Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01932)
| Name |
Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SGPL1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
SGPL1; KIAA1252
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SGPL1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr10:70,815,948-70,881,184[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MPSTDLLMLKAFEPYLEILEVYSTKAKNYVNGHCTKYEPWQLIAWSVVWTLLIVWGYEFV
FQPESLWSRFKKKCFKLTRKMPIIGRKIQDKLNKTKDDISKNMSFLKVDKEYVKALPSQG LSSSAVLEKLKEYSSMDAFWQEGRASGTVYSGEEKLTELLVKAYGDFAWSNPLHPDIFPG LRKIEAEIVRIACSLFNGGPDSCGCVTSGGTESILMACKAYRDLAFEKGIKTPEIVAPQS AHAAFNKAASYFGMKIVRVPLTKMMEVDVRAMRRAISRNTAMLVCSTPQFPHGVIDPVPE VAKLAVKYKIPLHVDACLGGFLIVFMEKAGYPLEHPFDFRVKGVTSISADTHKYGYAPKG SSLVLYSDKKYRNYQFFVDTDWQGGIYASPTIAGSRPGGISAACWAALMHFGENGYVEAT KQIIKTARFLKSELENIKGIFVFGNPQLSVIALGSRDFDIYRLSNLMTAKGWNLNQLQFP PSIHFCITLLHARKRVAIQFLKDIRESVTQIMKNPKAKTTGMGAIYGMAQTTVDRNMVAE LSSVFLDSLYSTDTVTQGSQMNGSPKPH Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Cleaves phosphorylated sphingoid bases (PSBs), such as sphingosine-1-phosphate, into fatty aldehydes and phosphoethanolamine. Elevates stress-induced ceramide production and apoptosis. Required for global lipid homeostasis in liver and cholesterol homeostasis in fibroblasts. Involved in the regulation of pro-inflammatory response and neutrophil trafficking. Modulates neuronal autophagy via phosphoethanolamine production which regulates accumulation of aggregate-prone proteins such as APP. Seems to play a role in establishing neuronal contact sites and axonal maintenance.