Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01280)
| Name |
Mitosis associated long intergenic non-coding RNA 1 (MALINC1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MALINC1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
LncRNA
|
||||
| Gene Name |
HOXA-AS6, HOXA13-AS1, NCRNA00213, RP1-170O19.3
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr5:140071312-140109274[-]
|
||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.58E-01 Fold-change: 2.06E-01 Z-score: 1.41E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Silencing of MA-linc1 in unsynchronized cells results in fewer cells in G1 and a concomitant increase in the number of cells in all other stages of the cell cycle, particularly in G2/M. Moreover, its silencing in M phase-arrested cells inhibits mitosis exit. The effect of MA-linc1 on cell cycle progression is mediated, at least in part, by repression of its neighboring gene, Puralpha, a cell cycle regulator whose expression induces cell cycle arrest. Importantly, high levels of MA-linc1 are correlated with decreased survival of breast and lung cancer patients and its silencing sensitizes cancer cells to the apoptotic effect of the M phase specific chemotherapeutic drug, Paclitaxel. This enhancement of Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis is also Puralpha-related. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Silencing of MA-linc1 in unsynchronized cells results in fewer cells in G1 and a concomitant increase in the number of cells in all other stages of the cell cycle, particularly in G2/M. Moreover, its silencing in M phase-arrested cells inhibits mitosis exit. The effect of MA-linc1 on cell cycle progression is mediated, at