Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00547)
| Name |
Polyadenylate-binding protein 1 (PABPC1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PABP-1; Poly(A)-binding protein 1; PAB1; PABP; PABP1; PABPC2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PABPC1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:100685816-100722809[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MNPSAPSYPMASLYVGDLHPDVTEAMLYEKFSPAGPILSIRVCRDMITRRSLGYAYVNFQ
QPADAERALDTMNFDVIKGKPVRIMWSQRDPSLRKSGVGNIFIKNLDKSIDNKALYDTFS AFGNILSCKVVCDENGSKGYGFVHFETQEAAERAIEKMNGMLLNDRKVFVGRFKSRKERE AELGARAKEFTNVYIKNFGEDMDDERLKDLFGKFGPALSVKVMTDESGKSKGFGFVSFER HEDAQKAVDEMNGKELNGKQIYVGRAQKKVERQTELKRKFEQMKQDRITRYQGVNLYVKN LDDGIDDERLRKEFSPFGTITSAKVMMEGGRSKGFGFVCFSSPEEATKAVTEMNGRIVAT KPLYVALAQRKEERQAHLTNQYMQRMASVRAVPNPVINPYQPAPPSGYFMAAIPQTQNRA AYYPPSQIAQLRPSPRWTAQGARPHPFQNMPGAIRPAAPRPPFSTMRPASSQVPRVMSTQ RVANTSTQTMGPRPAAAAAAATPAVRTVPQYKYAAGVRNPQQHLNAQPQVTMQQPAVHVQ GQEPLTASMLASAPPQEQKQMLGERLFPLIQAMHPTLAGKITGMLLEIDNSELLHMLESP ESLRSKVDEAVAVLQAHQAKEAAQKAVNSATGVPTV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Binds the poly(A) tail of mRNA, including that of its own transcript, and regulates processes of mRNA metabolism such as pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA stability. Its function in translational initiation regulation can either be enhanced by PAIP1 or repressed by PAIP2. Can probably bind to cytoplasmic