Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01930)
| Name |
TNF superfamily member 11 (TNFSF11)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
TNFSF11; OPGL; RANKL; TRANCE
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
TNFSF11
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr13:42,562,736-42,608,013[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MRRASRDYTKYLRGSEEMGGGPGAPHEGPLHAPPPPAPHQPPAASRSMFVALLGLGLGQV
VCSVALFFYFRAQMDPNRISEDGTHCIYRILRLHENADFQDTTLESQDTKLIPDSCRRIK QAFQGAVQKELQHIVGSQHIRAEKAMVDGSWLDLAKRSKLEAQPFAHLTINATDIPSGSH KVSLSSWYHDRGWAKISNMTFSNGKLIVNQDGFYYLYANICFRHHETSGDLATEYLQLMV YVTKTSIKIPSSHTLMKGGSTKYWSGNSEFHFYSINVGGFFKLRSGEEISIEVSNPSLLD PDQDATYFGAFKVRDID Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF11B/OPG and to TNFRSF11A/RANK. Osteoclast differentiation and activation factor. Augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T-cell proliferation. May be an important regulator of interactions between T-cells and dendritic cells and may play a role in the regulation of the T-cell-dependent immune response. May also play an important role in enhanced bone-resorption in humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. Induces osteoclastogenesis by activating multiple signaling pathways in osteoclast precursor cells, chief among which is induction of long lasting oscillations in the intracellular concentration of Ca (2+) resulting in the activation of NFATC1, which translocates to the nucleus and induces osteoclast-specific gene transcription to allow differentiation of osteoclasts. During osteoclast differentiation, in a TMEM64 and ATP2A2-dependent manner induces activation of CREB1 and mitochondrial ROS generation necessary for proper osteoclast generation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Matrine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | RAW264.7 cells | Ascites | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0493 |
