGNVSTPLMCLSESTNSTERNVMWGGCGTKIFSFSNDFTIQKLIETRT SQLFSYAAFSDSNIITVVVDTALYIAKQNSPVVEVWDKKTEKLCGLIDCVHFLREVMVKE NKESKHKMSYSGRVKTLCLQKNTALWIGTGGGHILLLDLSTRRLIRVIYNFCNSVRVMMT AQLGSLKNVMLVLGYNRKNTEGTQKQKEIQSCLTVWDINLPHEVQNLEKHIEVRKELAEK MRRTSVE Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase which phosphorylates a broad range of proteins involved in multiple processes such as neuronal plasticity, autophagy, and vesicle trafficking. Is a key regulator of RAB GTPases by regulating the GTP/GDP exchange and interaction partners of RABs through phosphorylation. Phosphorylates RAB3A, RAB3B, RAB3C, RAB3D, RAB5A, RAB5B, RAB5C, RAB8A, RAB8B, RAB10, RAB12, RAB35, and RAB43. Regulates the RAB3IP-catalyzed GDP/GTP exchange for RAB8A through the phosphorylation of 'Thr-72' on RAB8A. Inhibits the interaction between RAB8A and GDI1 and/or GDI2 by phosphorylating 'Thr-72' on RAB8A. Regulates primary ciliogenesis through phosphorylation of RAB8A and RAB10, which promotes SHH signaling in the brain. Together with RAB29, plays a role in the retrograde trafficking pathway for recycling proteins, such as mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6PR), between lysosomes and the Golgi apparatus in a retromer-dependent manner. Regulates neuronal process morphology in the intact central nervous system (CNS). Plays a role in synaptic vesicle trafficking. Plays an important role in recruiting SEC16A to endoplasmic reticulum exit sites (ERES) and in regulating ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport and ERES organization. Positively regulates autophagy through a calcium-dependent activation of the CaMKK/AMPK signaling pathway. The process involves activation of nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) receptors, increase in lysosomal pH, and calcium release from lysosomes. Phosphorylates PRDX3. By phosphorylating APP on 'Thr-743', which promotes the production and the nuclear translocation of the APP intracellular domain (AICD), regulates dopaminergic neuron apoptosis. Independent of its kinase activity, inhibits the proteosomal degradation of MAPT, thus promoting MAPT oligomerization and secretion. In addition, has GTPase activity via its Roc domain which regulates LRRK2 kinase activity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00.0] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Levedopa | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I2020T |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 2.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
L
L
M
M
I
I
1340
|
V
V
G
G
N
N
T
T
G
G
S
S
G
G
K
K
T
T
T
T
1350
|
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
K
K
K
K
1360
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
G
G
M
M
Q
Q
S
S
A
