Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00626)
| Name |
Splicing factor/proline/glutamine-rich (SFPQ)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
100 kDa DNA-pairing protein; hPOMp100; DNA-binding p52/p100 complex; 100 kDa subunit; Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-associated-splicing factor; PSF; PTB-associated-splicing factor; PSF
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SFPQ
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:35176378-35193446[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSRDRFRSRGGGGGGFHRRGGGGGRGGLHDFRSPPPGMGLNQNRGPMGPGPGQSGPKPPI
PPPPPHQQQQQPPPQQPPPQQPPPHQPPPHPQPHQQQQPPPPPQDSSKPVVAQGPGPAPG VGSAPPASSSAPPATPPTSGAPPGSGPGPTPTPPPAVTSAPPGAPPPTPPSSGVPTTPPQ AGGPPPPPAAVPGPGPGPKQGPGPGGPKGGKMPGGPKPGGGPGLSTPGGHPKPPHRGGGE PRGGRQHHPPYHQQHHQGPPPGGPGGRSEEKISDSEGFKANLSLLRRPGEKTYTQRCRLF VGNLPADITEDEFKRLFAKYGEPGEVFINKGKGFGFIKLESRALAEIAKAELDDTPMRGR QLRVRFATHAAALSVRNLSPYVSNELLEEAFSQFGPIERAVVIVDDRGRSTGKGIVEFAS KPAARKAFERCSEGVFLLTTTPRPVIVEPLEQLDDEDGLPEKLAQKNPMYQKERETPPRF AQHGTFEYEYSQRWKSLDEMEKQQREQVEKNMKDAKDKLESEMEDAYHEHQANLLRQDLM RRQEELRRMEELHNQEMQKRKEMQLRQEEERRRREEEMMIRQREMEEQMRRQREESYSRM GYMDPRERDMRMGGGGAMNMGDPYGSGGQKFPPLGGGGGIGYEANPGVPPATMSGSMMGS DMRTERFGQGGAGPVGGQGPRGMGPGTPAGYGRGREEYEGPNKKPRF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
DNA- and RNA binding protein, involved in several nuclear processes. Essential pre-mRNA splicing factor required early in spliceosome formation and for splicing catalytic step II, probably as a heteromer with NONO. Binds to pre-mRNA in spliceosome C complex, and specifically binds to intronic polypyrimidine tracts. Involved in regulation of signal-induced alternative splicing. During splicing of PTPRC/CD45, a phosphorylated form is sequestered by THRAP3 from the pre-mRNA in resting T-cells; T-cell activation and subsequent reduced phosphorylation is proposed to lead to release from THRAP3 allowing binding to pre-mRNA splicing regulatotry elements which represses exon inclusion. Interacts with U5 snRNA, probably by binding to a purine-rich sequence located on the 3' side of U5 snRNA stem 1b. May be involved in a pre-mRNA coupled splicing and polyadenylation process as component of a snRNP-free complex with SNRPA/U1A. The SFPQ-NONO heteromer associated with MATR3 may play a role in nuclear retention of defective RNAs. SFPQ may be involved in homologous DNA pairing; in vitro, promotes the invasion of ssDNA between a duplex DNA and produces a D-loop formation. The SFPQ-NONO heteromer may be involved in DNA unwinding by modulating the function of topoisomerase I/TOP1; in vitro, stimulates dissociation of TOP1 from DNA after cleavage and enhances its jumping between separate DNA helices. The SFPQ-NONO heteromer binds DNA. The SFPQ-NONO