Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00670)
| Name |
TGF-beta receptor type I (TGFBR1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
TGFR-1; Activin A receptor type II-like protein kinase of 53kD; Activin receptor-like kinase 5; ALK-5; ALK5; Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R4; SKR4; TGF-beta type I receptor; Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I; TGF-beta receptor type I; TbetaR-I; ALK5; SKR4
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
TGFBR1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr9:99104038-99154192[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEAAVAAPRPRLLLLVLAAAAAAAAALLPGATALQCFCHLCTKDNFTCVTDGLCFVSVTE
TTDKVIHNSMCIAEIDLIPRDRPFVCAPSSKTGSVTTTYCCNQDHCNKIELPTTVKSSPG LGPVELAAVIAGPVCFVCISLMLMVYICHNRTVIHHRVPNEEDPSLDRPFISEGTTLKDL IYDMTTSGSGSGLPLLVQRTIARTIVLQESIGKGRFGEVWRGKWRGEEVAVKIFSSREER SWFREAEIYQTVMLRHENILGFIAADNKDNGTWTQLWLVSDYHEHGSLFDYLNRYTVTVE GMIKLALSTASGLAHLHMEIVGTQGKPAIAHRDLKSKNILVKKNGTCCIADLGLAVRHDS ATDTIDIAPNHRVGTKRYMAPEVLDDSINMKHFESFKRADIYAMGLVFWEIARRCSIGGI HEDYQLPYYDLVPSDPSVEEMRKVVCEQKLRPNIPNRWQSCEALRVMAKIMRECWYANGA ARLTALRIKKTLSQLSQQEGIKM Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Transmembrane serine/threonine kinase forming with the TGF-beta type II serine/threonine kinase receptor, TGFBR2, the non-promiscuous receptor for the TGF-beta cytokines TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3. Transduces the TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 signal from the cell surface to the cytoplasm and is thus regulating a plethora of physiological and pathological processes including cell cycle arrest in epithelial and hematopoietic cells, control of mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation, wound healing, extracellular matrix production, immunosuppression