Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00538)
| Name |
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase NSD2 (NSD2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Multiple myeloma SET domain-containing protein; MMSET; Nuclear SET domain-containing protein 2; Protein trithorax-5; Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1 protein; KIAA1090; MMSET; TRX5; WHSC1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NSD2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr4:1871393-1982207[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEFSIKQSPLSVQSVVKCIKMKQAPEILGSANGKTPSCEVNRECSVFLSKAQLSSSLQEG
VMQKFNGHDALPFIPADKLKDLTSRVFNGEPGAHDAKLRFESQEMKGIGTPPNTTPIKNG SPEIKLKITKTYMNGKPLFESSICGDSAADVSQSEENGQKPENKARRNRKRSIKYDSLLE QGLVEAALVSKISSPSDKKIPAKKESCPNTGRDKDHLLKYNVGDLVWSKVSGYPWWPCMV SADPLLHSYTKLKGQKKSARQYHVQFFGDAPERAWIFEKSLVAFEGEGQFEKLCQESAKQ APTKAEKIKLLKPISGKLRAQWEMGIVQAEEAASMSVEERKAKFTFLYVGDQLHLNPQVA KEAGIAAESLGEMAESSGVSEEAAENPKSVREECIPMKRRRRAKLCSSAETLESHPDIGK STPQKTAEADPRRGVGSPPGRKKTTVSMPRSRKGDAASQFLVFCQKHRDEVVAEHPDASG EEIEELLRSQWSLLSEKQRARYNTKFALVAPVQAEEDSGNVNGKKRNHTKRIQDPTEDAE AEDTPRKRLRTDKHSLRKRDTITDKTARTSSYKAMEAASSLKSQAATKNLSDACKPLKKR NRASTAASSALGFSKSSSPSASLTENEVSDSPGDEPSESPYESADETQTEVSVSSKKSER GVTAKKEYVCQLCEKPGSLLLCEGPCCGAFHLACLGLSRRPEGRFTCSECASGIHSCFVC KESKTDVKRCVVTQCGKFYHEACVKKYPLTVFESRGFRCPLHSCVSCHASNPSNPRPSKG KMMRCVRCPVAYHSGDACLAAGCSVIASNSIICTAHFTARKGKRHHAHVNVSWCFVCSKG GSLLCCESCPAAFHPDCLNIEMPDGSWFCNDCRAGKKLHFQDIIWVKLGNYRWWPAEVCH PKNVPPNIQKMKHEIGEFPVFFFGSKDYYWTHQARVFPYMEGDRGSRYQGVRGIGRVFKN ALQEAEARFREIKLQREARETQESERKPPPYKHIKVNKPYGKVQIYTADISEIPKCNCKP TDENPCGFDSECLNRMLMFECHPQVCPAGEFCQNQCFTKRQYPETKIIKTDGKGWGLVAK RDIRKGEFVNEYVGELIDEEECMARIKHAHENDITHFYMLTIDKDRIIDAGPKGNYSRFM NHSCQPNCETLKWTVNGDTRVGLFAVCDIPAGTELTFNYNLDCLGNEKTVCRCGASNCSG FLGDRPKTSTTLSSEEKGKKTKKKTRRRRAKGEGKRQSEDECFRCGDGGQLVLCDRKFCT KAYHLSCLGLGKRPFGKWECPWHHCDVCGKPSTSFCHLCPNSFCKEHQDGTAFSCTPDGR SYCCEHDLGAASVRSTKTEKPPPEPGKPKGKRRRRRGWRRVTEGK Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Histone methyltransferase which specifically dimethylates nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me2). Also monomethylates nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me) in vitro. Does not trimethylate nucleosomal histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me3). However, specifically trimethylates histone H3 at 'Lys-36' (H3K36me3) at