Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01082)
| Name |
Solute carrier family 16 member 1 (SLC16A1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MCT 1; Solute carrier family 16 member 1; MCT1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SLC16A1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:112911847-112957593[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MPPAVGGPVGYTPPDGGWGWAVVIGAFISIGFSYAFPKSITVFFKEIEGIFHATTSEVSW
ISSIMLAVMYGGGPISSILVNKYGSRIVMIVGGCLSGCGLIAASFCNTVQQLYVCIGVIG GLGLAFNLNPALTMIGKYFYKRRPLANGLAMAGSPVFLCTLAPLNQVFFGIFGWRGSFLI LGGLLLNCCVAGALMRPIGPKPTKAGKDKSKASLEKAGKSGVKKDLHDANTDLIGRHPKQ EKRSVFQTINQFLDLTLFTHRGFLLYLSGNVIMFFGLFAPLVFLSSYGKSQHYSSEKSAF LLSILAFVDMVARPSMGLVANTKPIRPRIQYFFAASVVANGVCHMLAPLSTTYVGFCVYA GFFGFAFGWLSSVLFETLMDLVGPQRFSSAVGLVTIVECCPVLLGPPLLGRLNDMYGDYK YTYWACGVVLIISGIYLFIGMGINYRLLAKEQKANEQKKESKEEETSIDVAGKPNEVTKA AESPDQKDTDGGPKEEESPV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Proton-coupled monocarboxylate transporter. Catalyzes the rapid transport across the plasma membrane of many monocarboxylates such as lactate, pyruvate, branched-chain oxo acids derived from leucine, valine and isoleucine, and the ketone bodies acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetate. Depending on the tissue and on cicumstances, mediates the import or export of lactic acid and ketone bodies. Required for normal nutrient assimilation, increase of white adipose tissue and body weight gain when on a high-fat diet. Plays a role in cellular responses to a high-fat diet by modulating the cellular levels of lactate and pyruvate, small molecules that contribute to the regulation of central metabolic pathways and insulin secretion, with concomitant effects on plasma insulin levels and blood glucose homeostasis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.57E-07 Fold-change: 3.14E-01 Z-score: 5.09E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| SK-BR-3 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We