Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00698)
| Name |
Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
VDR; 1;25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 1; NR1I1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
VDR
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr12:47841537-47943048[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEAMAASTSLPDPGDFDRNVPRICGVCGDRATGFHFNAMTCEGCKGFFRRSMKRKALFTC
PFNGDCRITKDNRRHCQACRLKRCVDIGMMKEFILTDEEVQRKREMILKRKEEEALKDSL RPKLSEEQQRIIAILLDAHHKTYDPTYSDFCQFRPPVRVNDGGGSHPSRPNSRHTPSFSG DSSSSCSDHCITSSDMMDSSSFSNLDLSEEDSDDPSVTLELSQLSMLPHLADLVSYSIQK VIGFAKMIPGFRDLTSEDQIVLLKSSAIEVIMLRSNESFTMDDMSWTCGNQDYKYRVSDV TKAGHSLELIEPLIKFQVGLKKLNLHEEEHVLLMAICIVSPDRPGVQDAALIEAIQDRLS NTLQTYIRCRHPPPGSHLLYAKMIQKLADLRSLNEEHSKQYRCLSFQPECSMKLTPLVLE VFGNEIS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Nuclear receptor for calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D3 which mediates the action of this vitamin on cells. Enters the nucleus upon vitamin D3 binding where it forms heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor/RXR. The VDR-RXR heterodimers bind to specific response elements on DNA and activate the transcription of vitamin D3-responsive