Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01843)
| Name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 (STK11)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11; (Liver kinase B1; LKB1; hLKB1; Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-19
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
STK11
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr19:1,177,558-1,228,431[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEVVDPQQLGMFTEGELMSVGMDTFIHRIDSTEVIYQPRRKRAKLIGKYLMGDLLGEGSY
GKVKEVLDSETLCRRAVKILKKKKLRRIPNGEANVKKEIQLLRRLRHKNVIQLVDVLYNE EKQKMYMVMEYCVCGMQEMLDSVPEKRFPVCQAHGYFCQLIDGLEYLHSQGIVHKDIKPG NLLLTTGGTLKISDLGVAEALHPFAADDTCRTSQGSPAFQPPEIANGLDTFSGFKVDIWS AGVTLYNITTGLYPFEGDNIYKLFENIGKGSYAIPGDCGPPLSDLLKGMLEYEPAKRFSI RQIRQHSWFRKKHPPAEAPVPIPPSPDTKDRWRSMTVVPYLEDLHGADEDEDLFDIEDDI IYTQDFTVPGQVPEEEASHNGQRRGLPKAVCMNGTEAAQLSTKSRAEGRAPNPARKACSA SSKIRRLSACKQQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Tumor suppressor serine/threonine-protein kinase that controls the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) family members, thereby playing a role in various processes such as cell metabolism, cell polarity, apoptosis and DNA damage response. Acts by phosphorylating the T-loop of AMPK family proteins, thus promoting their activity: phosphorylates PRKAA1, PRKAA2, BRSK1, BRSK2, MARK1, MARK2, MARK3, MARK4, NUAK1, NUAK2, SIK1, SIK2, SIK3 and SNRK but not MELK. Also phosphorylates non-AMPK family proteins such as STRADA, PTEN and possibly p53/TP53. Acts as a key upstream regulator of AMPK by mediating phosphorylation and activation of AMPK catalytic subunits PRKAA1 and PRKAA2 and thereby regulates processes including: inhibition of signaling pathways that promote cell growth and proliferation when energy levels are low, glucose homeostasis in liver, activation of autophagy when cells undergo nutrient deprivation, and B-cell differentiation in the germinal center in response to DNA damage. Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton. Required for cortical neuron polarization by mediating phosphorylation and activation of BRSK1 and BRSK2, leading to axon initiation and specification. Involved in DNA damage response: interacts with p53/TP53 and recruited to the CDKN1A/WAF1 promoter to participate in transcription activation. Able to phosphorylate p53/TP53; the relevance of such result in vivo is however unclear and phosphorylation may be indirect and mediated by downstream STK11/LKB1 kinase NUAK1. Also acts as a mediator of p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis via interaction with p53/TP53: translocates to the mitochondrion during apoptosis and regulates p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis pathways. Regulates UV radiation-induced DNA damage response mediated by CDKN1A. In association with NUAK1, phosphorylates CDKN1A in response to UV radiation and contributes to its degradation which is necessary for optimal DNA repair.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Durvalumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | |
| In Vitro Model | 4T1-Luc2 cells | Mammary gland | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_A4BM |
| CD138+ myeloma cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| HTH7 cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6289 | |
| EMT6 WT cells | Breast | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_1923 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse tumor model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to Durvalumab and Durvalumab plus Tremelimumab Is Associated with Functional STK11 Mutations in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Is Reversed by STAT3 Knockdown. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Trametinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q37* (c.109C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MEK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04011 | |
| In Vitro Model | H292 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0455 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Calu-3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0609 | |
| HCC78 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2061 | |
| HCC515 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5136 | |
| HCC2935 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1265 | |
| HCC193 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5130 | |
