Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01823)
| Name |
Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 (CD33)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 3; Siglec-3; gp67; CD antigen CD33; SIGLEC3
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CD33
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr19:51,225,064-51,243,860[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MPLLLLLPLLWAGALAMDPNFWLQVQESVTVQEGLCVLVPCTFFHPIPYYDKNSPVHGYW
FREGAIISRDSPVATNKLDQEVQEETQGRFRLLGDPSRNNCSLSIVDARRRDNGSYFFRM ERGSTKYSYKSPQLSVHVTDLTHRPKILIPGTLEPGHSKNLTCSVSWACEQGTPPIFSWL SAAPTSLGPRTTHSSVLIITPRPQDHGTNLTCQVKFAGAGVTTERTIQLNVTYVPQNPTT GIFPGDGSGKQETRAGVVHGAIGGAGVTALLALCLCLIFFIVKTHRRKAARTAVGRNDTH PTTGSASPKHQKKSKLHGPTETSSCSGAAPTVEMDEELHYASLNFHGMNPSKDTSTEYSE VRTQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Sialic-acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) that plays a role in mediating cell-cell interactions and in maintaining immune cells in a resting state. Preferentially recognizes and binds alpha-2,3- and more avidly alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid-bearing glycans. Upon engagement of ligands such as C1q or syalylated glycoproteins, two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) located in CD33 cytoplasmic tail are phosphorylated by Src-like kinases such as LCK. These phosphorylations provide docking sites for the recruitment and activation