Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00678)
| Name |
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 10 (TNFSF10)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
TNFSF10
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr3:172505508-172523475[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAMMEVQGGPSLGQTCVLIVIFTVLLQSLCVAVTYVYFTNELKQMQDKYSKSGIACFLKE
DDSYWDPNDEESMNSPCWQVKWQLRQLVRKMILRTSEETISTVQEKQQNISPLVRERGPQ RVAAHITGTRGRSNTLSSPNSKNEKALGRKINSWESSRSGHSFLSNLHLRNGELVIHEKG FYYIYSQTYFRFQEEIKENTKNDKQMVQYIYKYTSYPDPILLMKSARNSCWSKDAEYGLY SIYQGGIFELKENDRIFVSVTNEHLIDMDHEASFFGAFLVG Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF10A/TRAILR1, TNFRSF10B/TRAILR2, TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4 and possibly also to TNFRSF11B/OPG. Induces apoptosis. Its activity may be modulated by binding to the decoy receptors TNFRSF10C/TRAILR3, TNFRSF10D/TRAILR4 and TNFRSF11B/OPG that cannot induce apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.66E-01 Fold-change: -7.23E-04 Z-score: -4.34E-02 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| VCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2235 | |
| LTAD cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TUNEL assay; MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Androgen-induced Long Noncoding RNA (LncRNA) SOCS2-AS1 Promotes Cell Growth and Inhibits Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells.suppressor of cytokine signaling 2-antisense transcript 1 (SOCS2-AS1), the expression of which was higher in castration-resistant prostate cancer model cells.SOCS2-AS1 promoted castration-resistant and androgen-dependent cell growth. We found that SOCS2-AS1 knockdown up-regulated genes related to the apoptosis pathway, including tumor necrosis factor superfamily 10 (TNFSF10), and sensitized prostate cancer cells to docetaxel treatment. Moreover, we also demonstrated that SOCS2-AS1 promotes androgen signaling by modulating the epigenetic control for AR target genes including TNFSF10 These findings suggest that SOCS2-AS1 plays an important role in the development of castration-resistant prostate cancer by repressing apoptosis. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.66E-01; Fold-change: 1.85E-01; Z-score: 3.72E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
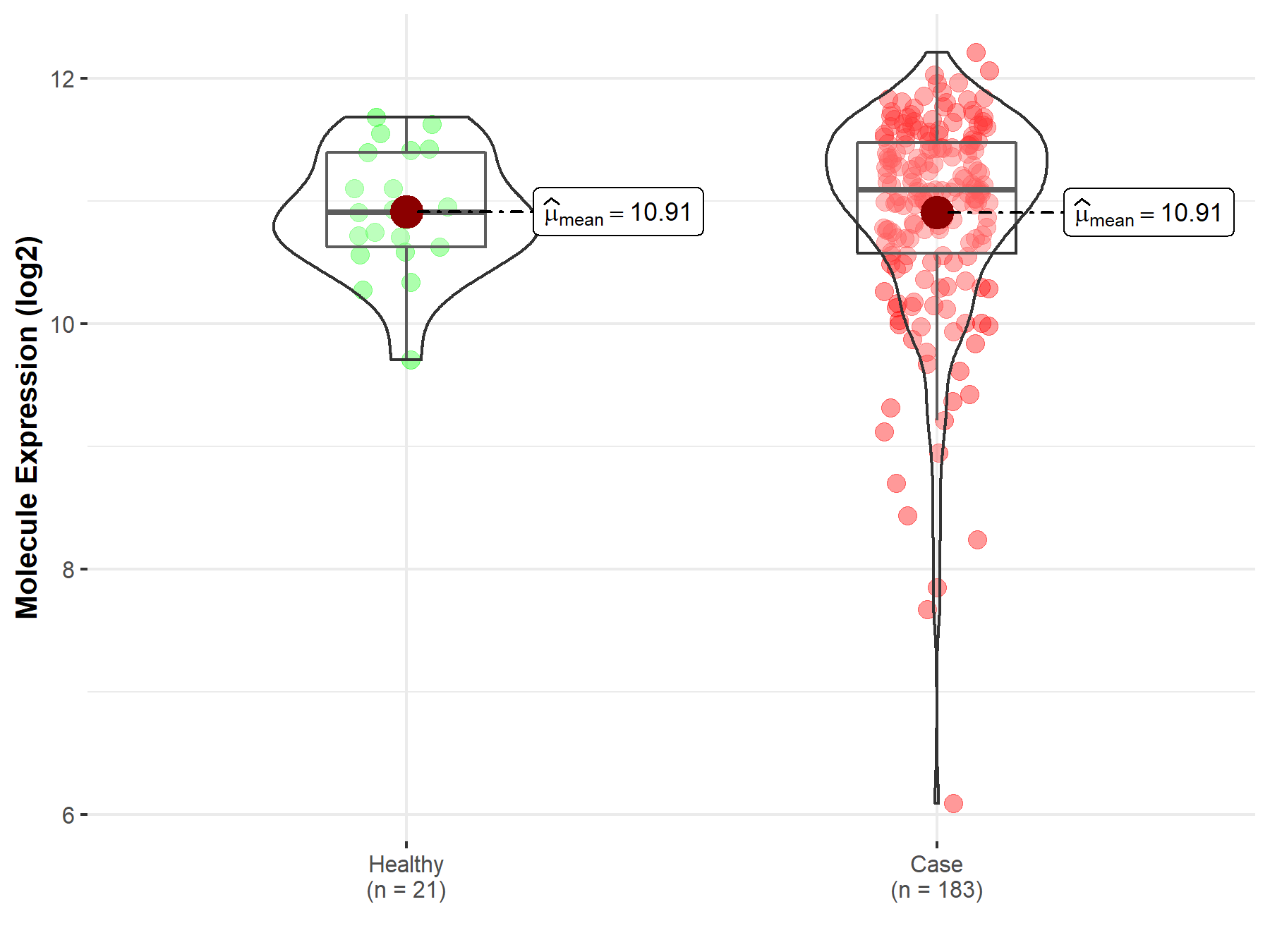
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

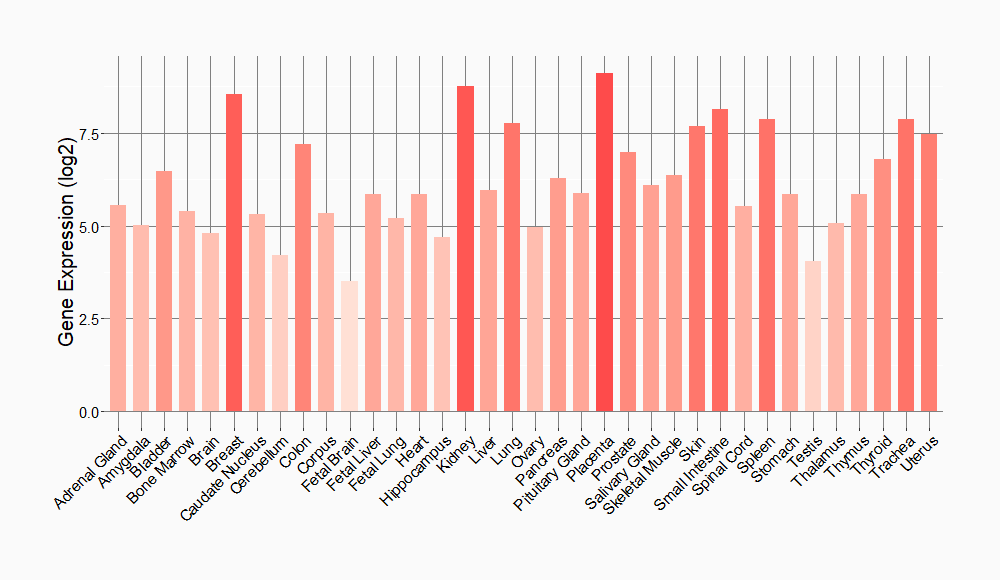
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