A
T
T
V
V
1370
|
G
G
I
I
D
D
V
V
K
K
D
D
W
W
P
P
I
I
Q
Q
1380
|
I
I
R
R
D
D
K
K
R
R
K
K
R
R
D
D
L
L
V
V
1390
|
L
L
N
N
V
V
W
W
D
D
F
F
A
A
G
G
R
R
E
E
1400
|
E
E
F
F
Y
Y
S
S
T
T
H
H
P
P
H
H
F
F
M
M
1410
|
T
T
Q
Q
R
R
A
A
L
L
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
V
V
Y
Y
1420
|
D
D
L
L
S
S
K
K
G
G
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
V
V
D
D
1430
|
A
A
M
M
K
K
P
P
W
W
L
L
F
F
N
N
I
I
K
K
1440
|
A
A
R
R
A
A
S
S
S
S
S
S
P
P
V
V
I
I
L
L
1450
|
V
V
G
G
T
T
H
H
L
L
D
D
V
V
S
S
D
D
E
E
1460
|
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
K
K
A
A
C
C
M
M
S
S
K
K
I
I
1470
|
T
T
K
K
E
E
L
L
L
L
N
N
K
K
R
R
G
G
F
F
1480
|
P
P
A
A
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
H
H
F
F
V
V
N
N
1490
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
E
E
S
S
D
D
A
A
L
L
A
A
K
K
1500
|
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
I
I
I
I
N
N
E
E
S
S
L
L
1510
|
N
N
F
F
K
K
I
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
V
V
1520
|
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
P
P
D
D
C
C
Y
Y
V
V
E
E
1530
|
L
L
E
E
K
K
I
I
I
I
L
L
S
S
E
E
R
R
K
K
1540
|
N
N
V
V
P
P
I
I
E
E
F
F
P
P
V
V
I
I
D
D
1550
|
R
R
K
K
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
R
R
E
E
1560
|
N
N
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
L
L
D
D
E
E
N
N
E
E
L
L
1570
|
P
P
H
H
A
A
V
V
H
H
F
F
L
L
N
N
E
E
S
S
1580
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
H
H
F
F
Q
Q
D
D
P
P
A
A
1590
|
L
L
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
F
F
V
V
E
E
1600
|
P
P
K
K
W
W
L
L
C
C
K
K
I
I
M
M
A
A
Q
Q
1610
|
I
I
L
L
T
T
V
V
K
K
V
V
E
E
G
G
C
C
P
P
1620
|
K
K
H
H
P
P
K
K
G
G
I
I
I
I
S
S
R
R
R
R
1630
|
D
D
V
V
E
E
K
K
F
F
L
L
S
S
K
K
K
K
R
R
1640
|
K
K
F
F
P
P
K
K
N
N
Y
Y
M
M
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
1650
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
E
E
K
K
F
F
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
1660
|
L
L
P
P
I
I
G
G
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
V
V
1670
|
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
S
S
D
D
H
H
R
R
P
P
V
V
1680
|
I
I
E
E
L
L
P
P
H
H
C
C
E
E
N
N
S
S
E
E
1690
|
I
I
I
I
I
I
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
1700
|
F
F
P
P
M
M
G
G
F
F
W
W
S
S
R
R
L
L
I
I
1710
|
N
N
R
R
L
L
L
L
E
E
I
I
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
M
M
1720
|
L
L
S
S
G
G
R
R
E
E
R
R
A
A
L
L
R
R
P
P
1730
|
N
N
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
W
W
R
R
Q
Q
G
G
I
I
Y
Y
1740
|
L
L
N
N
W
W
S
S
P
P
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
C
C
L
L
1750
|
V
V
G
G
S
S
E
E
V
V
L
L
D
D
N
N
H
H
P
P
1760
|
E
E
S
S
F
F
L
L
K
K
I
I
T
T
V
V
P
P
S
S
1770
|
C
C
R
R
K
K
G
G
C
C
I
I
L
L
L
L
G
G
Q
Q
1780
