Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00573)
| Name |
Proteasome assembly chaperone 2 (PSMG2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PAC-2; Hepatocellular carcinoma-susceptibility protein 3; Tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 5-induced protein 1; HCCA3; PAC2; TNFSF5IP1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PSMG2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr18:12658043-12725740[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MFVPCGESAPDLAGFTLLMPAVSVGNVGQLAMDLIISTLNMSKIGYFYTDCLVPMVGNNP
YATTEGNSTELSINAEVYSLPSRKLVALQLRSIFIKYKSKPFCEKLLSWVKSSGCARVIV LSSSHSYQRNDLQLRSTPFRYLLTPSMQKSVQNKIKSLNWEEMEKSRCIPEIDDSEFCIR IPGGGITKTLYDESCSKEIQMAVLLKFVSEGDNIPDALGLVEYLNEWLQILKPLSDDPTV SASRWKIPSSWRLLFGSGLPPALF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Chaperone protein which promotes assembly of the 20S proteasome as part of a heterodimer with PSMG1. The PSMG1-PSMG2 heterodimer binds to the PSMA5 and PSMA7 proteasome subunits, promotes assembly of the proteasome alpha subunits into the heteroheptameric alpha ring and prevents alpha ring dimerization.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bortezomib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E171K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cortiosteroids | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E171K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.24E-06; Fold-change: 1.10E+00; Z-score: 4.96E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
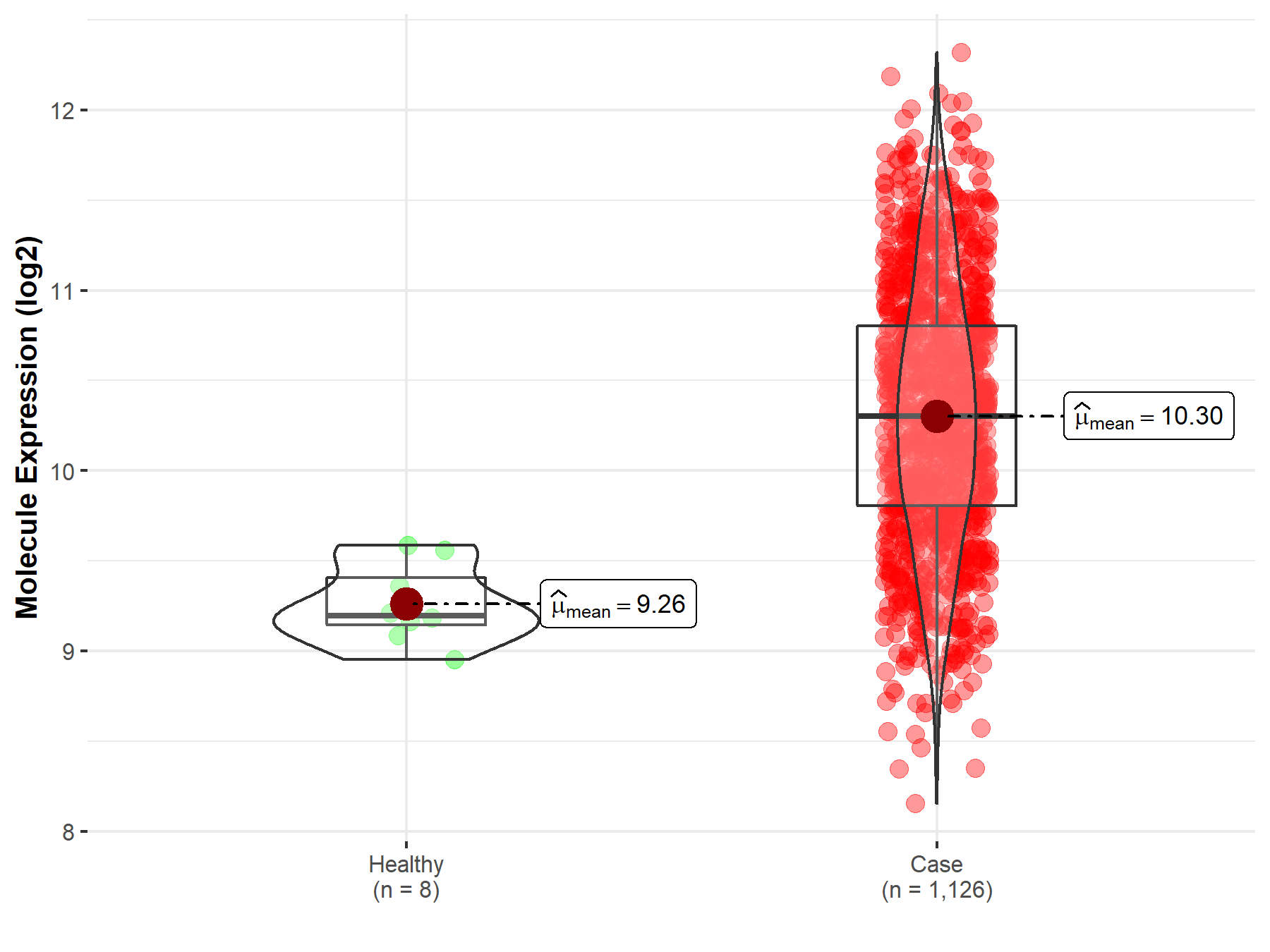
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Peripheral blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.65E-01; Fold-change: -4.08E-02; Z-score: -1.46E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
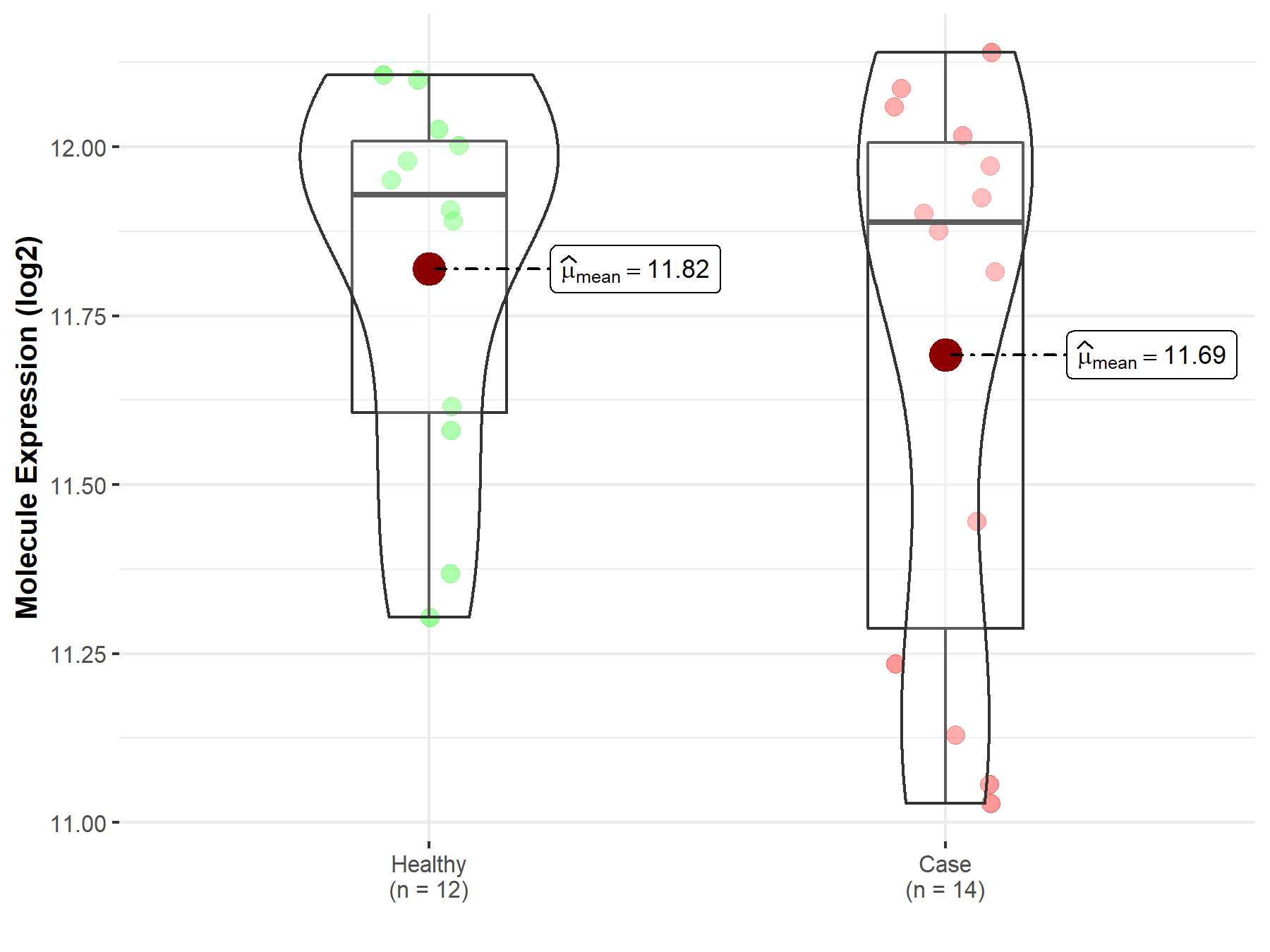
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

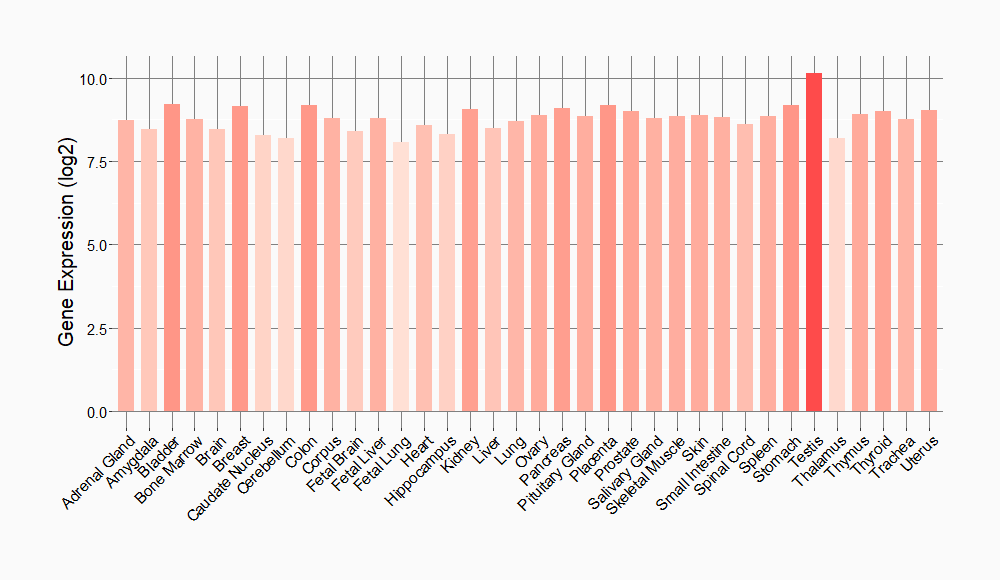
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