of protein-tyrosine phosphatases PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2. In turn, these phosphatases regulate downstream pathways through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. One of the repressive effect of CD33 on monocyte activation requires phosphoinositide 3-kinase/PI3K.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemtuzumab ozogamicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 |
| KG-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0374 | |
| GDM-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1230 | |
| HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 | |
| NB4 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0005 | |
| TF-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western Blot Analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometric SCNP assays | |||
| Mechanism Description | AKT signaling modulates GO/calicheamicin-gamma1 cytotoxicity and is associated with cellular-resistance to these drugs. In turn, inhibition of AKT activation can greatly increase GO/calicheamicin-gamma1 sensitivity. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.37E-13; Fold-change: 5.78E-01; Z-score: 1.13E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
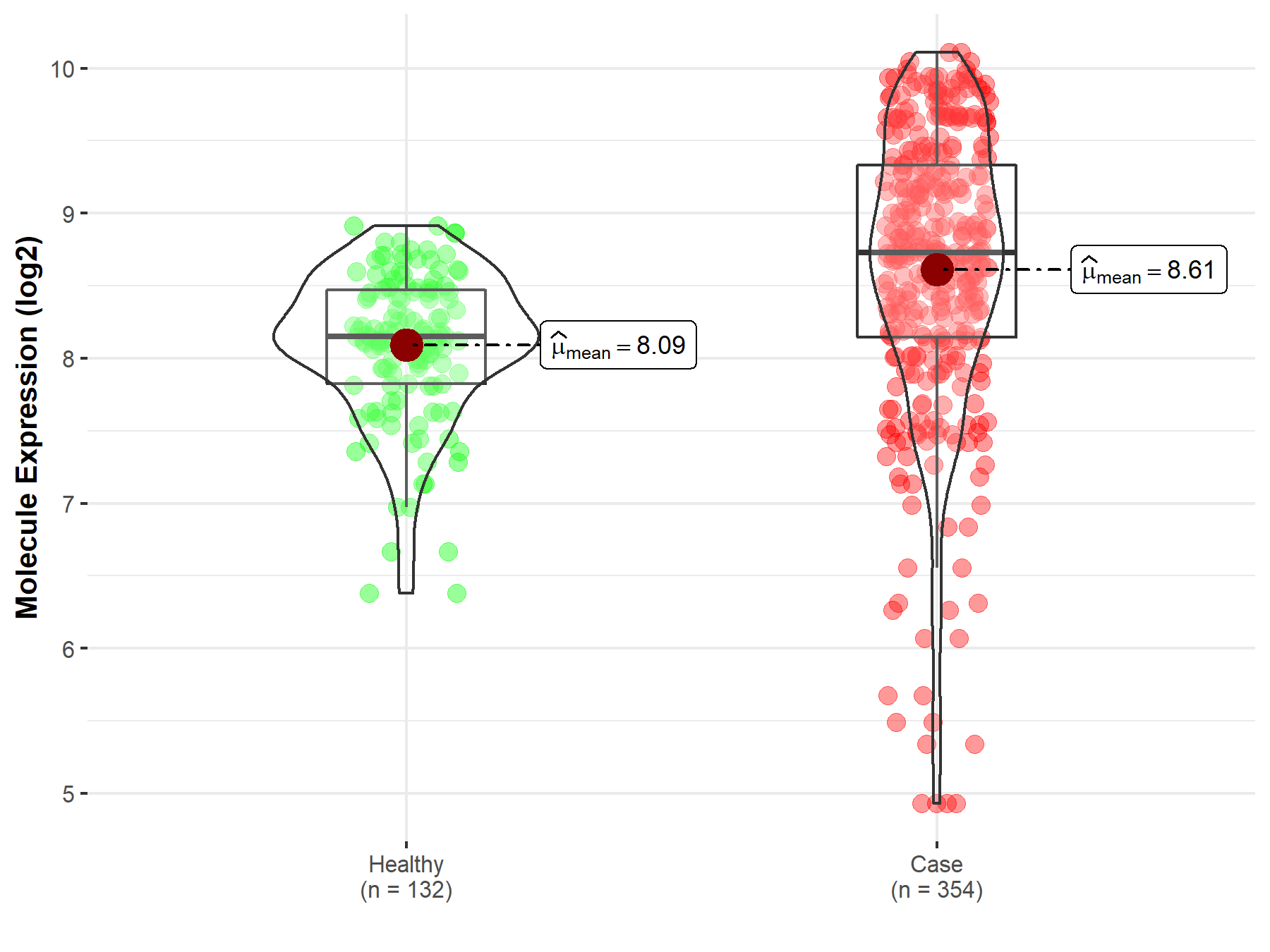
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

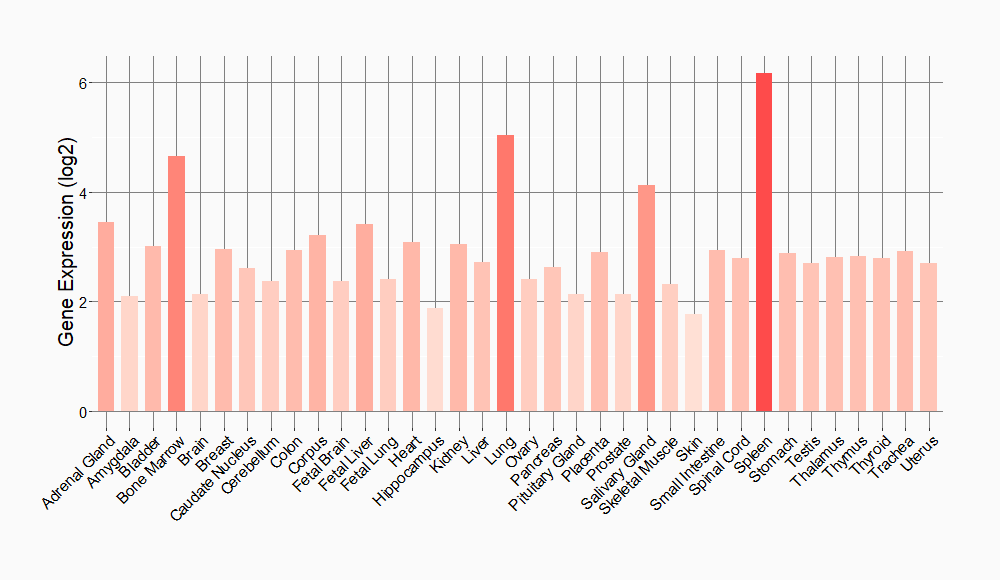
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