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
H
H
I
I
D
D
S
S
L
L
M
M
E
E
1790
|
E
E
W
W
F
F
P
P
G
G
L
L
L
L
E
E
I
I
D
D
1800
|
I
I
C
C
G
G
E
E
G
G
E
E
T
T
L
L
L
L
K
K
1810
|
K
K
W
W
A
A
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
N
N
D
D
G
G
1820
|
E
E
E
E
H
H
Q
Q
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
D
D
D
D
1830
|
L
L
M
M
K
K
K
K
A
A
E
E
E
E
G
G
D
D
L
L
1840
|
L
L
V
V
N
N
P
P
D
D
Q
Q
P
P
R
R
L
L
T
T
1850
|
I
I
P
P
I
I
S
S
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
P
P
D
D
L
L
1860
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
D
D
L
L
P
P
R
R
N
N
I
I
M
M
1870
|
L
L
N
N
N
N
D
D
E
E
L
L
E
E
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
1880
|
A
A
P
P
E
E
F
F
L
L
L
L
G
G
D
D
G
G
S
S
1890
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
V
V
Y
Y
R
R
A
A
A
A
Y
Y
E
E
1900
|
G
G
E
E
E
E
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
I
I
F
F
N
N
1910
|
K
K
H
H
T
T
S
S
L
L
R
R
L
L
L
L
R
R
Q
Q
1920
|
E
E
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
C
C
H
H
L
L
H
H
H
H
1930
|
P
P
S
S
L
L
I
I
S
S
L
L
L
L
A
A
A
A
G
G
1940
|
I
I
R
R
P
P
R
R
M
M
L
L
V
V
M
M
E
E
L
L
1950
|
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
S
S
L
L
D
D
R
R
L
L
L
L
1960
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
D
D
K
K
A
A
S
S
L
L
T
T
R
R
T
T
1970
|
L
L
Q
Q
H
H
R
R
I
I
A
A
L
L
H
H
V
V
A
A
1980
|
D
D
G
G
L
L
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
S
S
A
A
M
M
1990
|
I
I
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
P
P
H
H
N
N
2000
|
V
V
L
L
L
L
F
F
T
T
L
L
Y
Y
P
P
N
N
A
A
2010
|
A
A
I
I
I
I
A
A
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
Y
Y
G
G
2020
|
I
T
A
A
Q
Q
Y
Y
C
C
C
C
R
R
M
M
G
G
I
I
2030
|
K
K
T
T
S
S
E
E
G
G
T
T
P
P
G
G
F
F
R
R
2040
|
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
N
N
V
V
I
I
2050
|
Y
Y
N
N
Q
Q
Q
Q
A
A
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
2060
|
G
G
L
L
L
L
L
L
Y
Y
D
D
I
I
L
L
T
T
T
T
2070
|
G
G
G
G
R
R
I
I
V
V
E
E
G
G
L
L
K
K
F
F
2080
|
P
P
N
N
E
E
F
F
D
D
E
E
L
L
E
E
I
I
Q
Q
2090
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
P
P
D
D
P
P
V
V
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
2100
|
G
G
C
C
A
A
P
P
W
W
P
P
M
M
V
V
E
E
K
K
2110
|
L
L
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
C
C
L
L
K
K
E
E
N
N
P
P
2120
|
Q
Q
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
S
S
A
A
Q
Q
V
V
F
F
2130
|
D
D
I
I
L
L
N
N
S
S
A
A
E
E
L
L
V
V
C
C
2140
|
L
L
T
T
R
R
R
R
I
I
L
L
L
L
P
P
K
K
N
N
2150
|
V
V
I
I
V
V
E
E
C
C
M
M
V
V
A
A
T
T
H
H
2160
|
H
H
N
N
S
S
R
R
N
N
A
A
S
S
I
I
W
W
L
L
2170
|
G
G
C
C
G
G
H
H
T
T
D
D
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
2180
|
S
S
F
F
L
L
D
D
L
L
N
N
T
T
E
E
G
G
Y
Y
2190
|
T
T
S
S
E
E
