Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00605)
| Name |
Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit M2 (RRM2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ribonucleotide reductase small chain; Ribonucleotide reductase small subunit; RR2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
RRM2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:10120698-10211725[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MLSLRVPLAPITDPQQLQLSPLKGLSLVDKENTPPALSGTRVLASKTARRIFQEPTEPKT
KAAAPGVEDEPLLRENPRRFVIFPIEYHDIWQMYKKAEASFWTAEEVDLSKDIQHWESLK PEERYFISHVLAFFAASDGIVNENLVERFSQEVQITEARCFYGFQIAMENIHSEMYSLLI DTYIKDPKEREFLFNAIETMPCVKKKADWALRWIGDKEATYGERVVAFAAVEGIFFSGSF ASIFWLKKRGLMPGLTFSNELISRDEGLHCDFACLMFKHLVHKPSEERVREIIINAVRIE QEFLTEALPVKLIGMNCTLMKQYIEFVADRLMLELGFSKVFRVENPFDFMENISLEGKTN FFEKRVGEYQRMGVMSSPTENSFTLDADF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. Inhibits Wnt signaling.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.61E-249 Fold-change: 6.99E-01 Z-score: 5.85E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Increased expression of ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 (RRM2) was found to be significantly linked to poor survival in all breast cancer patients as well as in ER-positive patients resistant to TAM. Azacytidine treatment in the TAMR cell line results in reduced proliferation and consequently resensitizes cells to TAM treatment. RRM2 is one of the isoforms of the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase, which is involved in the conversion of deoxyribonucleotides from their corresponding ribonucleotides that are required for DNA synthesis. A DNA methyl transferase inhibitor azacytidine has been shown to inhibit the expression of RRM2. Down-regulation of RRM2 by siRNA-mediated approaches significantly reduces TAMR cell growth, invasion and motility. RRM2 inhibition also leads to decreased expression of DNA repair enzymes and elevated expression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as BIM and BAX leading to apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0428 