Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00631)
| Name |
Schlafen family member 11 (SLFN11)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SLFN11
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr17:35350305-35373701[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEANQCPLVVEPSYPDLVINVGEVTLGEENRKKLQKIQRDQEKERVMRAACALLNSGGGV
IRMAKKVEHPVEMGLDLEQSLRELIQSSDLQAFFETKQQGRCFYIFVKSWSSGPFPEDRS VKPRLCSLSSSLYRRSETSVRSMDSREAFCFLKTKRKPKILEEGPFHKIHKGVYQELPNS DPADPNSDPADLIFQKDYLEYGEILPFPESQLVEFKQFSTKHFQEYVKRTIPEYVPAFAN TGGGYLFIGVDDKSREVLGCAKENVDPDSLRRKIEQAIYKLPCVHFCQPQRPITFTLKIV NVLKRGELYGYACMIRVNPFCCAVFSEAPNSWIVEDKYVCSLTTEKWVGMMTDTDPDLLQ LSEDFECQLSLSSGPPLSRPVYSKKGLEHKKELQQLLFSVPPGYLRYTPESLWRDLISEH RGLEELINKQMQPFFRGILIFSRSWAVDLNLQEKPGVICDALLIAQNSTPILYTILREQD AEGQDYCTRTAFTLKQKLVNMGGYTGKVCVRAKVLCLSPESSAEALEAAVSPMDYPASYS LAGTQHMEALLQSLVIVLLGFRSLLSDQLGCEVLNLLTAQQYEIFSRSLRKNRELFVHGL PGSGKTIMAMKIMEKIRNVFHCEAHRILYVCENQPLRNFISDRNICRAETRKTFLRENFE HIQHIVIDEAQNFRTEDGDWYGKAKSITRRAKGGPGILWIFLDYFQTSHLDCSGLPPLSD QYPREELTRIVRNADPIAKYLQKEMQVIRSNPSFNIPTGCLEVFPEAEWSQGVQGTLRIK KYLTVEQIMTCVADTCRRFFDRGYSPKDVAVLVSTAKEVEHYKYELLKAMRKKRVVQLSD ACDMLGDHIVLDSVRRFSGLERSIVFGIHPRTADPAILPNVLICLASRAKQHLYIFPWGG H Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Inhibitor of DNA replication that promotes cell death in response to DNA damage. Acts as a guardian of the genome by killing cells with defective replication. Persistently blocks stressed replication forks by opening chromatin across replication initiation sites at stressed replication forks, possibly leading to unwind DNA ahead of the MCM helicase and block fork progression, ultimately leading to cell death. Acts independently of ATR. Also acts as an interferon (IFN)-induced antiviral protein which acts as an inhibitor of retrovirus protein synthesis. Specifically abrogates the production of retroviruses such as human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) by acting as a specific inhibitor of the synthesis of retroviruses encoded proteins in a codon-usage-dependent manner. Binds to tRNAs and exploits the unique viral codon bias towards A/T nucleotides. The exact inhibition mechanism is unclear: may either sequester tRNAs, prevent their maturation via post-transcriptional processing or may accelerate their deacylation. Does not inhibit reverse transcription, integration or production and nuclear export of viral RNA.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Primary prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.Z] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Primary prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Platinum | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Alteration | Epigenetic silencing |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Methyl-CpG binding domain protein-enriched genome sequencing assay;Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation Sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Epigenetic silencing of SLFN11 has been associated with resistance to platinum-based chemotherapies in a number of cell lines including DU-145 and PC3. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.29E-01; Fold-change: 1.64E+00; Z-score: 9.45E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
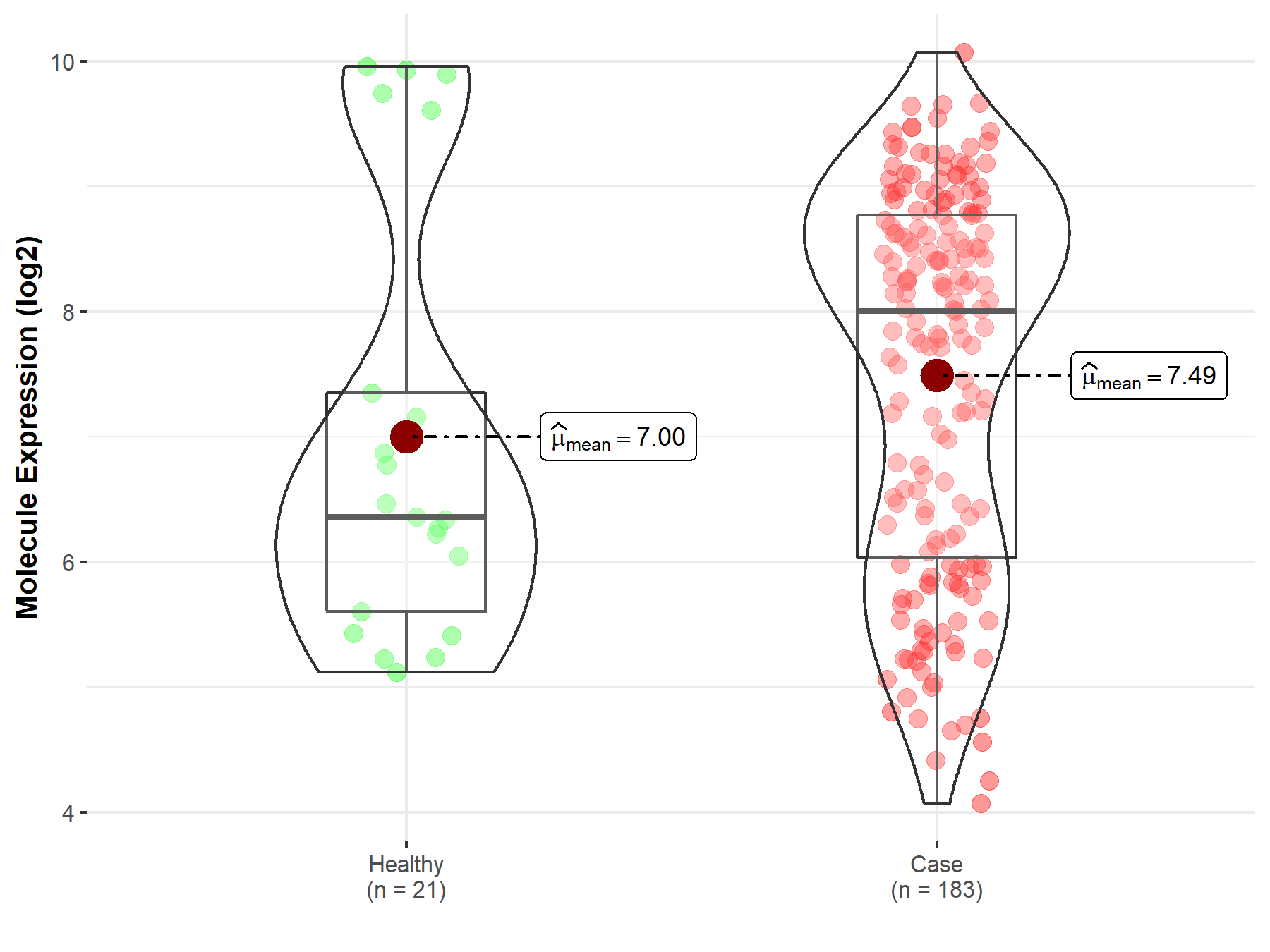
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