heteromer may be involved in DNA non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) required for double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination and may stabilize paired DNA ends; in vitro, the complex strongly stimulates DNA end joining, binds directly to the DNA substrates and cooperates with the Ku70/G22P1-Ku80/XRCC5 (Ku) dimer to establish a functional preligation complex. SFPQ is involved in transcriptional regulation. Functions as transcriptional activator. Transcriptional repression is mediated by an interaction of SFPQ with SIN3A and subsequent recruitment of histone deacetylases (HDACs). The SFPQ-NONO-NR5A1 complex binds to the CYP17 promoter and regulates basal and cAMP-dependent transcriptional activity. SFPQ isoform Long binds to the DNA binding domains (DBD) of nuclear hormone receptors, like RXRA and probably THRA, and acts as transcriptional corepressor in absence of hormone ligands. Binds the DNA sequence 5'-CTGAGTC-3' in the insulin-like growth factor response element (IGFRE) and inhibits IGF-I-stimulated transcriptional activity. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing the transcriptional activator activity of the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer. Required for the transcriptional repression of circadian target genes, such as PER1, mediated by the large PER complex through histone deacetylation. Required for the assembly of nuclear speckles. Plays a role in the regulation of DNA virus-mediated innate immune response by assembling into the HDP-RNP complex, a complex that serves as a platform for IRF3 phosphorylation and subsequent innate immune response activation through the cGAS-STING pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | DLD1 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0248 |
| KM12C cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9547 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
mRNA immunoprecipitation assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-19b and miR-21 were over-expressed in 5-FU-resistant cells. Ingenuity pathway analysis of mRNA targets significantly (P < 0.05) indicated the category "Cell Cycle" as a probable area of the molecular and cellular function related with 5-FU resistance. Among candidate mRNA targets, SFPQ and MYBL2 have been linked to cell cycle functions. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-08; Fold-change: 3.32E-01; Z-score: 5.54E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-10; Fold-change: 5.74E-01; Z-score: 6.50E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
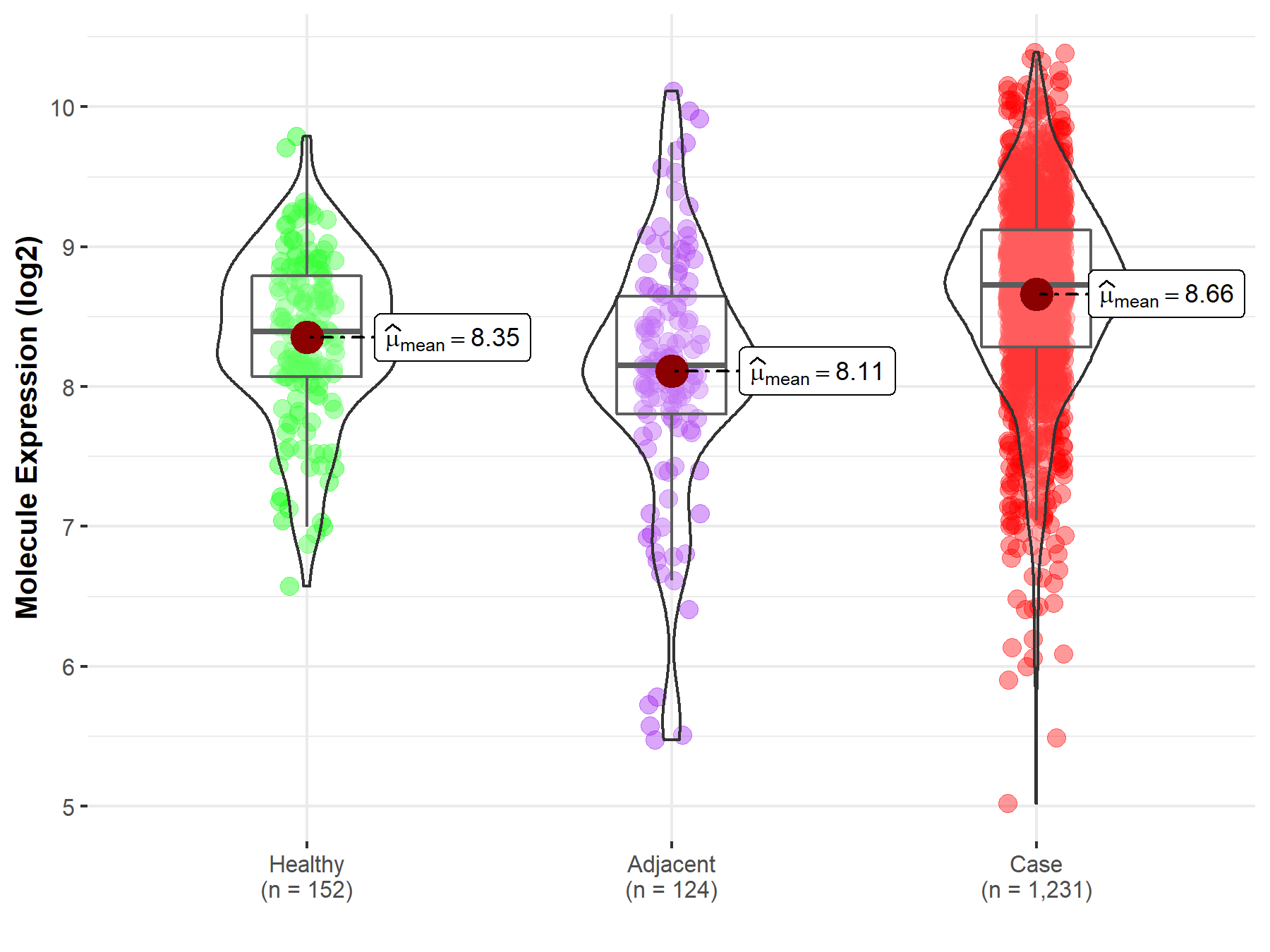
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

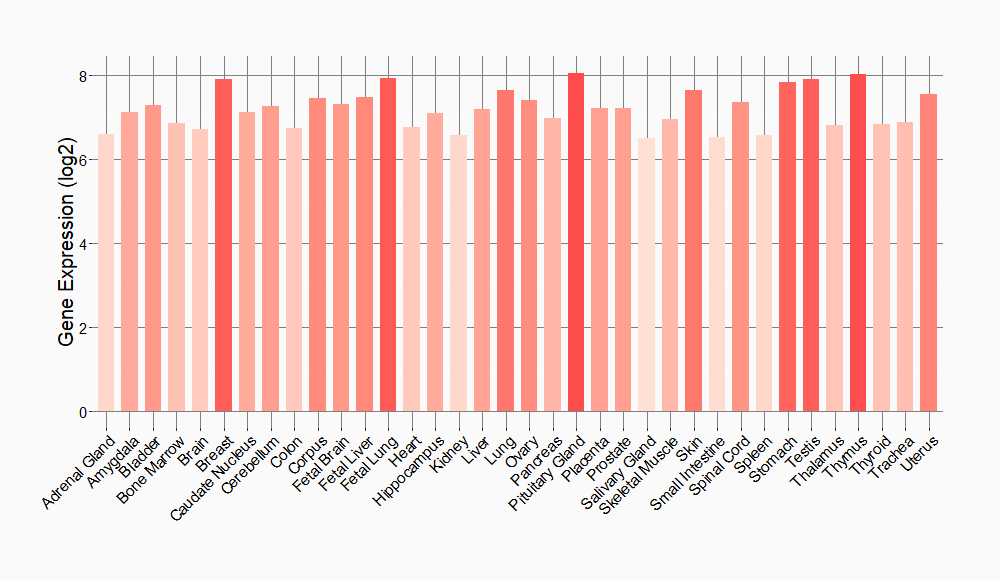
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