E
E
V
V
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
I
I
2200
|
L
L
C
C
L
L
A
A
L
L
V
V
H
H
L
L
P
P
V
V
2210
|
E
E
K
K
E
E
S
S
W
W
I
I
V
V
S
S
G
G
T
T
2220
|
Q
Q
S
S
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
2230
|
E
E
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
R
R
H
H
T
T
L
L
E
E
2240
|
K
K
M
M
T
T
D
D
S
S
V
V
T
T
C
C
L
L
Y
Y
2250
|
C
C
N
N
S
S
F
F
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
2260
|
K
K
N
N
F
F
L
L
L
L
V
V
G
G
T
T
A
A
D
D
2270
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
A
A
I
I
F
F
E
E
D
D
K
K
T
T
2280
|
V
V
K
K
L
L
K
K
G
G
A
A
A
A
P
P
L
L
K
K
2290
|
I
I
L
L
N
N
I
I
G
G
N
N
V
V
S
S
T
T
P
P
2300
|
L
L
M
M
C
C
L
L
S
S
E
E
S
S
T
T
N
N
S
S
2310
|
T
T
E
E
R
R
N
N
V
V
M
M
W
W
G
G
G
G
C
C
2320
|
G
G
T
T
K
K
I
I
F
F
S
S
F
F
S
S
N
N
D
D
2330
|
F
F
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
K
K
L
L
I
I
E
E
T
T
R
R
2340
|
T
T
S
S
Q
Q
L
L
F
F
S
S
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
F
F
2350
|
S
S
D
D
S
S
N
N
I
I
I
I
T
T
V
V
V
V
V
V
2360
|
D
D
T
T
A
A
L
L
Y
Y
I
I
A
A
K
K
Q
Q
N
N
2370
|
S
S
P
P
V
V
V
V
E
E
V
V
W
W
D
D
K
K
K
K
2380
|
T
T
E
E
K
K
L
L
C
C
G
G
L
L
I
I
D
D
C
C
2390
|
V
V
H
H
F
F
L
L
R
R
E
E
V
V
M
M
V
V
K
K
2400
|
E
E
N
N
K
K
E
E
S
S
K
K
H
H
K
K
M
M
S
S
2410
|
Y
Y
S
S
G
G
R
R
V
V
K
K
T
T
L
L
C
C
L
L
2420
|
Q
Q
K
K
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
W
W
I
I
G
G
T
T
2430
|
G
G
G
G
G
G
H
H
I
I
L
L
L
L
L
L
D
D
L
L
2440
|
S
S
T
T
R
R
R
R
L
L
I
I
R
R
V
V
I
I
Y
Y
2450
|
N
N
F
F
C
C
N
N
S
S
V
V
R
R
V
V
M
M
M
M
2460
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
G
G
S
S
L
L
K
K
N
N
V
V
2470
|
M
M
L
L
V
V
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
N
N
R
R
K
K
N
N
2480
|
T
T
E
E
G
G
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
K
K
E
E
I
I
2490
|
Q
Q
S
S
C
C
L
L
T
T
V
V
W
W
D
D
I
I
N
N
2500
|
L
L
P
P
H
H
E
E
V
V
Q
Q
N
N
L
L
E
E
K
K
2510
|
H
H
I
I
E
E
V
V
R
R
K
K
E
E
L
L
A
A
E
E
2520
|
K
K
M
M
R
R
R
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
E
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Molecular docking analysis; Molecular dynamic simulation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The deleterious mutations G2019S and I2020T in the kinase domain were playing a key role in causing resistance to drug levedopa. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00.0] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Levedopa | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G2019S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 2.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
L
L
M
M
I
I
1340
|
V
V
G
G
N
N
T
T
G
G
S
S
G
G
K
K
T
T
T
T
1350
|
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
K
K
K
K
1360