least in part, by repression of its neighboring gene, Puralpha, a cell cycle regulator whose expression induces cell cycle arrest. Importantly, high levels of MA-linc1 are correlated with decreased survival of breast and lung cancer patients and its silencing sensitizes cancer cells to the apoptotic effect of the M phase specific chemotherapeutic drug, Paclitaxel. This enhancement of Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis is also Puralpha-related. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Silencing of MA-linc1 in unsynchronized cells results in fewer cells in G1 and a concomitant increase in the number of cells in all other stages of the cell cycle, particularly in G2/M. Moreover, its silencing in M phase-arrested cells inhibits mitosis exit. The effect of MA-linc1 on cell cycle progression is mediated, at least in part, by repression of its neighboring gene, Puralpha, a cell cycle regulator whose expression induces cell cycle arrest. Importantly, high levels of MA-linc1 are correlated with decreased survival of breast and lung cancer patients and its silencing sensitizes cancer cells to the apoptotic effect of the M phase specific chemotherapeutic drug, Paclitaxel. This enhancement of Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis is also Puralpha-related. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.68E-04; Fold-change: 5.47E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
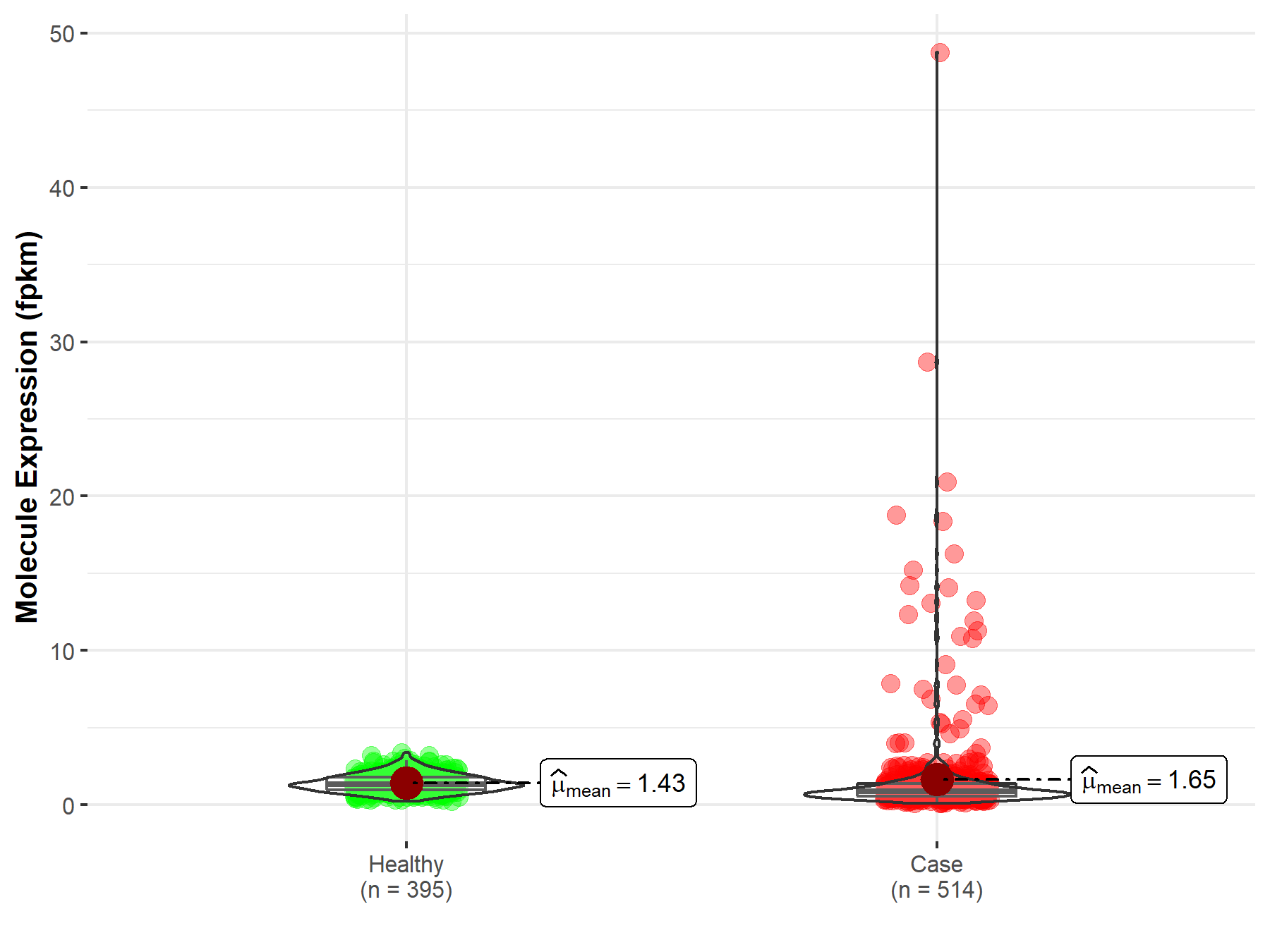
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.72E-50; Fold-change: 1.63E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

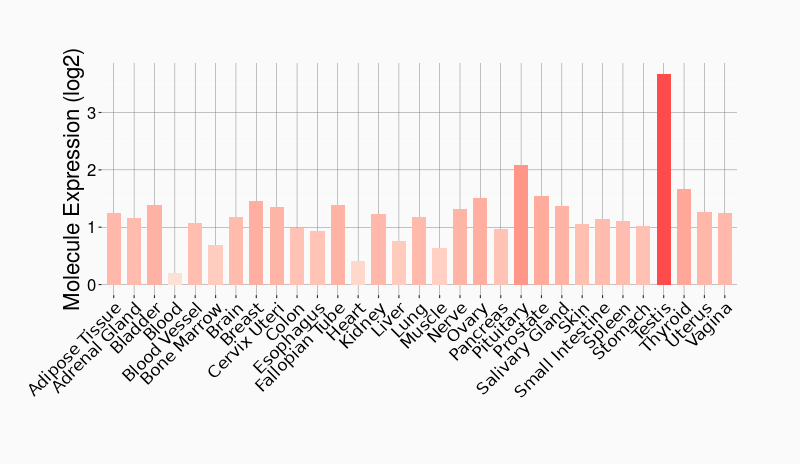
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