and carcinogenesis. The formation of the receptor complex composed of 2 TGFBR1 and 2 TGFBR2 molecules symmetrically bound to the cytokine dimer results in the phosphorylation and the activation of TGFBR1 by the constitutively active TGFBR2. Activated TGFBR1 phosphorylates SMAD2 which dissociates from the receptor and interacts with SMAD4. The SMAD2-SMAD4 complex is subsequently translocated to the nucleus where it modulates the transcription of the TGF-beta-regulated genes. This constitutes the canonical SMAD-dependent TGF-beta signaling cascade. Also involved in non-canonical, SMAD-independent TGF-beta signaling pathways. For instance, TGFBR1 induces TRAF6 autoubiquitination which in turn results in MAP3K7 ubiquitination and activation to trigger apoptosis. Also regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition through a SMAD-independent signaling pathway through PARD6A phosphorylation and activation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | TE10 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1760 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Elisa assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-27 in serum originated mainly from esophageal cancer cells, because its serum expression level in patients with esophageal cancer was significantly higher than that of healthy volunteers and decreased significantly after surgery compared with the baseline (before surgery). Moreover, co-culture of fibroblasts with anti-miR-27-transfected esophageal cancer cells resulted in a major decrease in the antiapoptotic function of fibroblasts, compared with fibroblasts co-cultured with control esophageal cancer cells that secrete extracellular miR-27. Serum miR-27 level may reflect the expression level of extracellular miR-27 derived from esophageal