Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01045)
| Name |
Phosphofructo-1-kinase isozyme B (PFKB)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ATP-PFK; PFK-L; 6-phosphofructokinase type B; Phosphofructo-1-kinase isozyme B; PFK-B; Phosphohexokinase
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PFKL
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr21:44300051-44327376[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAAVDLEKLRASGAGKAIGVLTSGGDAQGMNAAVRAVTRMGIYVGAKVFLIYEGYEGLVE
GGENIKQANWLSVSNIIQLGGTIIGSARCKAFTTREGRRAAAYNLVQHGITNLCVIGGDG SLTGANIFRSEWGSLLEELVAEGKISETTARTYSHLNIAGLVGSIDNDFCGTDMTIGTDS ALHRIMEVIDAITTTAQSHQRTFVLEVMGRHCGYLALVSALASGADWLFIPEAPPEDGWE NFMCERLGETRSRGSRLNIIIIAEGAIDRNGKPISSSYVKDLVVQRLGFDTRVTVLGHVQ RGGTPSAFDRILSSKMGMEAVMALLEATPDTPACVVTLSGNQSVRLPLMECVQMTKEVQK AMDDKRFDEATQLRGGSFENNWNIYKLLAHQKPPKEKSNFSLAILNVGAPAAGMNAAVRS AVRTGISHGHTVYVVHDGFEGLAKGQVQEVGWHDVAGWLGRGGSMLGTKRTLPKGQLESI VENIRIYGIHALLVVGGFEAYEGVLQLVEARGRYEELCIVMCVIPATISNNVPGTDFSLG SDTAVNAAMESCDRIKQSASGTKRRVFIVETMGGYCGYLATVTGIAVGADAAYVFEDPFN IHDLKVNVEHMTEKMKTDIQRGLVLRNEKCHDYYTTEFLYNLYSSEGKGVFDCRTNVLGH LQQGGAPTPFDRNYGTKLGVKAMLWLSEKLREVYRKGRVFANAPDSACVIGLKKKAVAFS PVTELKKDTDFEHRMPREQWWLSLRLMLKMLAQYRISMAAYVSGELEHVTRRTLSMDKGF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the phosphorylation of D-fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by ATP, the first committing step of glycolysis. Negatively regulates the phagocyte