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
G
G
M
M
Q
Q
S
S
A
A
T
T
V
V
1370
|
G
G
I
I
D
D
V
V
K
K
D
D
W
W
P
P
I
I
Q
Q
1380
|
I
I
R
R
D
D
K
K
R
R
K
K
R
R
D
D
L
L
V
V
1390
|
L
L
N
N
V
V
W
W
D
D
F
F
A
A
G
G
R
R
E
E
1400
|
E
E
F
F
Y
Y
S
S
T
T
H
H
P
P
H
H
F
F
M
M
1410
|
T
T
Q
Q
R
R
A
A
L
L
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
V
V
Y
Y
1420
|
D
D
L
L
S
S
K
K
G
G
Q
Q
A
A
E
E
V
V
D
D
1430
|
A
A
M
M
K
K
P
P
W
W
L
L
F
F
N
N
I
I
K
K
1440
|
A
A
R
R
A
A
S
S
S
S
S
S
P
P
V
V
I
I
L
L
1450
|
V
V
G
G
T
T
H
H
L
L
D
D
V
V
S
S
D
D
E
E
1460
|
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
K
K
A
A
C
C
M
M
S
S
K
K
I
I
1470
|
T
T
K
K
E
E
L
L
L
L
N
N
K
K
R
R
G
G
F
F
1480
|
P
P
A
A
I
I
R
R
D
D
Y
Y
H
H
F
F
V
V
N
N
1490
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
E
E
S
S
D
D
A
A
L
L
A
A
K
K
1500
|
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
I
I
I
I
N
N
E
E
S
S
L
L
1510
|
N
N
F
F
K
K
I
I
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
V
V
1520
|
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
P
P
D
D
C
C
Y
Y
V
V
E
E
1530
|
L
L
E
E
K
K
I
I
I
I
L
L
S
S
E
E
R
R
K
K
1540
|
N
N
V
V
P
P
I
I
E
E
F
F
P
P
V
V
I
I
D
D
1550
|
R
R
K
K
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
R
R
E
E
1560
|
N
N
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
L
L
D
D
E
E
N
N
E
E
L
L
1570
|
P
P
H
H
A
A
V
V
H
H
F
F
L
L
N
N
E
E
S
S
1580
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
H
H
F
F
Q
Q
D
D
P
P
A
A
1590
|
L
L
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
F
F
V
V
E
E
1600
|
P
P
K
K
W
W
L
L
C
C
K
K
I
I
M
M
A
A
Q
Q
1610
|
I
I
L
L
T
T
V
V
K
K
V
V
E
E
G
G
C
C
P
P
1620
|
K
K
H
H
P
P
K
K
G
G
I
I
I
I
S
S
R
R
R
R
1630
|
D
D
V
V
E
E
K
K
F
F
L
L
S
S
K
K
K
K
R
R
1640
|
K
K
F
F
P
P
K
K
N
N
Y
Y
M
M
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
1650
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
E
E
K
K
F
F
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
1660
|
L
L
P
P
I
I
G
G
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
V
V
1670
|
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
S
S
D
D
H
H
R
R
P
P
V
V
1680
|
I
I
E
E
L
L
P
P
H
H
C
C
E
E
N
N
S
S
E
E
1690
|
I
I
I
I
I
I
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
1700
|
F
F
P
P
M
M
G
G
F
F
W
W
S
S
R
R
L
L
I
I
1710
|
N
N
R
R
L
L
L
L
E
E
I
I
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
M
M
1720
|
L
L
S
S
G
G
R
R
E
E
R
R
A
A
L
L
R
R
P
P
1730
|
N
N
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
W
W
R
R
Q
Q
G
G
I
I
Y
Y
1740
|
L
L
N
N
W
W
S
S
P
P
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
C
C
L
L
1750
|
V
V
G
G
S
S
E
E
V
V
L
L
D
D
N
N
H
H
P
P
1760
|
E
E
S
S
F
F
L
L
K
K
I
I
T
T
V
V
P
P
S
S
1770
|
C
C
R
R
K
K
G
G
C
C
I
I
L
L
L
L
G
G
Q
Q
1780
