Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01928)
| Name |
O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) transferase (OGT)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
OGT
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
OGT
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chrX:71,533,104-71,575,892[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MASSVGNVADSTEPTKRMLSFQGLAELAHREYQAGDFEAAERHCMQLWRQEPDNTGVLLL
LSSIHFQCRRLDRSAHFSTLAIKQNPLLAEAYSNLGNVYKERGQLQEAIEHYRHALRLKP DFIDGYINLAAALVAAGDMEGAVQAYVSALQYNPDLYCVRSDLGNLLKALGRLEEAKACY LKAIETQPNFAVAWSNLGCVFNAQGEIWLAIHHFEKAVTLDPNFLDAYINLGNVLKEARI FDRAVAAYLRALSLSPNHAVVHGNLACVYYEQGLIDLAIDTYRRAIELQPHFPDAYCNLA NALKEKGSVAEAEDCYNTALRLCPTHADSLNNLANIKREQGNIEEAVRLYRKALEVFPEF AAAHSNLASVLQQQGKLQEALMHYKEAIRISPTFADAYSNMGNTLKEMQDVQGALQCYTR AIQINPAFADAHSNLASIHKDSGNIPEAIASYRTALKLKPDFPDAYCNLAHCLQIVCDWT DYDERMKKLVSIVADQLEKNRLPSVHPHHSMLYPLSHGFRKAIAERHGNLCLDKINVLHK PPYEHPKDLKLSDGRLRVGYVSSDFGNHPTSHLMQSIPGMHNPDKFEVFCYALSPDDGTN FRVKVMAEANHFIDLSQIPCNGKAADRIHQDGIHILVNMNGYTKGARNELFALRPAPIQA MWLGYPGTSGALFMDYIITDQETSPAEVAEQYSEKLAYMPHTFFIGDHANMFPHLKKKAV IDFKSNGHIYDNRIVLNGIDLKAFLDSLPDVKIVKMKCPDGGDNADSSNTALNMPVIPMN TIAEAVIEMINRGQIQITINGFSISNGLATTQINNKAATGEEVPRTIIVTTRSQYGLPED AIVYCNFNQLYKIDPSTLQMWANILKRVPNSVLWLLRFPAVGEPNIQQYAQNMGLPQNRI IFSPVAPKEEHVRRGQLADVCLDTPLCNGHTTGMDVLWAGTPMVTMPGETLASRVAASQL TCLGCLELIAKNRQEYEDIAVKLGTDLEYLKKVRGKVWKQRISSPLFNTKQYTMELERLY LQMWEHYAAGNKPDHMIKPVEVTESA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the transfer of a single N-acetylglucosamine from UDP-GlcNAc to a serine or threonine residue in cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins resulting in their modification with a beta-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc). Glycosylates a large and diverse number of proteins including histone H2B, AKT1, ATG4B, EZH2, PFKL, KMT2E/MLL5, MAPT/TAU and HCFC1. Can regulate their cellular processes via cross-talk between glycosylation and phosphorylation or by affecting proteolytic processing. Probably by glycosylating KMT2E/MLL5, stabilizes KMT2E/MLL5 by preventing its ubiquitination. Involved in insulin resistance in muscle and adipocyte cells via glycosylating insulin signaling components and inhibiting the 'Thr-308' phosphorylation of AKT1, enhancing IRS1 phosphorylation and attenuating insulin signaling. Involved in glycolysis regulation by mediating glycosylation of 6-phosphofructokinase PFKL, inhibiting its activity. Component of a THAP1/THAP3-HCFC1-OGT complex that is required for the regulation of the transcriptional activity of RRM1. Plays a key role in chromatin structure by mediating O-GlcNAcylation of 'Ser-112' of histone H2B: recruited to CpG-rich transcription start sites of active genes via its interaction with TET proteins (TET1, TET2 or TET3). As part of the NSL complex indirectly involved in acetylation of nucleosomal histone H4 on several lysine residues. O-GlcNAcylation of 'Ser-75' of EZH2 increases its stability, and facilitating the formation of H3K27me3 by the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex. Regulates circadian oscillation of the clock genes and glucose homeostasis in the liver. Stabilizes clock proteins ARNTL/BMAL1 and CLOCK through O-glycosylation, which prevents their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Promotes the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1-mediated transcription of genes in the negative loop of the circadian clock such as PER1/2 and CRY1/2. O-glycosylates HCFC1 and regulates its proteolytic processing and transcriptional activity. Regulates mitochondrial motility in neurons by mediating glycosylation of TRAK1. Glycosylates HOXA1. O-glycosylates FNIP1. Promotes autophagy by mediating O-glycosylation of ATG4B.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Insulin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recently, skeletal muscle-specific O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) knockout mice on a HFD were reported to have low plasma glucose levels and glucose tolerances. Moreover, the overexpression of O-GlcNAcase (OGA), which removes O-GlcNAc from proteins, significantly improved whole-body glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in db/db mice, and O-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranosylidene) amino-N-phenylcarbamate (PUGNAc) (an OGA inhibitor) suppressed insulin-mediated glucose uptake in adipocytes. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 05

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Omental adipose tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Obesity related type 2 diabetes | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.96E-01; Fold-change: 3.42E-03; Z-score: 7.70E-03 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Type 2 diabetes mellitus | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.53E-01; Fold-change: -2.64E-01; Z-score: -9.77E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

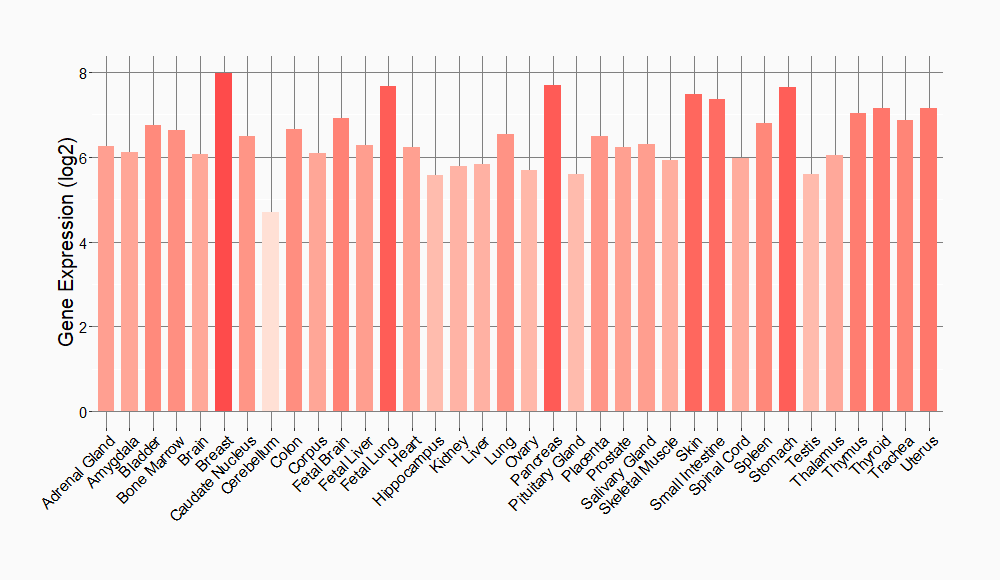
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