cancer cells. miR-27 is involved in resistance to chemotherapy in esophageal cancer, through miR-27 -induced transformation of NOF into CAF, and that TGF-beta secreted from these CAF-like fibroblasts induces chemoresistance to cisplatin in esophageal cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| TGF-BetaR1/Smad signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04350 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1650 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1483 | |
| A549/DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-181b inhibited cell proliferation, augmented the chemosensitivity to DDP, suppressed migration and invasion in NSCLC cells miR-181b inhibited cell proliferation, augmented the chemosensitivity to DDP, suppressed migration and invasion in NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, miR-181b may increase chemosensitivity to DDP and suppress the invasion and metastasis of NSCLC cells through directly targeting the TGFbetaR1 signaling miR-181b may increase chemosensitivity to DDP and suppress the invasion and metastasis of NSCLC cells through directly targeting the TGFbetaR1 signaling pathway. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.40E-03; Fold-change: 1.26E+00; Z-score: 3.19E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
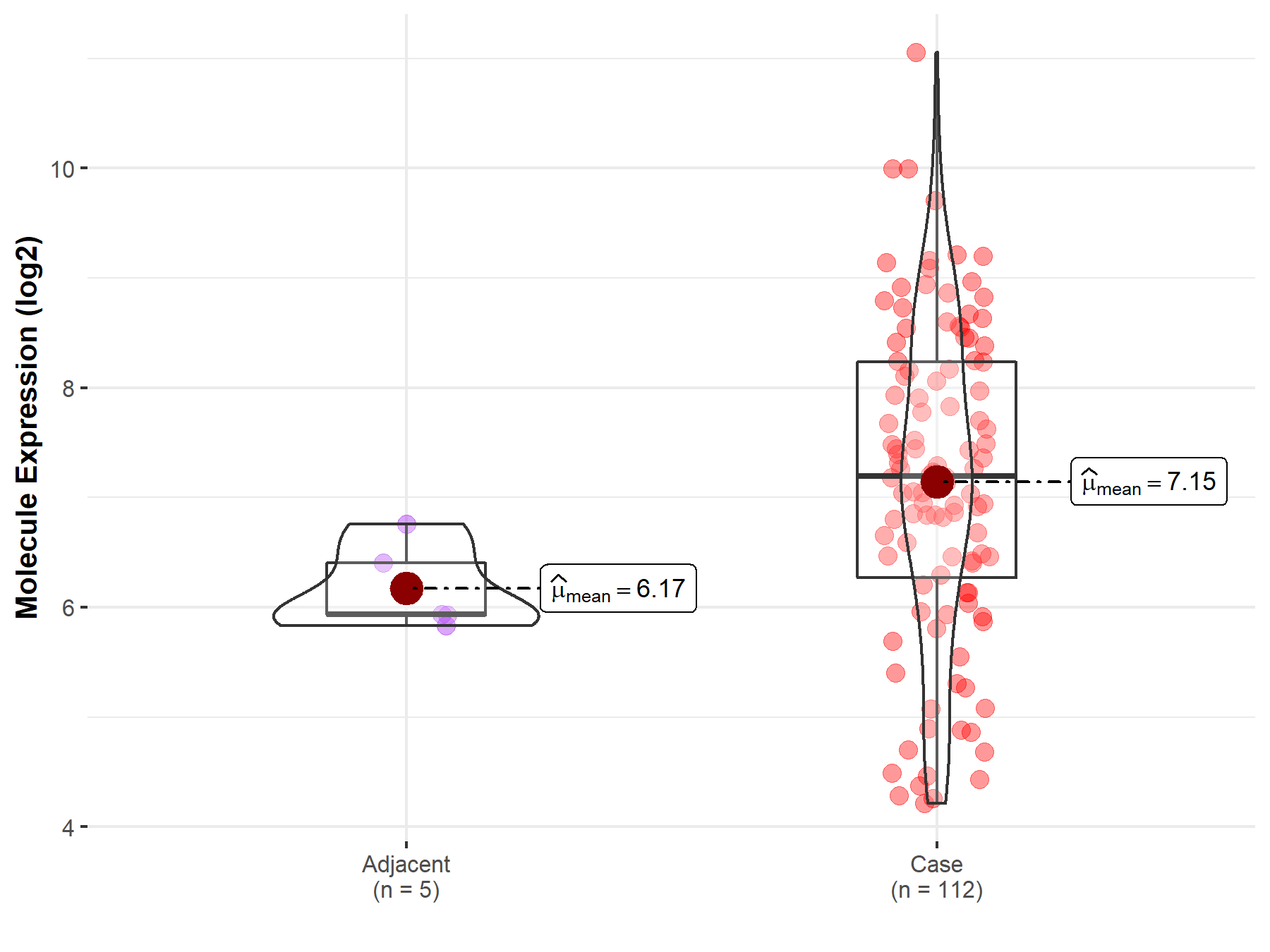
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.22E-02; Fold-change: 3.96E-01; Z-score: 4.08E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.29E-02; Fold-change: 4.46E-01; Z-score: 4.72E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
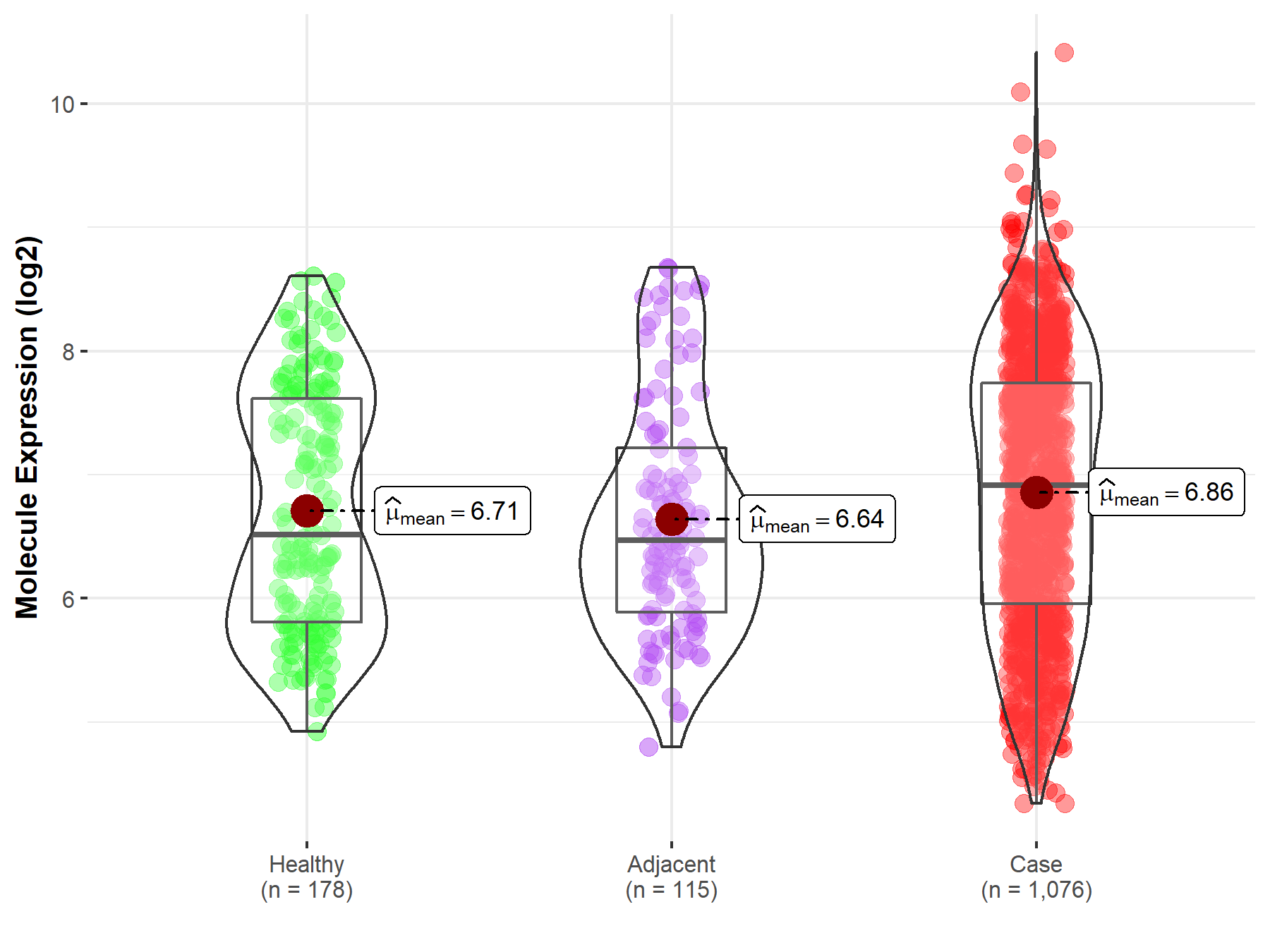
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

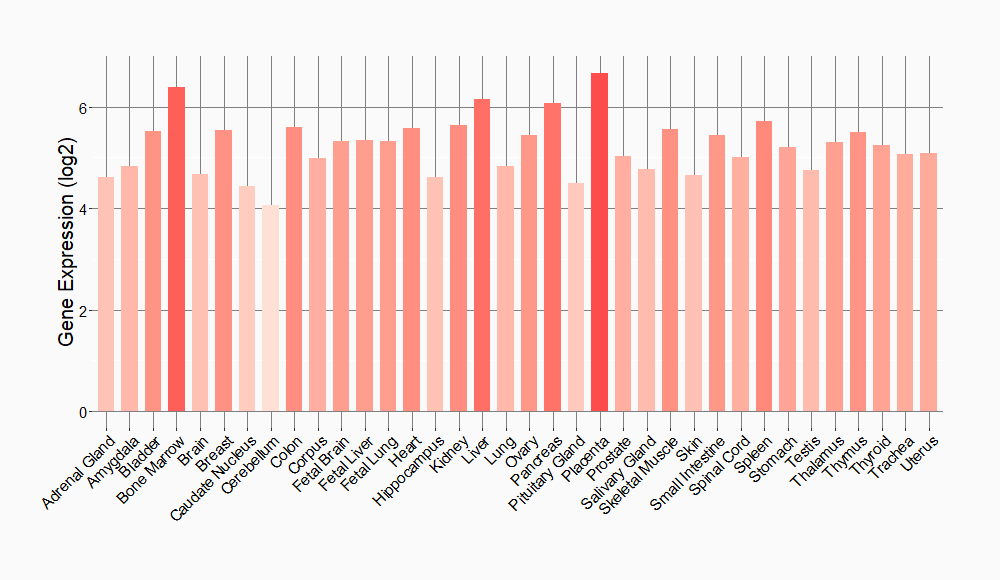
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