identified monocarboxylate transporter1 (MCT1) and lactate dehydrogenase B (LDHB) as important mediators of lactate influx and its conversion to pyruvate, respectively. Consistently, AR-C155858 (MCT1 inhibitor) inhibited the proliferation, migration, spheroid formation, and in vivo tumor growth of TAMR-MCF-7 cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.16E-02 Fold-change: -8.65E-02 Z-score: -1.75E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Curcumin mediated the amputation of chemoresistance by repressing the hyperglycolytic behavior of malignant cells via modulated expression of metabolic enzymes (HkII, PFk1, GAPDH, PkM2, LDH, SDH, IDH, and FASN), transporters (GLUT-1, MCT-1, and MCT-4), and their regulators. Along altered constitution of extracellular milieu, these molecular changes culminated into improved drug accumulation, chromatin condensation, and induction of cell death. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.16E-02 Fold-change: -8.65E-02 Z-score: -1.75E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Curcumin mediated the amputation of chemoresistance by repressing the hyperglycolytic behavior of malignant cells via modulated expression of metabolic enzymes (HkII, PFk1, GAPDH, PkM2, LDH, SDH, IDH, and FASN), transporters (GLUT-1, MCT-1, and MCT-4), and their regulators. Along altered constitution of extracellular milieu, these molecular changes culminated into improved drug accumulation, chromatin condensation, and induction of cell death. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.42E-01; Fold-change: 2.57E-02; Z-score: 3.76E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.16E-05; Fold-change: -3.47E-01; Z-score: -5.06E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 2.83E-01; Fold-change: -4.29E-01; Z-score: -7.53E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
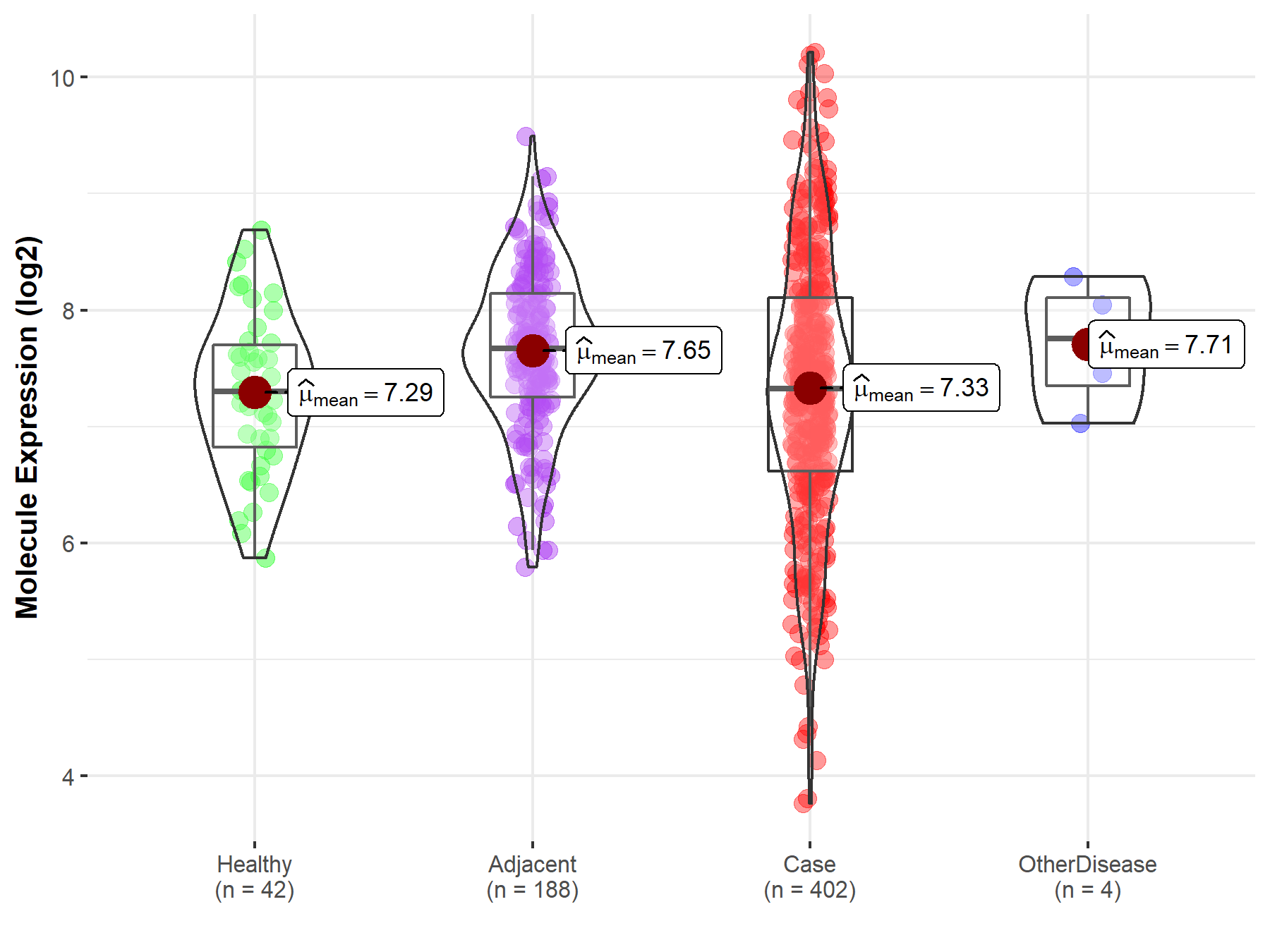
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