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-20a-5p inhibits protein expression of RRM2 and reverses gemcitabine resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: KRAS mutant breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.10] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | KRAS mutant breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.10] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MEK/ERK /PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7b repletion selectively sensitized kRAS mutant tumor cells to the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and gemcitabine. Transfection of let-7b mimic downregulated the expression of mutant but not wild-type kRAS. Combination of let-7b mimic with paclitaxel or gemcitabine diminished MEk/ERk and PI3k/AkT signaling concurrently, triggered the onset of apoptosis, and reverted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kRAS mutant tumor cells. In addition, let-7b repletion downregulated the expression of beta-tubulin III and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2, two proteins known to mediate tumor resistance to paclitaxel and gemcitabine, respectively. Let-7 may represent a new class of chemosensitizer for the treatment of kRAS mutant tumors. | |||
| Disease Class: kRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.9] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | kRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.9] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MEK/ERK /PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7b repletion selectively sensitized kRAS mutant tumor cells to the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and gemcitabine. Transfection of let-7b mimic downregulated the expression of mutant but not wild-type kRAS. Combination of let-7b mimic with paclitaxel or gemcitabine diminished MEk/ERk and PI3k/AkT signaling concurrently, triggered the onset of apoptosis, and reverted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kRAS mutant tumor cells. In addition, let-7b repletion downregulated the expression of beta-tubulin III and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2, two proteins known to mediate tumor resistance to paclitaxel and gemcitabine, respectively. Let-7 may represent a new class of chemosensitizer for the treatment of kRAS mutant tumors. | |||
| Disease Class: KRAS mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.5] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | KRAS mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MEK/ERK /PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7b repletion selectively sensitized kRAS mutant tumor cells to the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and gemcitabine. Transfection of let-7b mimic downregulated the expression of mutant but not wild-type kRAS. Combination of let-7b mimic with paclitaxel or gemcitabine diminished MEk/ERk and PI3k/AkT signaling concurrently, triggered the onset of apoptosis, and reverted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kRAS mutant tumor cells. In addition, let-7b repletion downregulated the expression of beta-tubulin III and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2, two proteins known to mediate tumor resistance to paclitaxel and gemcitabine, respectively. Let-7 may represent a new class of chemosensitizer for the treatment of kRAS mutant tumors. | |||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Suit2 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3172 |
| SUIT2-007 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B279 | |
| SUIT2-028 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B282 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The induction of the miR-211 expression in the cells increased the sensitivity to gemcitabine and reduced the expression of its target ribonucleotide reductase subunit 2 (RRM2). | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: KRAS mutant breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.10] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | KRAS mutant breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.10] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MEK/ERK /PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7b repletion selectively sensitized kRAS mutant tumor cells to the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and gemcitabine. Transfection of let-7b mimic downregulated the expression of mutant but not wild-type kRAS. Combination of let-7b mimic with paclitaxel or gemcitabine diminished MEk/ERk and PI3k/AkT signaling concurrently, triggered the onset of apoptosis, and reverted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kRAS mutant tumor cells. In addition, let-7b repletion downregulated the expression of beta-tubulin III and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2, two proteins known to mediate tumor resistance to paclitaxel and gemcitabine, respectively. Let-7 may represent a new class of chemosensitizer for the treatment of kRAS mutant tumors. | |||
| Disease Class: kRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.9] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | kRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.9] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MEK/ERK /PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7b repletion selectively sensitized kRAS mutant tumor cells to the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and gemcitabine. Transfection of let-7b mimic downregulated the expression of mutant but not wild-type kRAS. Combination of let-7b mimic with paclitaxel or gemcitabine diminished MEk/ERk and PI3k/AkT signaling concurrently, triggered the onset of apoptosis, and reverted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kRAS mutant tumor cells. In addition, let-7b repletion downregulated the expression of beta-tubulin III and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2, two proteins known to mediate tumor resistance to paclitaxel and gemcitabine, respectively. Let-7 may represent a new class of chemosensitizer for the treatment of kRAS mutant tumors. | |||