target genes. Plays a central role in calcium homeostasis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Calcitriol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.64E-44 Fold-change: -1.42E-01 Z-score: -1.78E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | DLD1 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0248 |
| HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | H19 overexpression induces resistance to 1,25(OH)2D3 by inhibiting the expression of VDR Through miR675-5p in colon cancer cells. vdr signaling was able to attenuate the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells via multiple mechanisms including inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, VDR signaling inhibits the expression of h19 by regulating the C-Myc/mad-1 Network. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.64E-44; Fold-change: -7.80E-01; Z-score: -1.61E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.33E-06; Fold-change: -4.28E-01; Z-score: -6.51E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
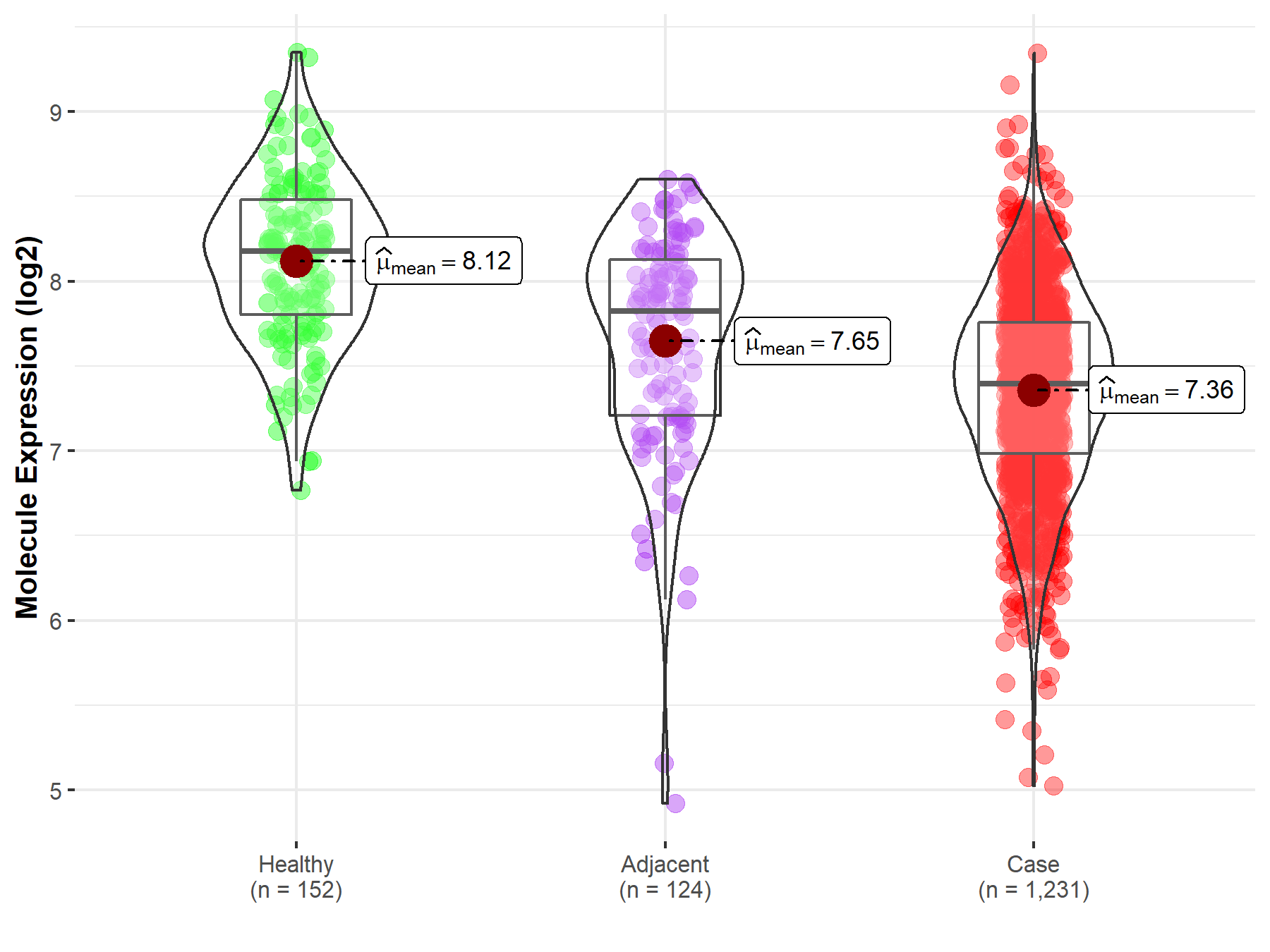
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

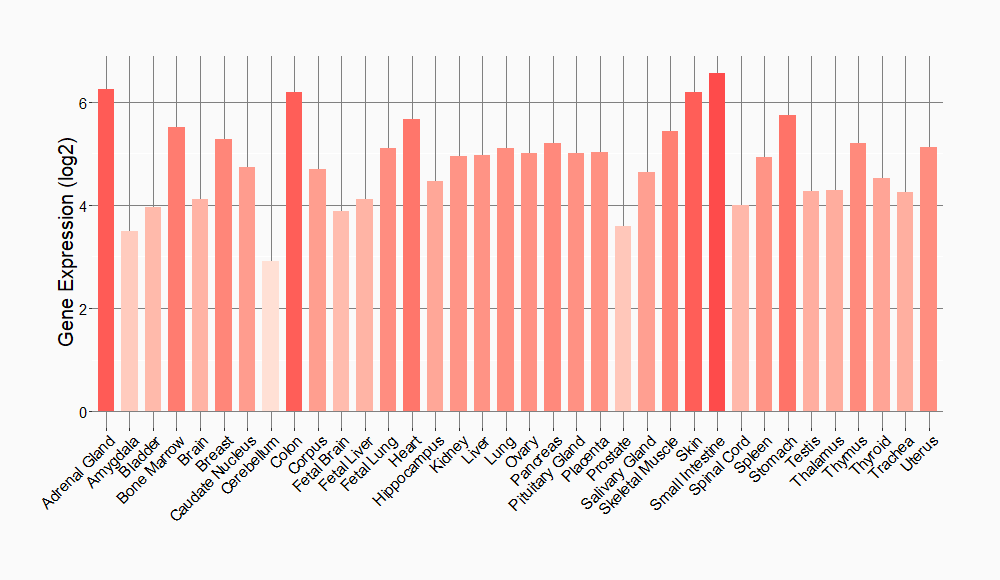
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