| HCC15 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2057 | |
| H520 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1566 | |
| H2126 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1532 | |
| H2122 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1531 | |
| H2085 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1523 | |
| H1993 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1512 | |
| H1435 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1470 | |
| H1395 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1467 | |
| H1355 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1464 | |
| Calu-6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0236 | |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| In Vivo Model | NOD-SCID mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Alamar blue proliferation assay | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Trametinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.E199* (c.595G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MEK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04011 | |
| In Vitro Model | H292 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0455 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Calu-3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0609 | |
| HCC78 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2061 | |
| HCC515 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5136 | |
| HCC2935 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1265 | |
| HCC193 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5130 | |
| HCC15 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2057 | |
| H520 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1566 | |
| H2126 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1532 | |
| H2122 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1531 | |
| H2085 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1523 | |
| H1993 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1512 | |
| H1435 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1470 | |
| H1395 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1467 | |
| H1355 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1464 | |
| Calu-6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0236 | |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| In Vivo Model | NOD-SCID mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Alamar blue proliferation assay | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Trametinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.W332* (c.995G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MEK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04011 | |
| In Vitro Model | H292 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0455 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Calu-3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0609 | |
| HCC78 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2061 | |
| HCC515 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5136 | |
| HCC2935 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1265 | |
| HCC193 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5130 | |
| HCC15 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2057 | |
| H520 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1566 | |
| H2126 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1532 | |
| H2122 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1531 | |
| H2085 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1523 | |
| H1993 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1512 | |
| H1435 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1470 | |
| H1395 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1467 | |
| H1355 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1464 | |
| Calu-6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0236 | |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| In Vivo Model | NOD-SCID mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Alamar blue proliferation assay | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.96E-09; Fold-change: -2.13E-01; Z-score: -8.55E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.41E-06; Fold-change: -1.85E-01; Z-score: -5.43E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
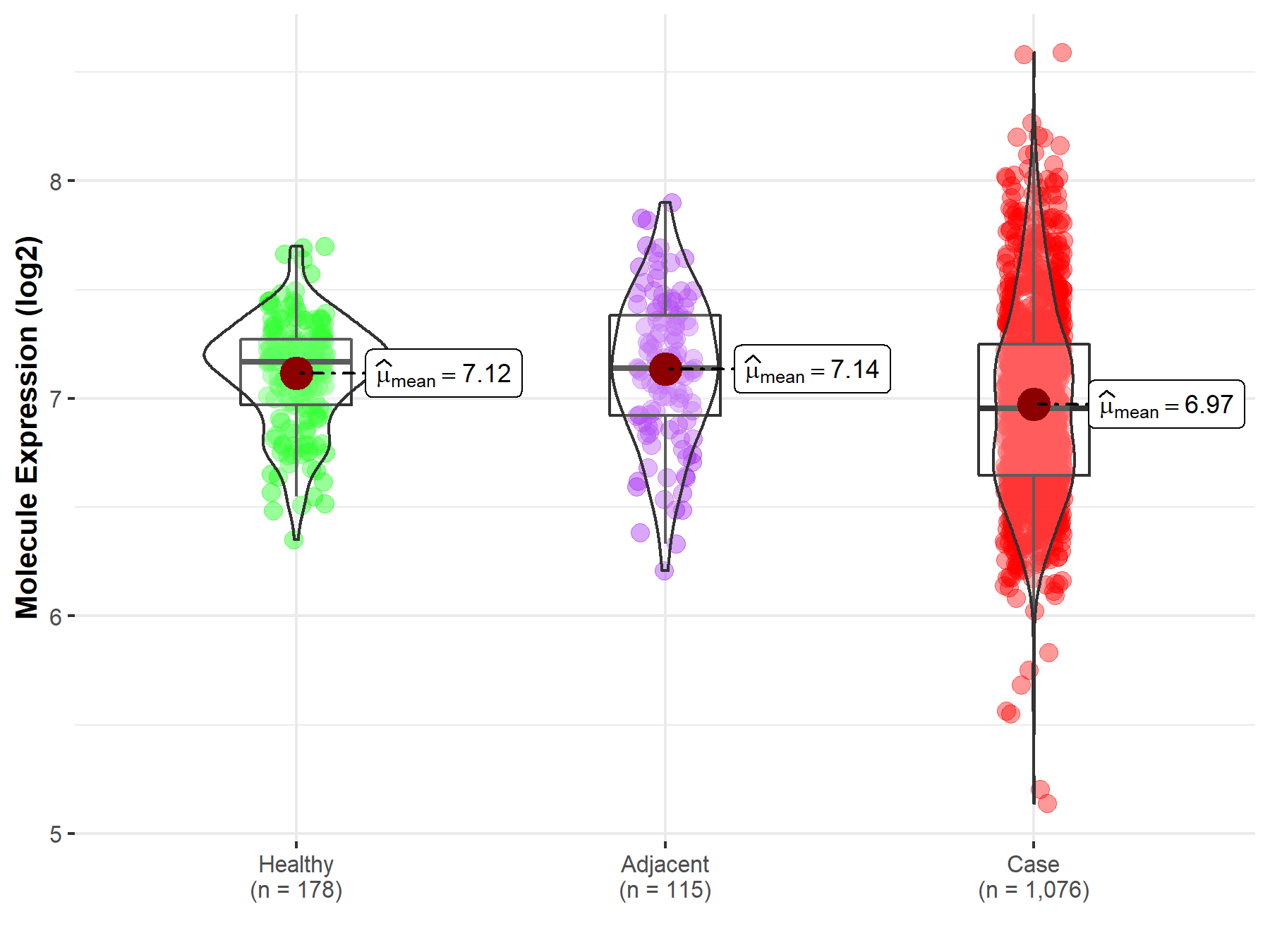
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

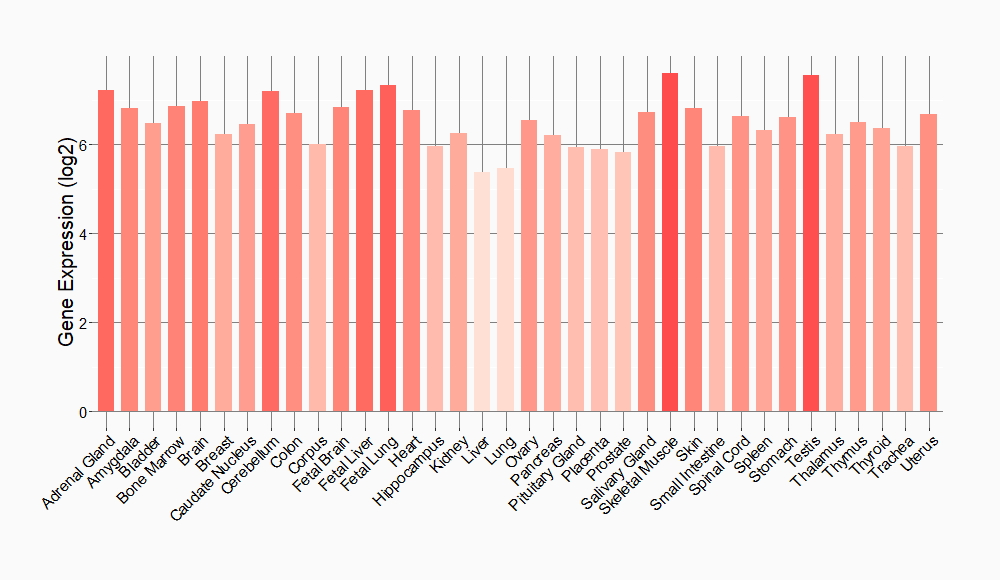
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