euchromatic regions in embryonic stem (ES) cells. By methylating histone H3 at 'Lys-36', involved in the regulation of gene transcription during various biological processes. In ES cells, associates with developmental transcription factors such as SALL1 and represses inappropriate gene transcription mediated by histone deacetylation. During heart development, associates with transcription factor NKX2-5 to repress transcription of NKX2-5 target genes. Plays an essential role in adipogenesis, by regulating expression of genes involved in pre-adipocyte differentiation. During T-cell receptor (TCR) and CD28-mediated T-cell activation, promotes the transcription of transcription factor BCL6 which is required for follicular helper T (Tfh) cell differentiation. During B-cell development, required for the generation of the B1 lineage. During B2 cell activation, may contribute to the control of isotype class switch recombination (CRS), splenic germinal center formation, and the humoral immune response. Plays a role in class switch recombination of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) locus during B-cell activation. By regulating the methylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-36' and histone H4 at 'Lys-20' at the IgH locus, involved in TP53BP1 recruitment to the IgH switch region and promotes the transcription of IgA.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.57E-54 Fold-change: 1.07E-01 Z-score: 1.75E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nu/nu athymic mice xenografts model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA kit assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NSD2 overexpression is significantly associated with high risk of relapse and poor survival in tamoxifen-treated ER-positive breast cancer patients. NSD2 drives tamoxifen therapy resistance through coordinated stimulation of key glucose metabolism enzymes and enhancement of the PPP. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.57E-54; Fold-change: 4.22E-01; Z-score: 1.15E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.79E-05; Fold-change: 4.66E-01; Z-score: 8.14E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
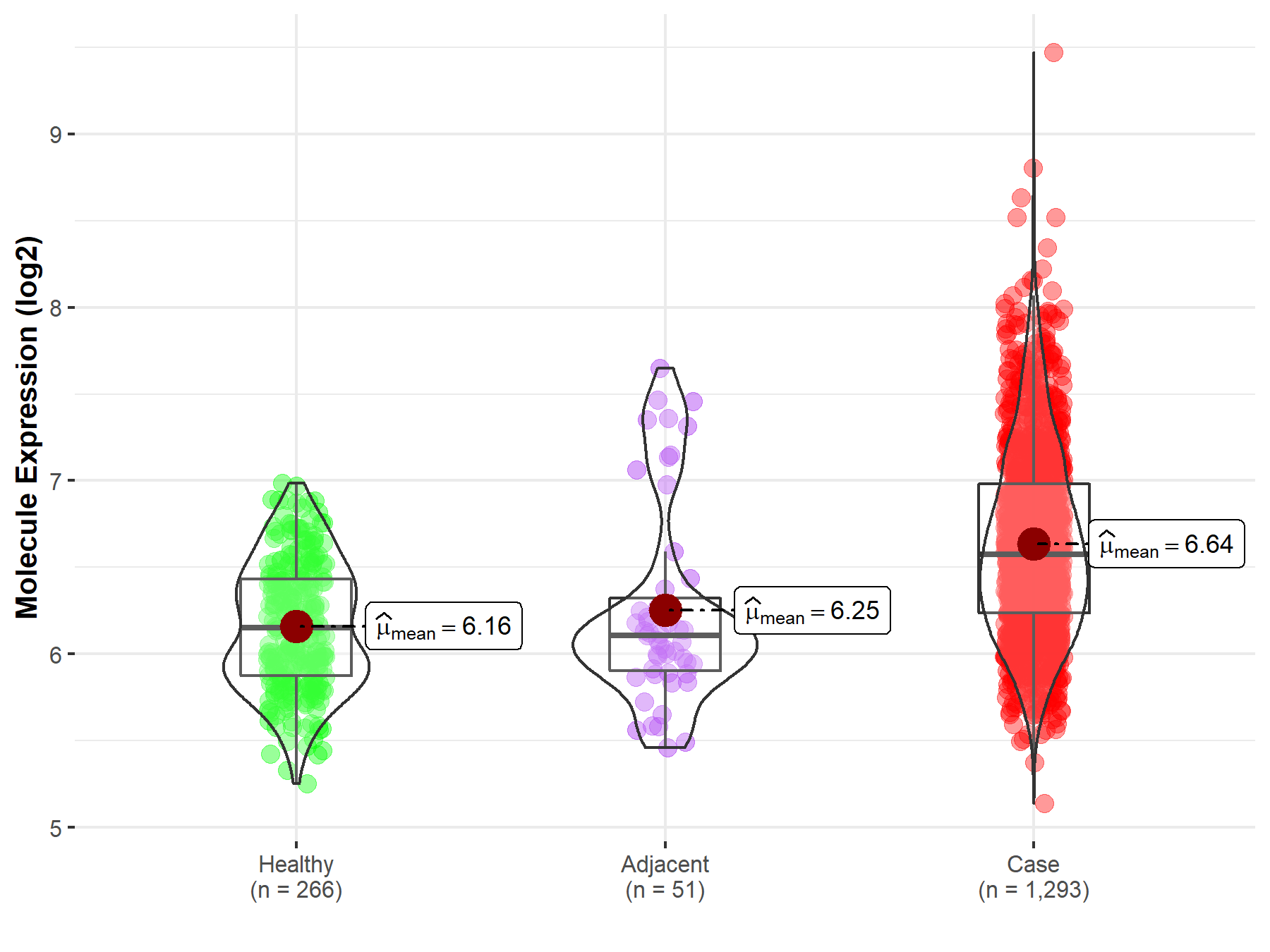
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

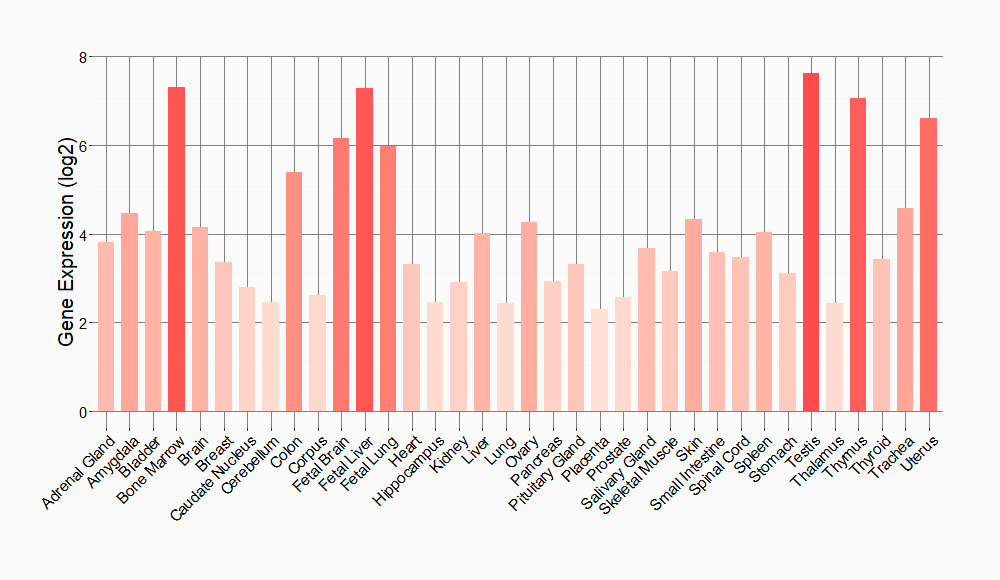
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