| Disease Class: KRAS mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.5] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | KRAS mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MEK/ERK /PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7b repletion selectively sensitized kRAS mutant tumor cells to the cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and gemcitabine. Transfection of let-7b mimic downregulated the expression of mutant but not wild-type kRAS. Combination of let-7b mimic with paclitaxel or gemcitabine diminished MEk/ERk and PI3k/AkT signaling concurrently, triggered the onset of apoptosis, and reverted the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kRAS mutant tumor cells. In addition, let-7b repletion downregulated the expression of beta-tubulin III and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2, two proteins known to mediate tumor resistance to paclitaxel and gemcitabine, respectively. Let-7 may represent a new class of chemosensitizer for the treatment of kRAS mutant tumors. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.66E-04; Fold-change: 2.66E+00; Z-score: 1.68E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.56E-10; Fold-change: 1.69E+00; Z-score: 1.19E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
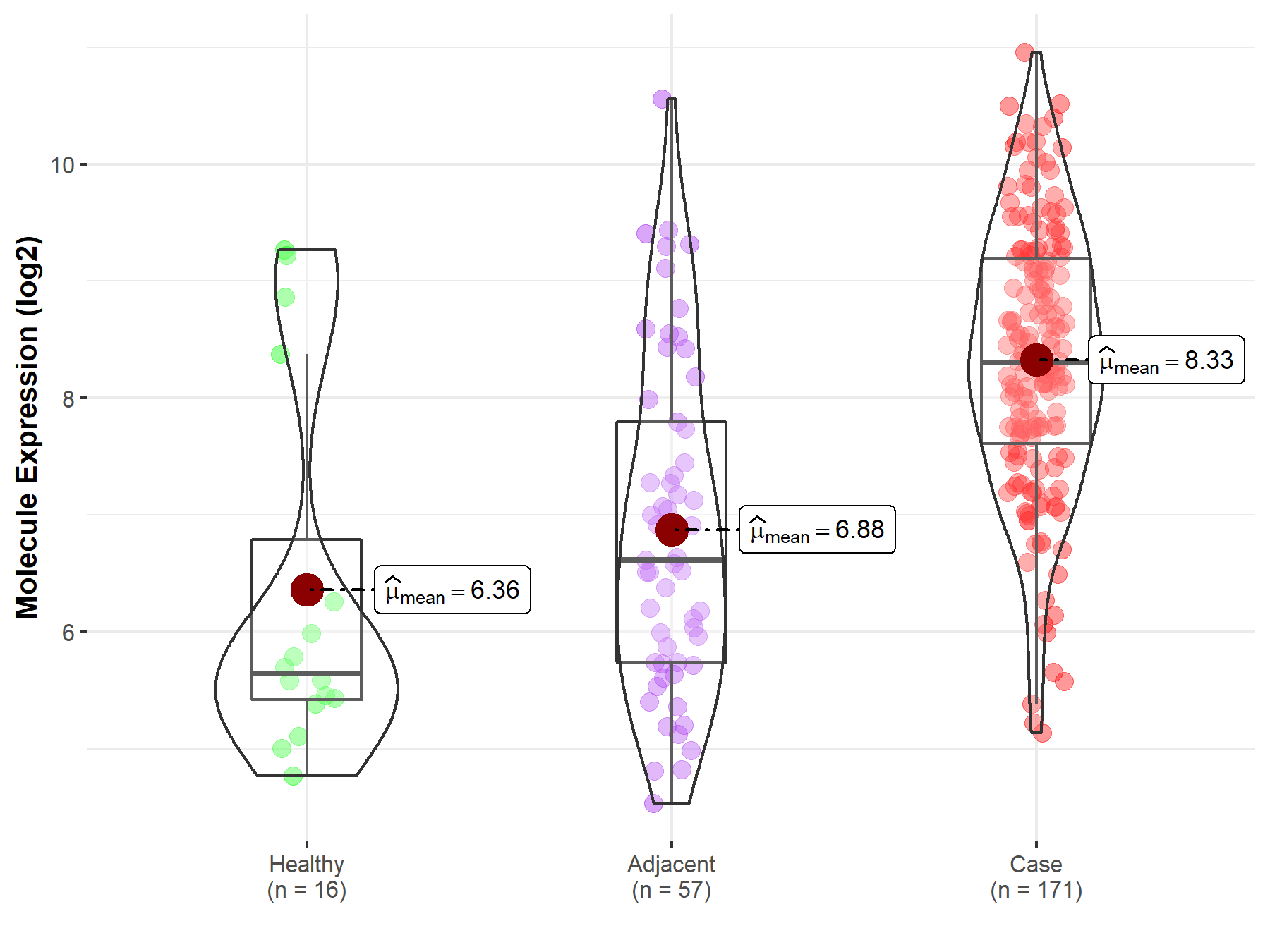
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.24E-102; Fold-change: 3.27E+00; Z-score: 3.29E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.12E-81; Fold-change: 3.60E+00; Z-score: 4.10E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
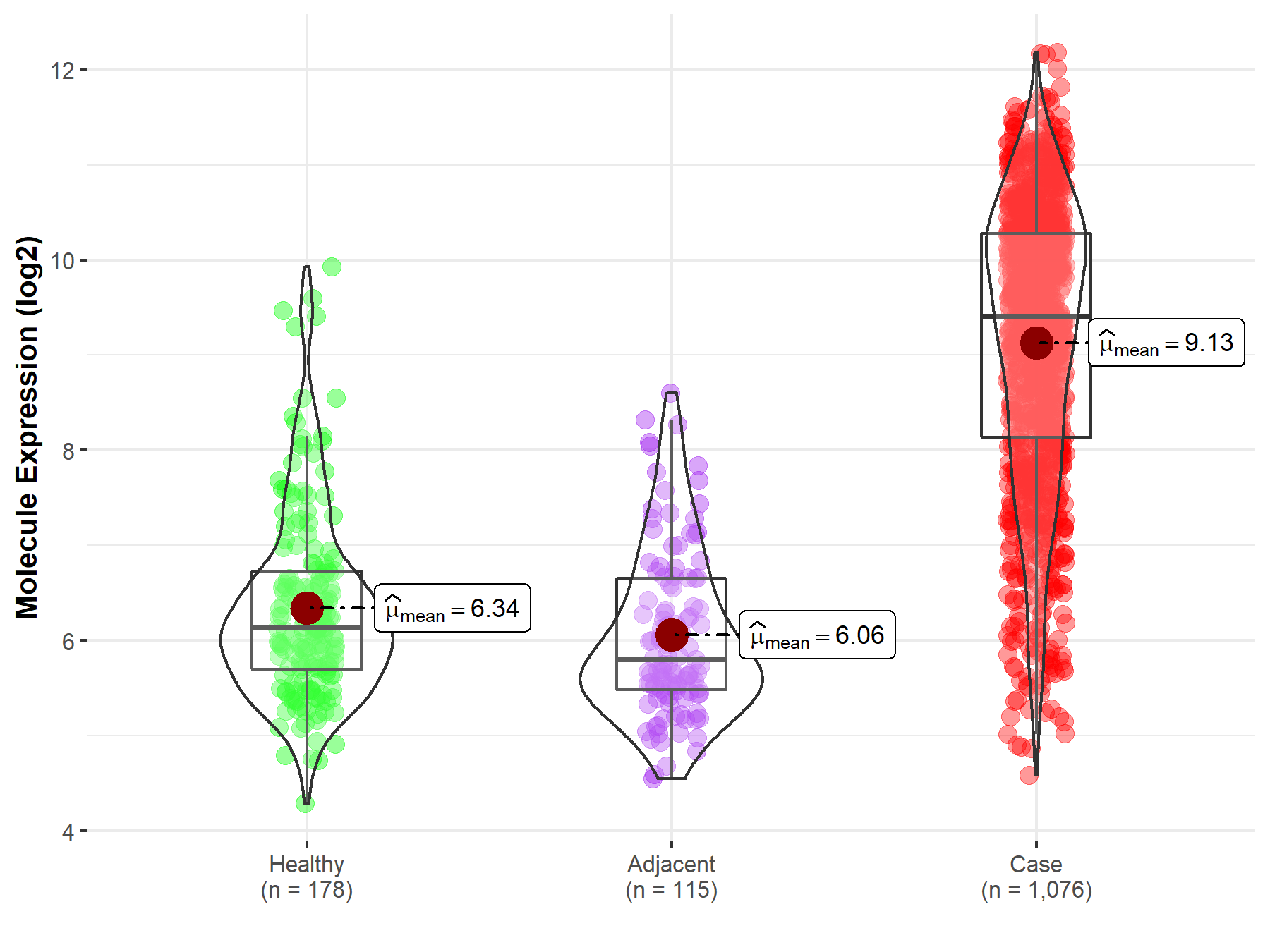
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.61E-249; Fold-change: 3.92E+00; Z-score: 4.82E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.60E-16; Fold-change: 2.75E+00; Z-score: 1.98E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
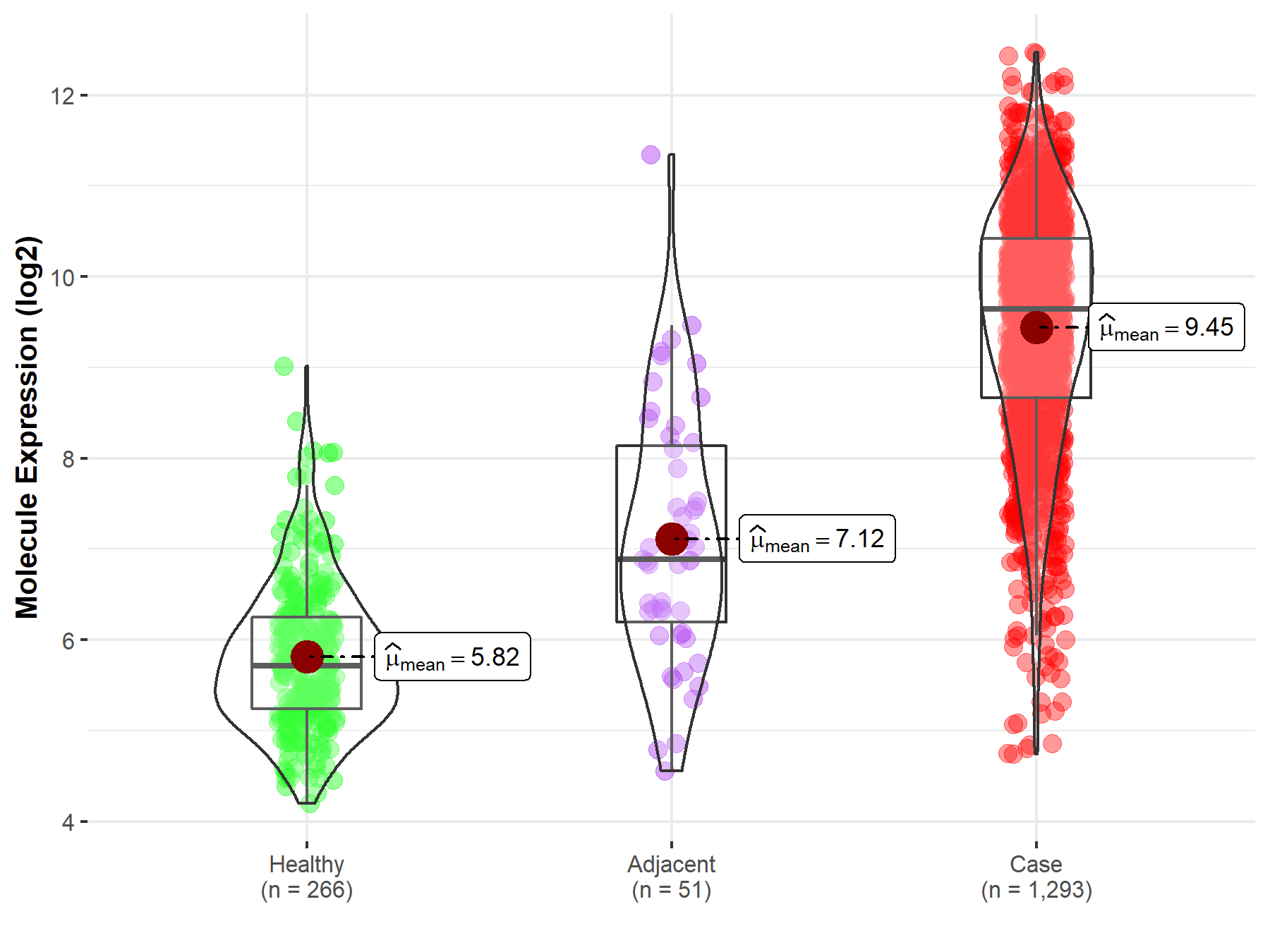
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

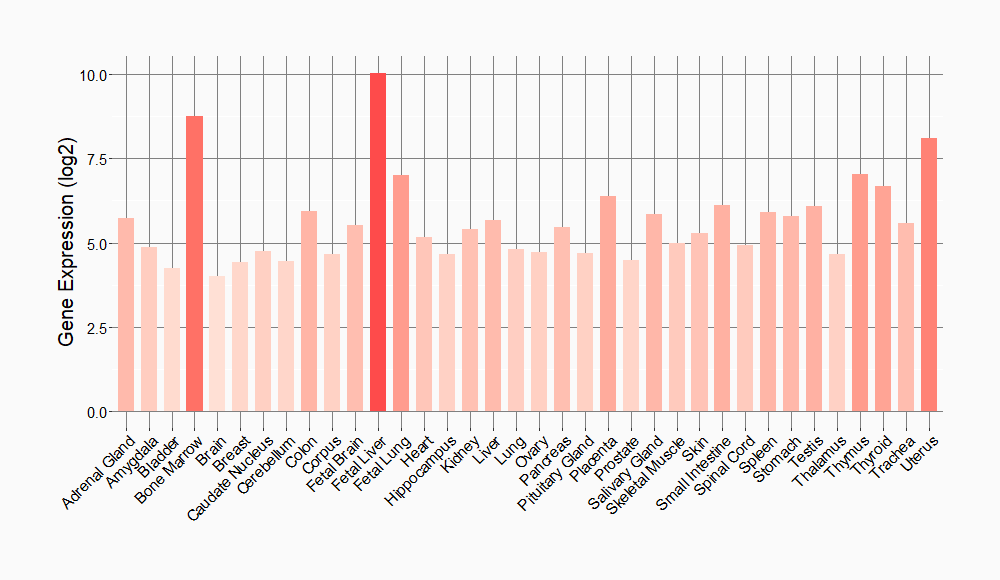
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
