Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01933)
| Name |
ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit d1 (ATP6V0D1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ATP6V0D1; ATP6D; VPATPD
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ATP6V0D1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr16:67,438,014-67,481,181[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSFFPELYFNVDNGYLEGLVRGLKAGVLSQADYLNLVQCETLEDLKLHLQSTDYGNFLAN
EASPLTVSVIDDRLKEKMVVEFRHMRNHAYEPLASFLDFITYSYMIDNVILLITGTLHQR SIAELVPKCHPLGSFEQMEAVNIAQTPAELYNAILVDTPLAAFFQDCISEQDLDEMNIEI IRNTLYKAYLESFYKFCTLLGGTTADAMCPILEFEADRRAFIITINSFGTELSKEDRAKL FPHCGRLYPEGLAQLARADDYEQVKNVADYYPEYKLLFEGAGSNPGDKTLEDRFFEHEVK LNKLAFLNQFHFGVFYAFVKLKEQECRNIVWIAECIAQRHRAKIDNYIPIF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Subunit of the V0 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons. V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment. May play a role in coupling of proton transport and ATP hydrolysis. In aerobic conditions, involved in intracellular iron homeostasis, thus triggering the activity of Fe(2+) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes, and leading to HIF1A hydroxylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation. May play a role in cilium biogenesis through regulation of the transport and the localization of proteins to the cilium.