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
H
H
I
I
D
D
S
S
L
L
M
M
E
E
1790
|
E
E
W
W
F
F
P
P
G
G
L
L
L
L
E
E
I
I
D
D
1800
|
I
I
C
C
G
G
E
E
G
G
E
E
T
T
L
L
L
L
K
K
1810
|
K
K
W
W
A
A
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
N
N
D
D
G
G
1820
|
E
E
E
E
H
H
Q
Q
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
D
D
D
D
1830
|
L
L
M
M
K
K
K
K
A
A
E
E
E
E
G
G
D
D
L
L
1840
|
L
L
V
V
N
N
P
P
D
D
Q
Q
P
P
R
R
L
L
T
T
1850
|
I
I
P
P
I
I
S
S
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
P
P
D
D
L
L
1860
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
D
D
L
L
P
P
R
R
N
N
I
I
M
M
1870
|
L
L
N
N
N
N
D
D
E
E
L
L
E
E
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
1880
|
A
A
P
P
E
E
F
F
L
L
L
L
G
G
D
D
G
G
S
S
1890
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
V
V
Y
Y
R
R
A
A
A
A
Y
Y
E
E
1900
|
G
G
E
E
E
E
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
I
I
F
F
N
N
1910
|
K
K
H
H
T
T
S
S
L
L
R
R
L
L
L
L
R
R
Q
Q
1920
|
E
E
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
C
C
H
H
L
L
H
H
H
H
1930
|
P
P
S
S
L
L
I
I
S
S
L
L
L
L
A
A
A
A
G
G
1940
|
I
I
R
R
P
P
R
R
M
M
L
L
V
V
M
M
E
E
L
L
1950
|
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
S
S
L
L
D
D
R
R
L
L
L
L
1960
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
D
D
K
K
A
A
S
S
L
L
T
T
R
R
T
T
1970
|
L
L
Q
Q
H
H
R
R
I
I
A
A
L
L
H
H
V
V
A
A
1980
|
D
D
G
G
L
L
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
S
S
A
A
M
M
1990
|
I
I
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
P
P
H
H
N
N
2000
|
V
V
L
L
L
L
F
F
T
T
L
L
Y
Y
P
P
N
N
A
A
2010
|
A
A
I
I
I
I
A
A
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
Y
Y
G
S
2020
|
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
Y
Y
C
C
C
C
R
R
M
M
G
G
I
I
2030
|
K
K
T
T
S
S
E
E
G
G
T
T
P
P
G
G
F
F
R
R
2040
|
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
N
N
V
V
I
I
2050
|
Y
Y
N
N
Q
Q
Q
Q
A
A
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
2060
|
G
G
L
L
L
L
L
L
Y
Y
D
D
I
I
L
L
T
T
T
T
2070
|
G
G
G
G
R
R
I
I
V
V
E
E
G
G
L
L
K
K
F
F
2080
|
P
P
N
N
E
E
F
F
D
D
E
E
L
L
E
E
I
I
Q
Q
2090
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
P
P
D
D
P
P
V
V
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
2100
|
G
G
C
C
A
A
P
P
W
W
P
P
M
M
V
V
E
E
K
K
2110
|
L
L
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
C
C
L
L
K
K
E
E
N
N
P
P
2120
|
Q
Q
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
S
S
A
A
Q
Q
V
V
F
F
2130
|
D
D
I
I
L
L
N
N
S
S
A
A
E
E
L
L
V
V
C
C
2140
|
L
L
T
T
R
R
R
R
I
I
L
L
L
L
P
P
K
K
N
N
2150
|
V
V
I
I
V
V
E
E
C
C
M
M
V
V
A
A
T
T
H
H
2160
|
H
H
N
N
S
S
R
R
N
N
A
A
S
S
I
I
W
W
L
L
2170
|
G
G
C
C
G
G
H
H
T
T
D
D
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
2180
|
S
S
F
F
L
L
D
D
L
L
N
N
T
T
E
E
G
G
Y