oxidative burst in response to bacterial infection by controlling cellular NADPH biosynthesis and NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Upon macrophage activation, drives the metabolic switch toward glycolysis, thus preventing glucose turnover that produces NADPH via pentose phosphate pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.12E-01 Fold-change: -2.17E-03 Z-score: -2.39E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Curcumin mediated the amputation of chemoresistance by repressing the hyperglycolytic behavior of malignant cells via modulated expression of metabolic enzymes (HkII, PFk1, GAPDH, PkM2, LDH, SDH, IDH, and FASN), transporters (GLUT-1, MCT-1, and MCT-4), and their regulators. Along altered constitution of extracellular milieu, these molecular changes culminated into improved drug accumulation, chromatin condensation, and induction of cell death. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.12E-01; Fold-change: -1.12E-03; Z-score: -3.85E-03 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.28E-02; Fold-change: 1.32E-01; Z-score: 3.19E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 2.55E-01; Fold-change: 2.67E-01; Z-score: 9.95E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
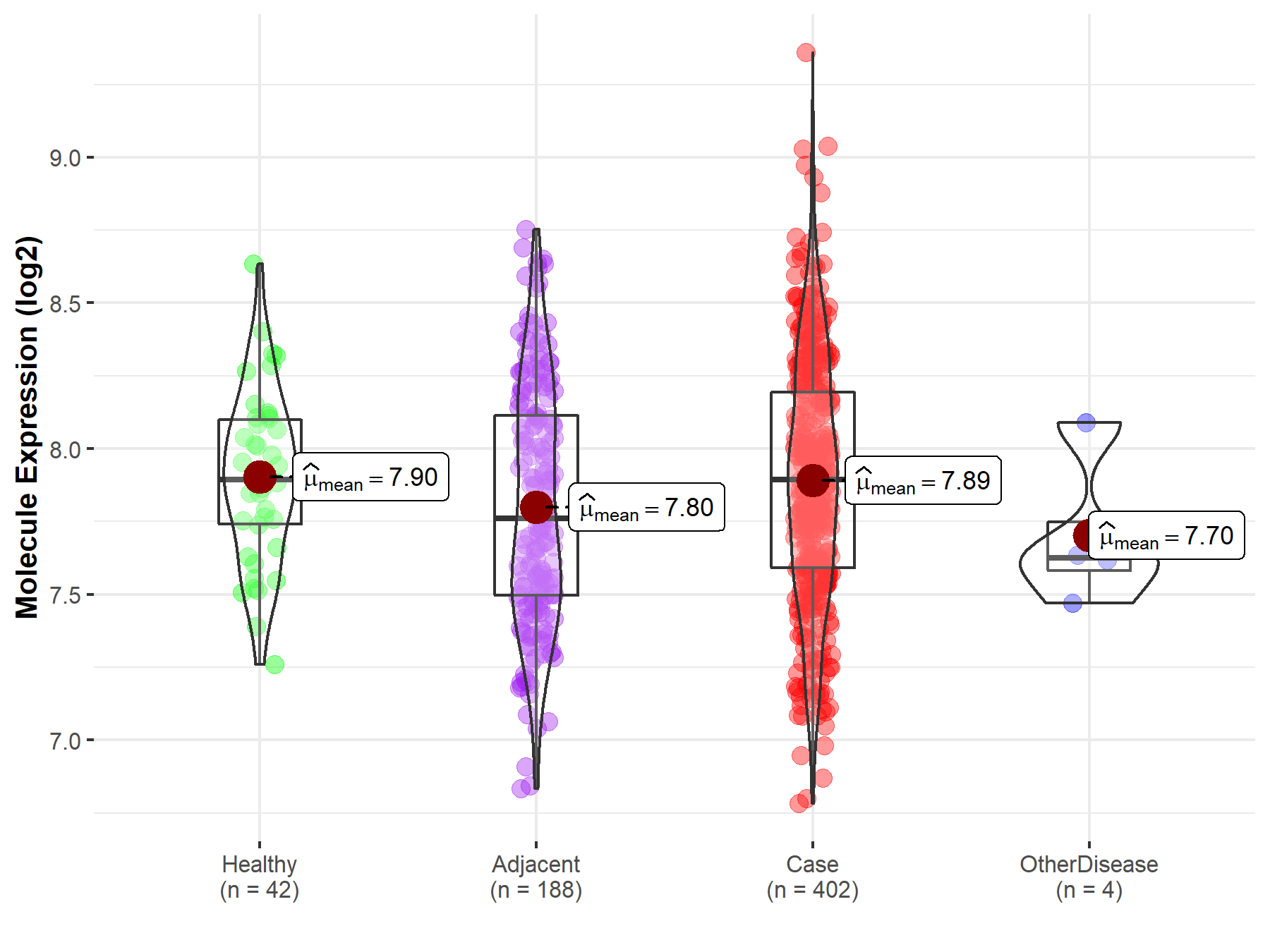
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

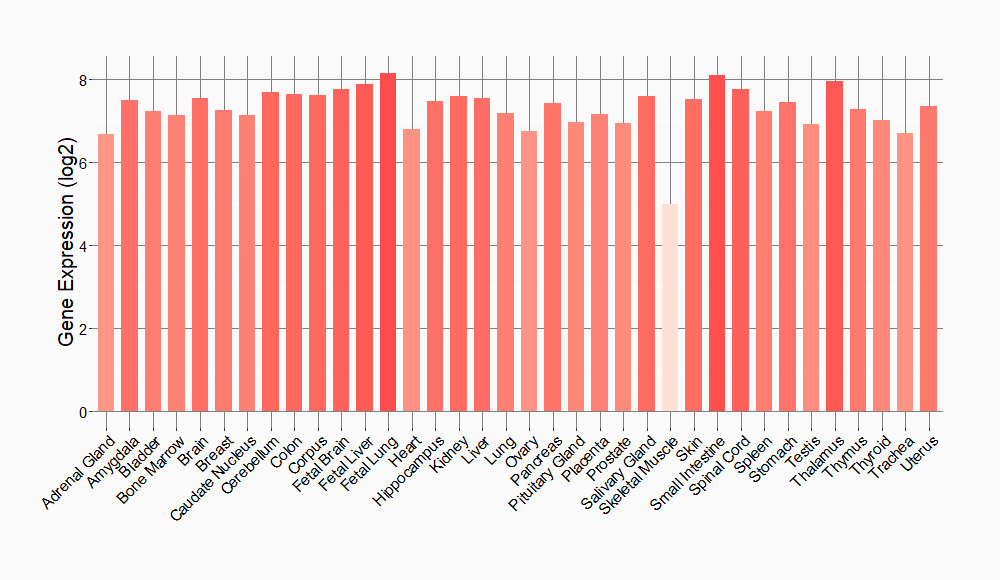
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