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cyclophosphamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cyclophosphamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cyclophosphamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Non-small cell lung cancer isolates | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunofluorescence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The drug resistance of cancer cells is likely to be related to the changes in pH gradient between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm.Vacuolar-H+ -ATPase(V-ATPase) plays a major role in the regulation of cellular pH conditions.The expression of V-ATPase was shown to be related to the pathological type and grade of the cancer and might be associated with the chemotherapy drug resistance in NSCLC. | |||
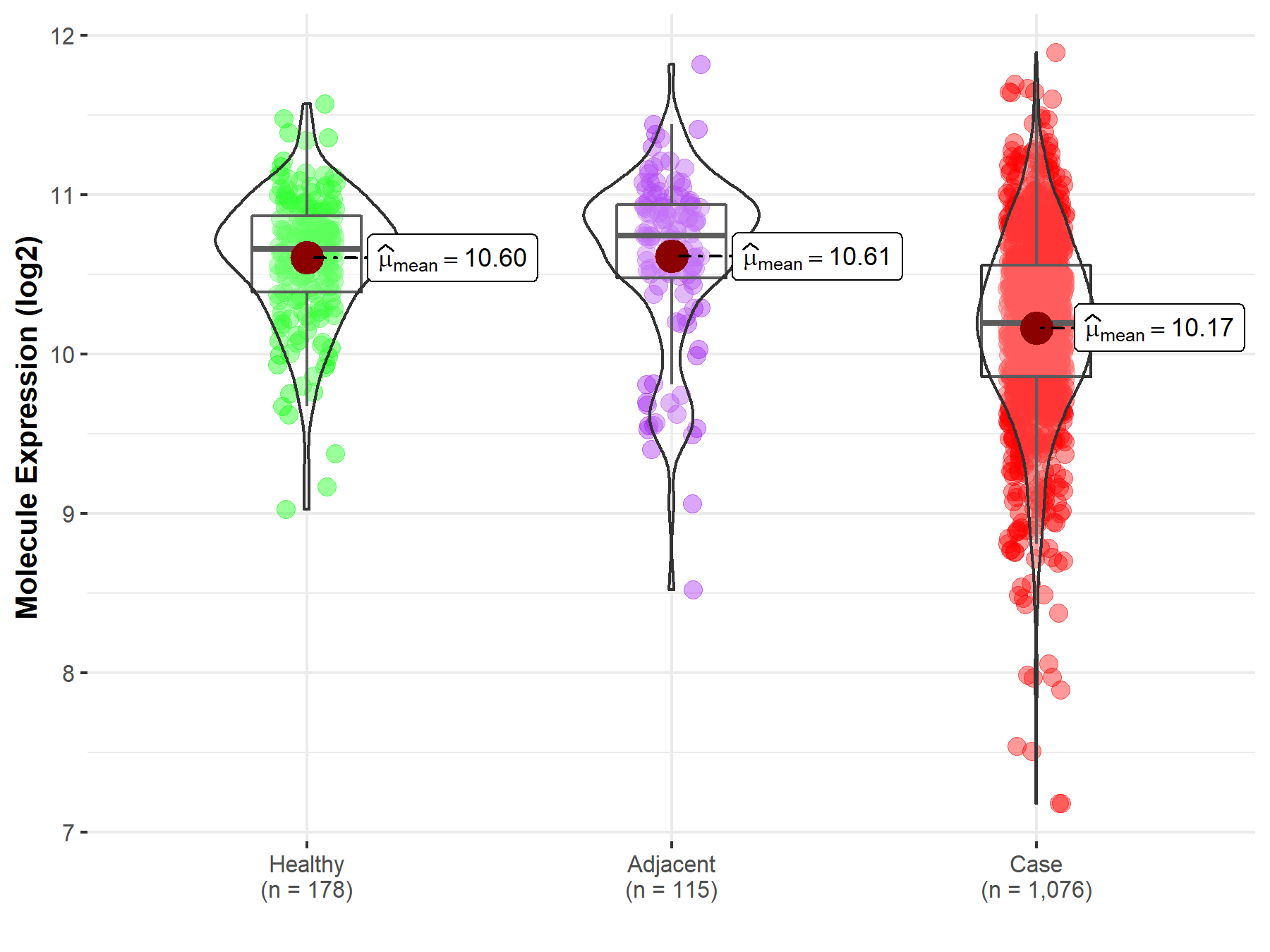
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.67E-29; Fold-change: -4.67E-01; Z-score: -1.15E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.40E-14; Fold-change: -5.52E-01; Z-score: -1.02E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
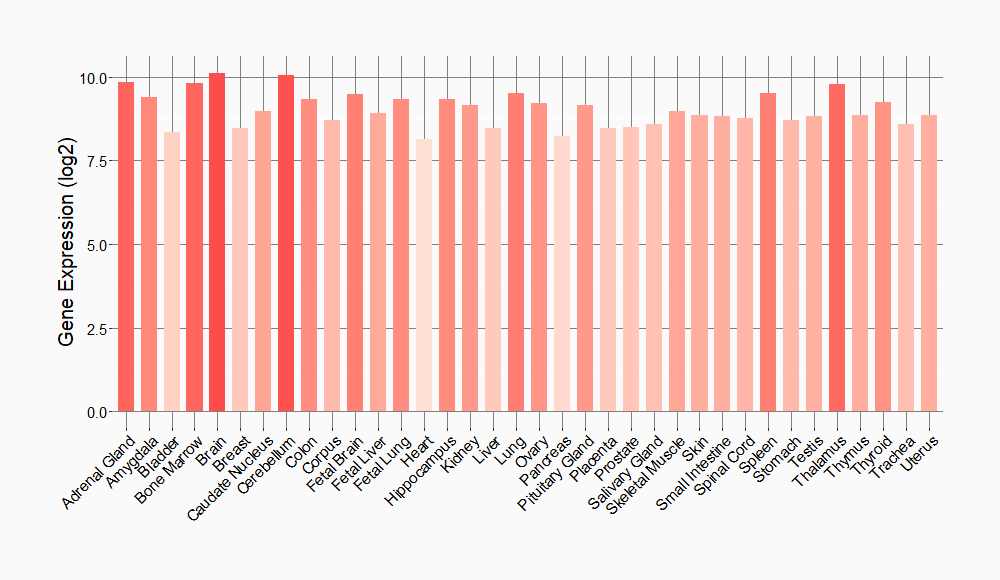
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