RNA sequences other than poly(A) in vivo. Involved in translationally coupled mRNA turnover. Implicated with other RNA-binding proteins in the cytoplasmic deadenylation/translational and decay interplay of the FOS mRNA mediated by the major coding-region determinant of instability (mCRD) domain. Involved in regulation of nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) of mRNAs containing premature stop codons; for the recognition of premature termination codons (PTC) and initiation of NMD a competitive interaction between UPF1 and PABPC1 with the ribosome-bound release factors is proposed. By binding to long poly(A) tails, may protect them from uridylation by ZCCHC6/ZCCHC11 and hence contribute to mRNA stability.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Acetylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long non-coding RNA SNHG14 induces trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer via inducing PABPC1 expression through H3k27 acetylation. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.27E-34; Fold-change: 1.54E-01; Z-score: 9.58E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.69E-07; Fold-change: 1.71E-01; Z-score: 8.01E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
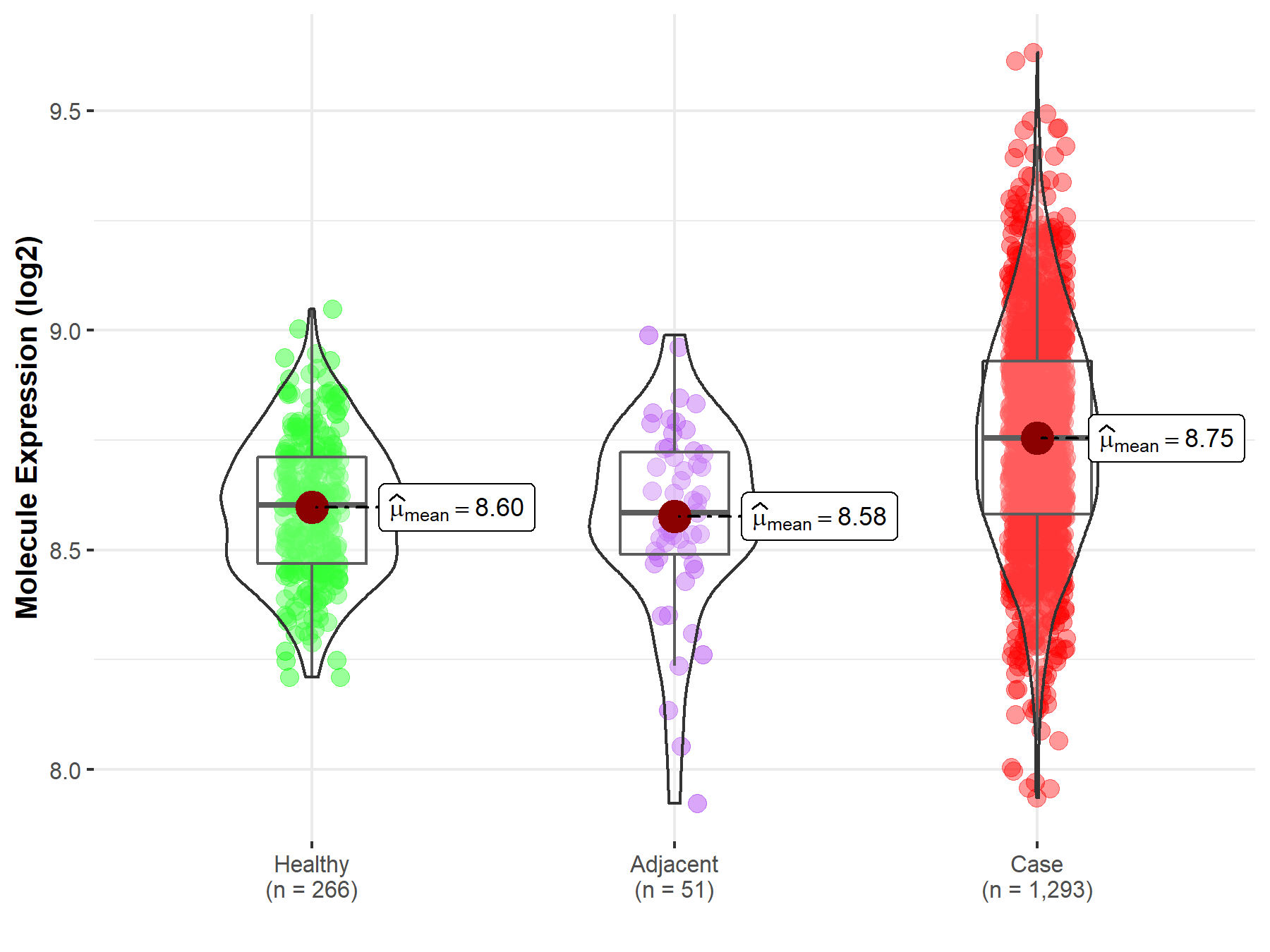
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

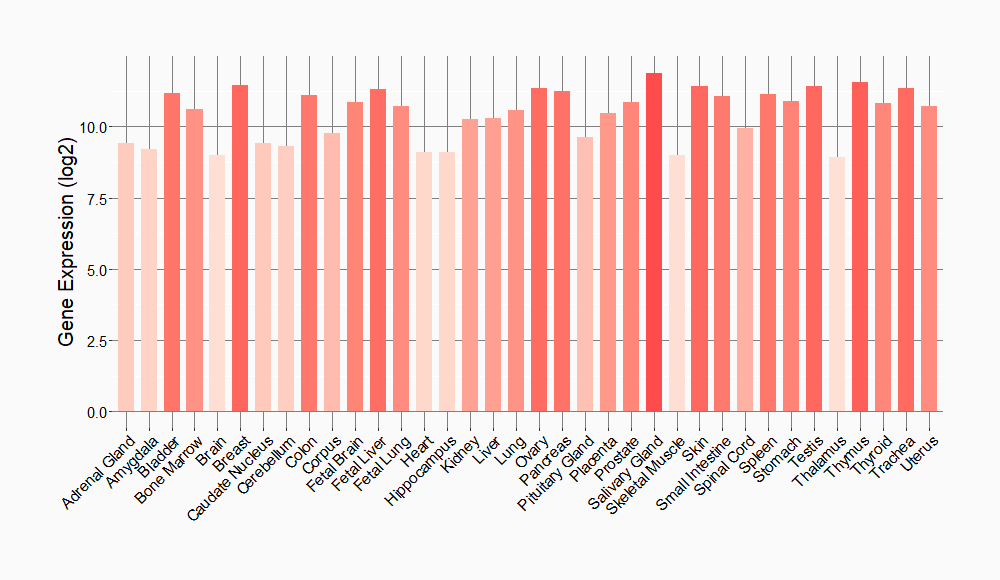
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