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | OE33 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0471 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | OE21 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2661 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastroesophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastroesophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Gastroesophageal cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | OE33 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0471 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | OE21 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2661 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastroesophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastroesophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Gastroesophageal cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cardia adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | OE33 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0471 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | OE21 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2661 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastroesophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastroesophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Gastroesophageal cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | S1P could lead to cytotoxic drug resistance in gastroesophegal cancer acting in an autocrine or paracrine manner via cell surface S1P receptors following transportation out of the cytosol. Alternatively S1P may mediate cytotoxic drug resistance acting intracellularly by counteracting apoptosis mediated by its pro-apoptotic precursor ceramide or interaction with known intracellular targets involved in cancer pathogenesis and cytotoxic drug resistance such as Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) to which S1P directly binds and inhibits, and TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 (TRAF 2), or Protein Kinase C (PKC). S1P production controlled by SPHK1 and SGPL1 are key determinants of cytotoxic drug resistance and that decreasing S1P production in cancer cells could lead to increased cytotoxic sensitivity. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.78E-02; Fold-change: 5.03E-01; Z-score: 9.58E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
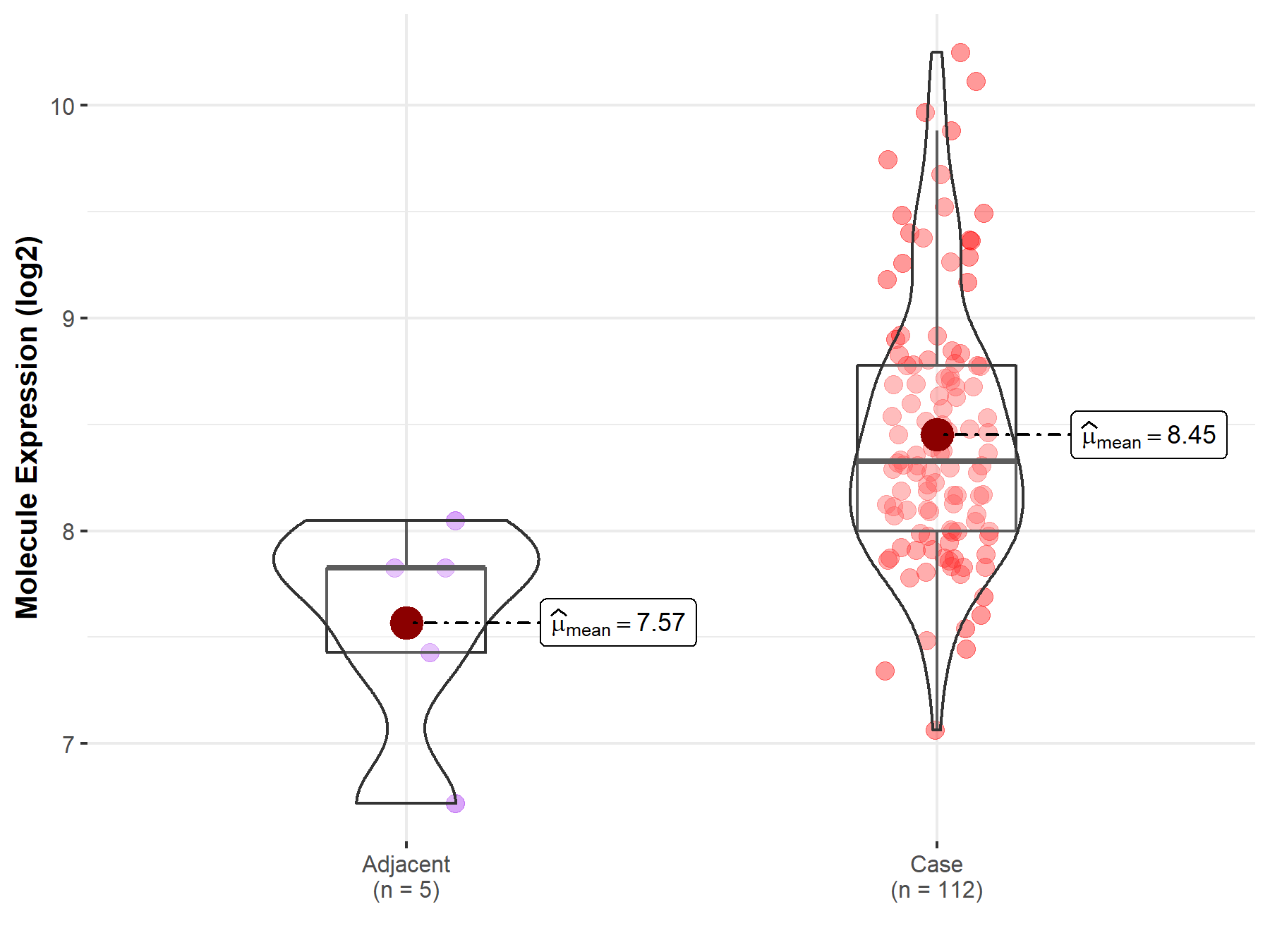
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.79E-03; Fold-change: 1.11E+00; Z-score: 5.26E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.37E-03; Fold-change: 4.58E-01; Z-score: 1.01E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
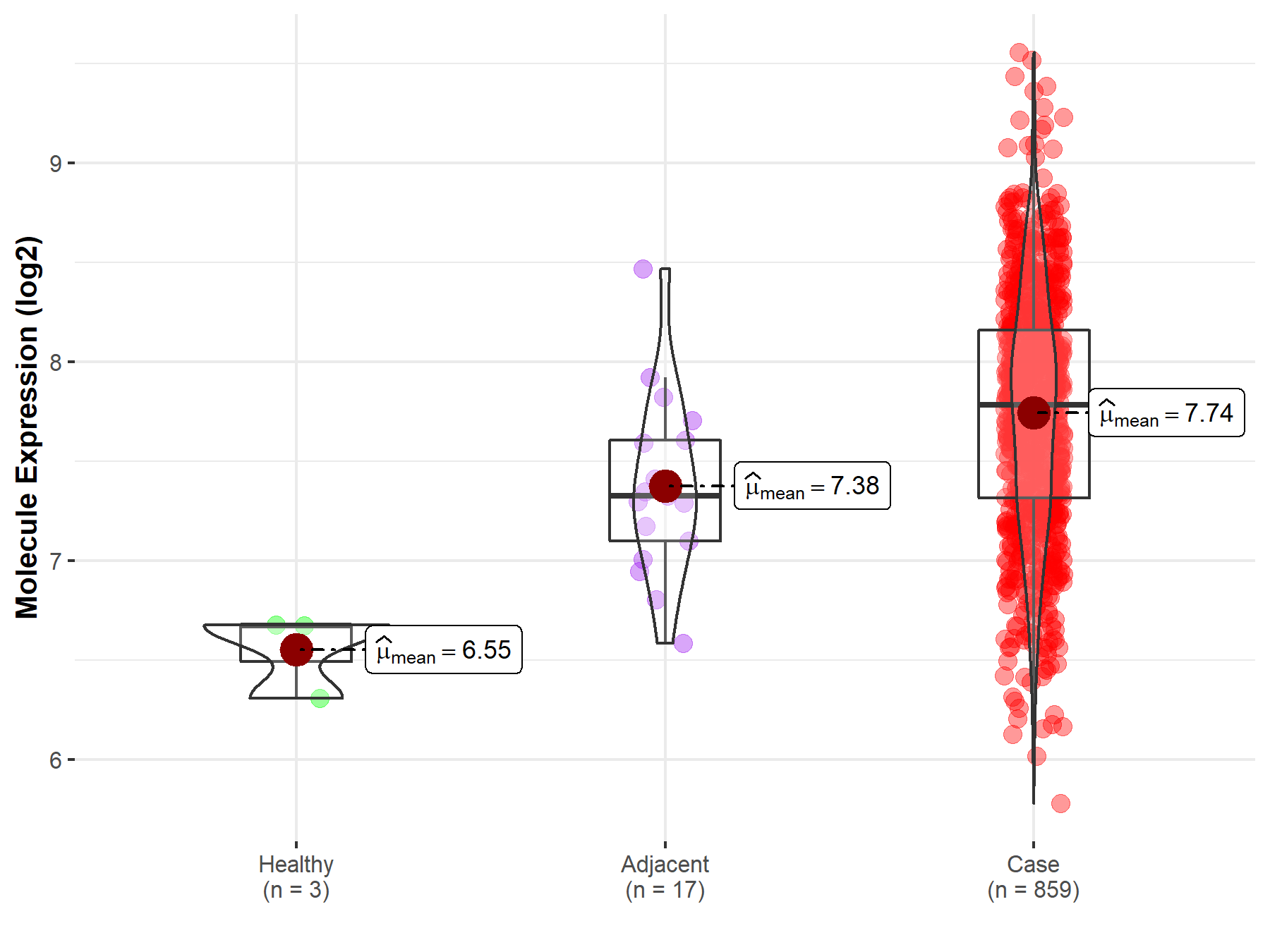
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

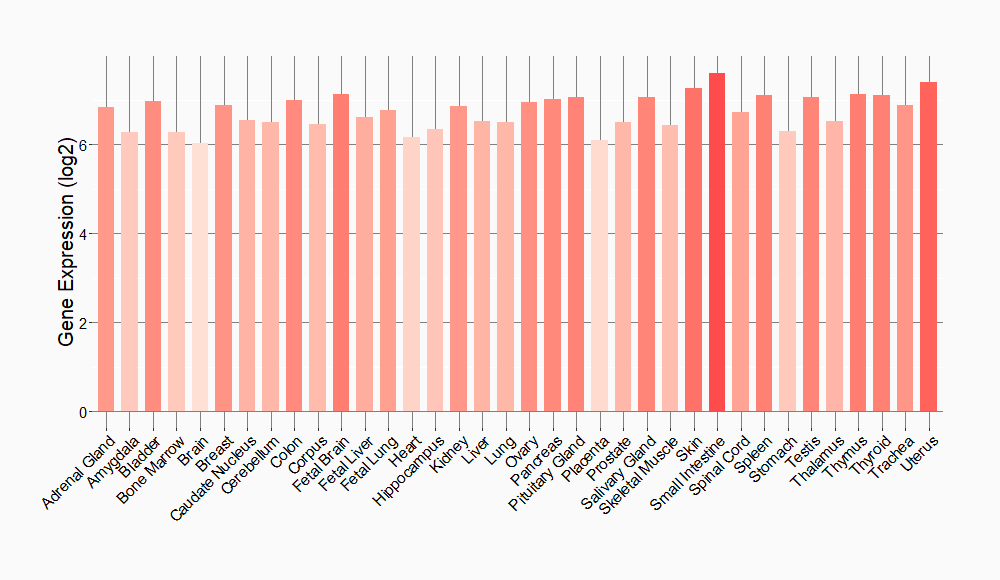
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