| In Vivo Model | C57BL/6 mice | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TRAP staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The imbalance between the osteogenic effects of osteoblasts and the osteoclasts of osteoclasts is one of the pathogenesis of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Secretion of estrogen causes an increase in the level of proinflammatory cytokines. Inflammation-induced osteoclast hyperactivity plays a crucial role in the imbalance. Matrine can inhibit osteoclastogenesis, inhibit inflammation and alleviate osteoporosis by regulating the NF-kappa-B/AKT/MAPK pathway. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteoporosis [ICD-11: FB83.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Matrine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | RAW264.7 cells | Ascites | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0493 |
| In Vivo Model | C57BL/6 mice | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TRAP staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The imbalance between the osteogenic effects of osteoblasts and the osteoclasts of osteoclasts is one of the pathogenesis of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Secretion of estrogen causes an increase in the level of proinflammatory cytokines. Inflammation-induced osteoclast hyperactivity plays a crucial role in the imbalance. Matrine can inhibit osteoclastogenesis, inhibit inflammation and alleviate osteoporosis by regulating the NF-kappa-B/AKT/MAPK pathway. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 15

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Osteoporosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.42E-01; Fold-change: -1.61E-01; Z-score: -3.69E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
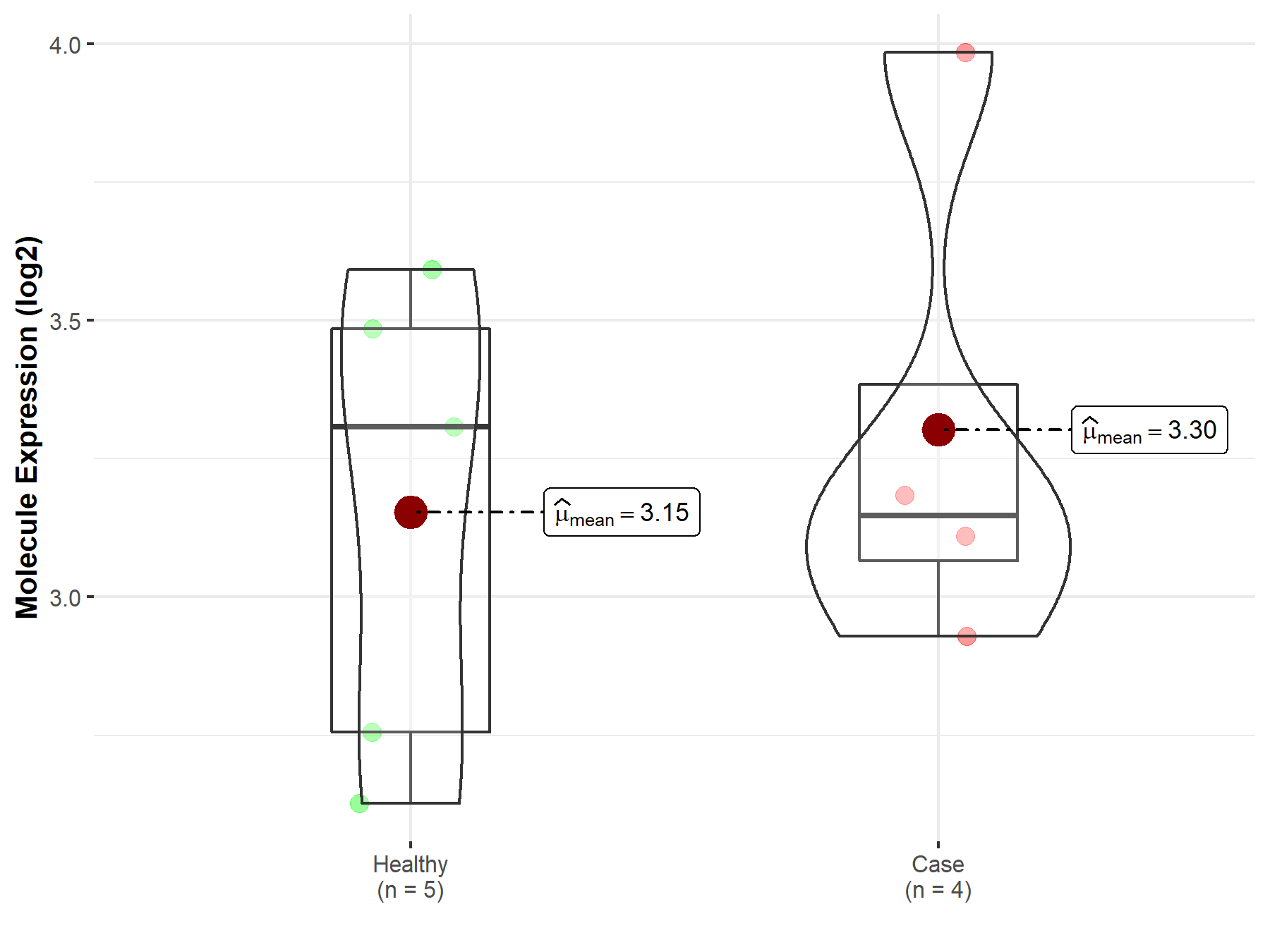
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

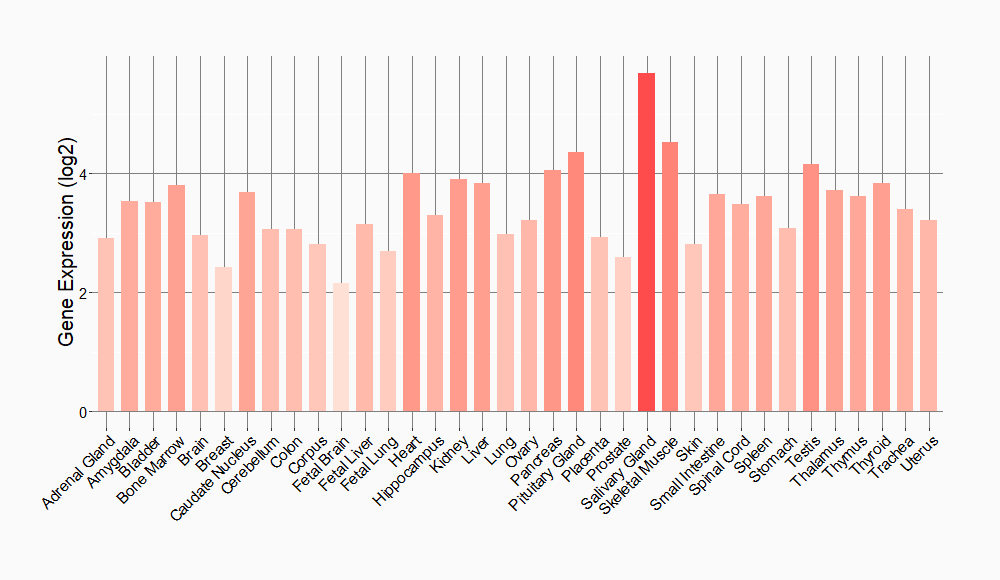
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