Y
2190
|
T
T
S
S
E
E
E
E
V
V
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
I
I
2200
|
L
L
C
C
L
L
A
A
L
L
V
V
H
H
L
L
P
P
V
V
2210
|
E
E
K
K
E
E
S
S
W
W
I
I
V
V
S
S
G
G
T
T
2220
|
Q
Q
S
S
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
2230
|
E
E
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
R
R
H
H
T
T
L
L
E
E
2240
|
K
K
M
M
T
T
D
D
S
S
V
V
T
T
C
C
L
L
Y
Y
2250
|
C
C
N
N
S
S
F
F
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
2260
|
K
K
N
N
F
F
L
L
L
L
V
V
G
G
T
T
A
A
D
D
2270
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
A
A
I
I
F
F
E
E
D
D
K
K
T
T
2280
|
V
V
K
K
L
L
K
K
G
G
A
A
A
A
P
P
L
L
K
K
2290
|
I
I
L
L
N
N
I
I
G
G
N
N
V
V
S
S
T
T
P
P
2300
|
L
L
M
M
C
C
L
L
S
S
E
E
S
S
T
T
N
N
S
S
2310
|
T
T
E
E
R
R
N
N
V
V
M
M
W
W
G
G
G
G
C
C
2320
|
G
G
T
T
K
K
I
I
F
F
S
S
F
F
S
S
N
N
D
D
2330
|
F
F
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
K
K
L
L
I
I
E
E
T
T
R
R
2340
|
T
T
S
S
Q
Q
L
L
F
F
S
S
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
F
F
2350
|
S
S
D
D
S
S
N
N
I
I
I
I
T
T
V
V
V
V
V
V
2360
|
D
D
T
T
A
A
L
L
Y
Y
I
I
A
A
K
K
Q
Q
N
N
2370
|
S
S
P
P
V
V
V
V
E
E
V
V
W
W
D
D
K
K
K
K
2380
|
T
T
E
E
K
K
L
L
C
C
G
G
L
L
I
I
D
D
C
C
2390
|
V
V
H
H
F
F
L
L
R
R
E
E
V
V
M
M
V
V
K
K
2400
|
E
E
N
N
K
K
E
E
S
S
K
K
H
H
K
K
M
M
S
S
2410
|
Y
Y
S
S
G
G
R
R
V
V
K
K
T
T
L
L
C
C
L
L
2420
|
Q
Q
K
K
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
W
W
I
I
G
G
T
T
2430
|
G
G
G
G
G
G
H
H
I
I
L
L
L
L
L
L
D
D
L
L
2440
|
S
S
T
T
R
R
R
R
L
L
I
I
R
R
V
V
I
I
Y
Y
2450
|
N
N
F
F
C
C
N
N
S
S
V
V
R
R
V
V
M
M
M
M
2460
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
G
G
S
S
L
L
K
K
N
N
V
V
2470
|
M
M
L
L
V
V
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
N
N
R
R
K
K
N
N
2480
|
T
T
E
E
G
G
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
Q
Q
K
K
E
E
I
I
2490
|
Q
Q
S
S
C
C
L
L
T
T
V
V
W
W
D
D
I
I
N
N
2500
|
L
L
P
P
H
H
E
E
V
V
Q
Q
N
N
L
L
E
E
K
K
2510
|
H
H
I
I
E
E
V
V
R
R
K
K
E
E
L
L
A
A
E
E
2520
|
K
K
M
M
R
R
R
R
T
T
S
S
V
V
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Molecular docking analysis; Molecular dynamic simulation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The deleterious mutations G2019S and I2020T in the kinase domain were playing a key role in causing resistance to drug levedopa. | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 07

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Substantia nigra tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Parkinson disease | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.16E-01; Fold-change: -2.90E-01; Z-score: -4.21E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
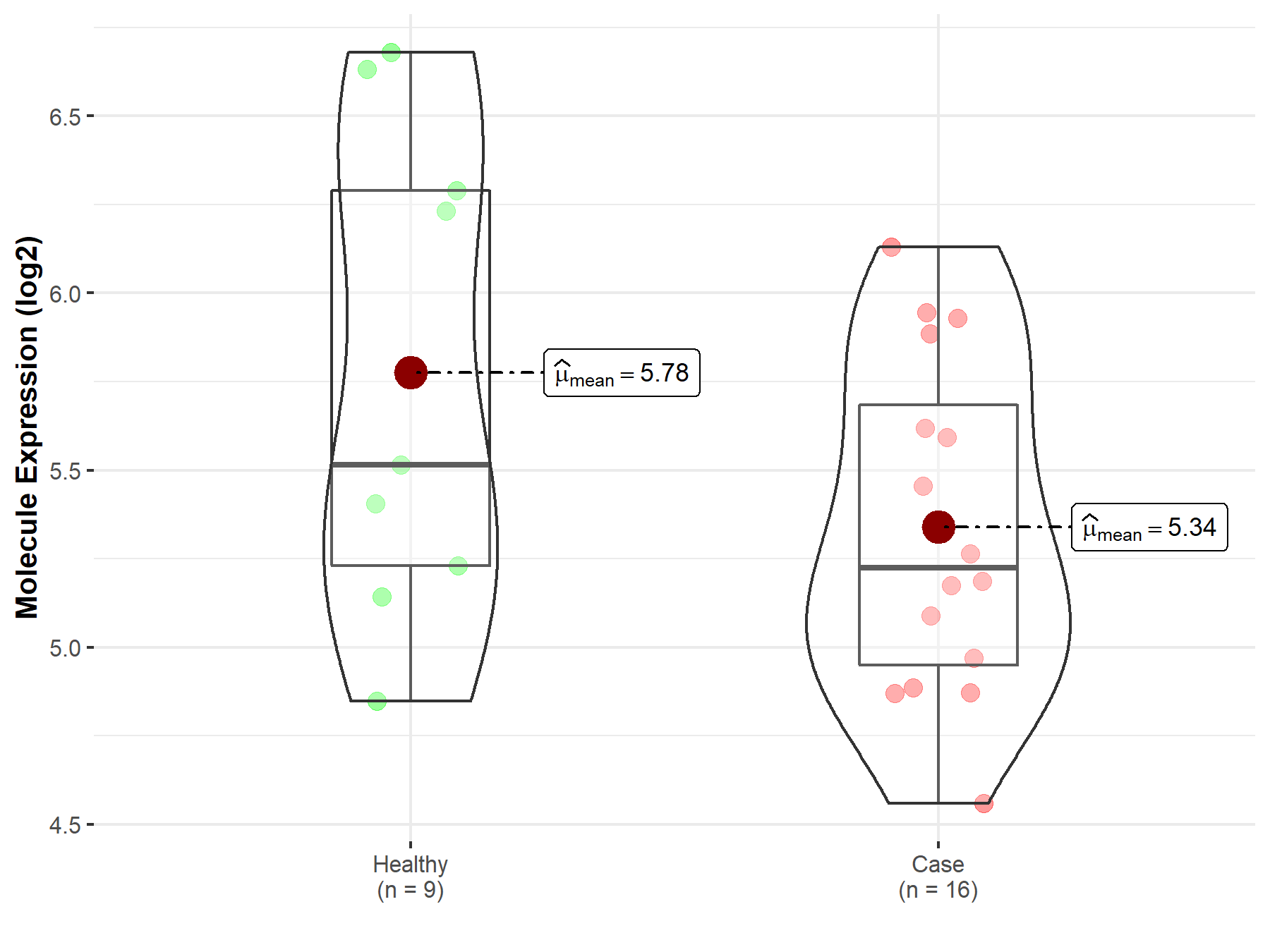
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
