Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00518)
| Name |
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 (MSH6)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
hMSH6; G/T mismatch-binding protein; GTBP; GTMBP; MutS protein homolog 6; MutS-alpha 160 kDa subunit; p160; GTBP
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MSH6
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:47695530-47810063[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSRQSTLYSFFPKSPALSDANKASARASREGGRAAAAPGASPSPGGDAAWSEAGPGPRPL
ARSASPPKAKNLNGGLRRSVAPAAPTSCDFSPGDLVWAKMEGYPWWPCLVYNHPFDGTFI REKGKSVRVHVQFFDDSPTRGWVSKRLLKPYTGSKSKEAQKGGHFYSAKPEILRAMQRAD EALNKDKIKRLELAVCDEPSEPEEEEEMEVGTTYVTDKSEEDNEIESEEEVQPKTQGSRR SSRQIKKRRVISDSESDIGGSDVEFKPDTKEEGSSDEISSGVGDSESEGLNSPVKVARKR KRMVTGNGSLKRKSSRKETPSATKQATSISSETKNTLRAFSAPQNSESQAHVSGGGDDSS RPTVWYHETLEWLKEEKRRDEHRRRPDHPDFDASTLYVPEDFLNSCTPGMRKWWQIKSQN FDLVICYKVGKFYELYHMDALIGVSELGLVFMKGNWAHSGFPEIAFGRYSDSLVQKGYKV ARVEQTETPEMMEARCRKMAHISKYDRVVRREICRIITKGTQTYSVLEGDPSENYSKYLL SLKEKEEDSSGHTRAYGVCFVDTSLGKFFIGQFSDDRHCSRFRTLVAHYPPVQVLFEKGN LSKETKTILKSSLSCSLQEGLIPGSQFWDASKTLRTLLEEEYFREKLSDGIGVMLPQVLK GMTSESDSIGLTPGEKSELALSALGGCVFYLKKCLIDQELLSMANFEEYIPLDSDTVSTT RSGAIFTKAYQRMVLDAVTLNNLEIFLNGTNGSTEGTLLERVDTCHTPFGKRLLKQWLCA PLCNHYAINDRLDAIEDLMVVPDKISEVVELLKKLPDLERLLSKIHNVGSPLKSQNHPDS RAIMYEETTYSKKKIIDFLSALEGFKVMCKIIGIMEEVADGFKSKILKQVISLQTKNPEG RFPDLTVELNRWDTAFDHEKARKTGLITPKAGFDSDYDQALADIRENEQSLLEYLEKQRN RIGCRTIVYWGIGRNRYQLEIPENFTTRNLPEEYELKSTKKGCKRYWTKTIEKKLANLIN AEERRDVSLKDCMRRLFYNFDKNYKDWQSAVECIAVLDVLLCLANYSRGGDGPMCRPVIL LPEDTPPFLELKGSRHPCITKTFFGDDFIPNDILIGCEEEEQENGKAYCVLVTGPNMGGK STLMRQAGLLAVMAQMGCYVPAEVCRLTPIDRVFTRLGASDRIMSGESTFFVELSETASI LMHATAHSLVLVDELGRGTATFDGTAIANAVVKELAETIKCRTLFSTHYHSLVEDYSQNV AVRLGHMACMVENECEDPSQETITFLYKFIKGACPKSYGFNAARLANLPEEVIQKGHRKA REFEKMNQSLRLFREVCLASERSTVDAEAVHKLLTLIKEL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Component of the post-replicative DNA mismatch repair system (MMR). Heterodimerizes with MSH2 to form MutS alpha, which binds to DNA mismatches thereby initiating DNA repair. When bound, MutS alpha bends the DNA helix and shields approximately 20 base pairs, and recognizes single base mismatches and dinucleotide insertion-deletion loops (IDL) in the DNA. After mismatch binding, forms a ternary complex with the MutL alpha heterodimer, which is thought to be responsible for directing the downstream MMR events, including strand discrimination, excision, and resynthesis. ATP binding and hydrolysis play a pivotal role in mismatch repair functions. The ATPase activity associated with MutS alpha regulates binding similar to a molecular switch: mismatched DNA provokes ADP-->ATP exchange, resulting in a discernible conformational transition that converts MutS alpha into a sliding clamp capable of hydrolysis-independent diffusion along the DNA backbone. This transition is crucial for mismatch repair. MutS alpha may also play a role in DNA homologous recombination repair. Recruited on chromatin in G1 and early S phase via its PWWP domain that specifically binds trimethylated 'Lys-36' of histone H3 (H3K36me3): early recruitment to chromatin to be replicated allowing a quick identification of mismatch repair to initiate the DNA mismatch repair reaction.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Mercaptopurine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number loss |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Peripheral blood | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Somatic copy number alteration assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Finally, relapse-specific focal deletion of MSH6 and, consequently, reduced gene expression were found in 2 of 20 cases. In an independent cohort of children with ALL, reduced expression of MSH6 was associated with resistance to mercaptopurine and prednisone, thereby providing a plausible mechanism by which this acquired deletion contributes to drug resistance at relapse. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number loss |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Peripheral blood | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Somatic copy number alteration assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Finally, relapse-specific focal deletion of MSH6 and, consequently, reduced gene expression were found in 2 of 20 cases. In an independent cohort of children with ALL, reduced expression of MSH6 was associated with resistance to mercaptopurine and prednisone, thereby providing a plausible mechanism by which this acquired deletion contributes to drug resistance at relapse. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pituitary cancer [ICD-11: 2F37.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pituitary cancer [ICD-11: 2F37.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number loss |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Loss of MSH6 occurred during the progression from an atypical prolactinoma to a pituitary carcinoma, which may have caused resistance to TMZ treatment. | |||
| Disease Class: FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SSCP assay; Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prominent example of therapy-induced molecular alterations in gliomas which themselves ensue therapeutic consequences are MSH6 mutations in glioblastomas which arise during temozolomide chemotherapy and which are able to convey temozolomide resistance in affected tumors. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.40E-44; Fold-change: 8.01E-01; Z-score: 8.89E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
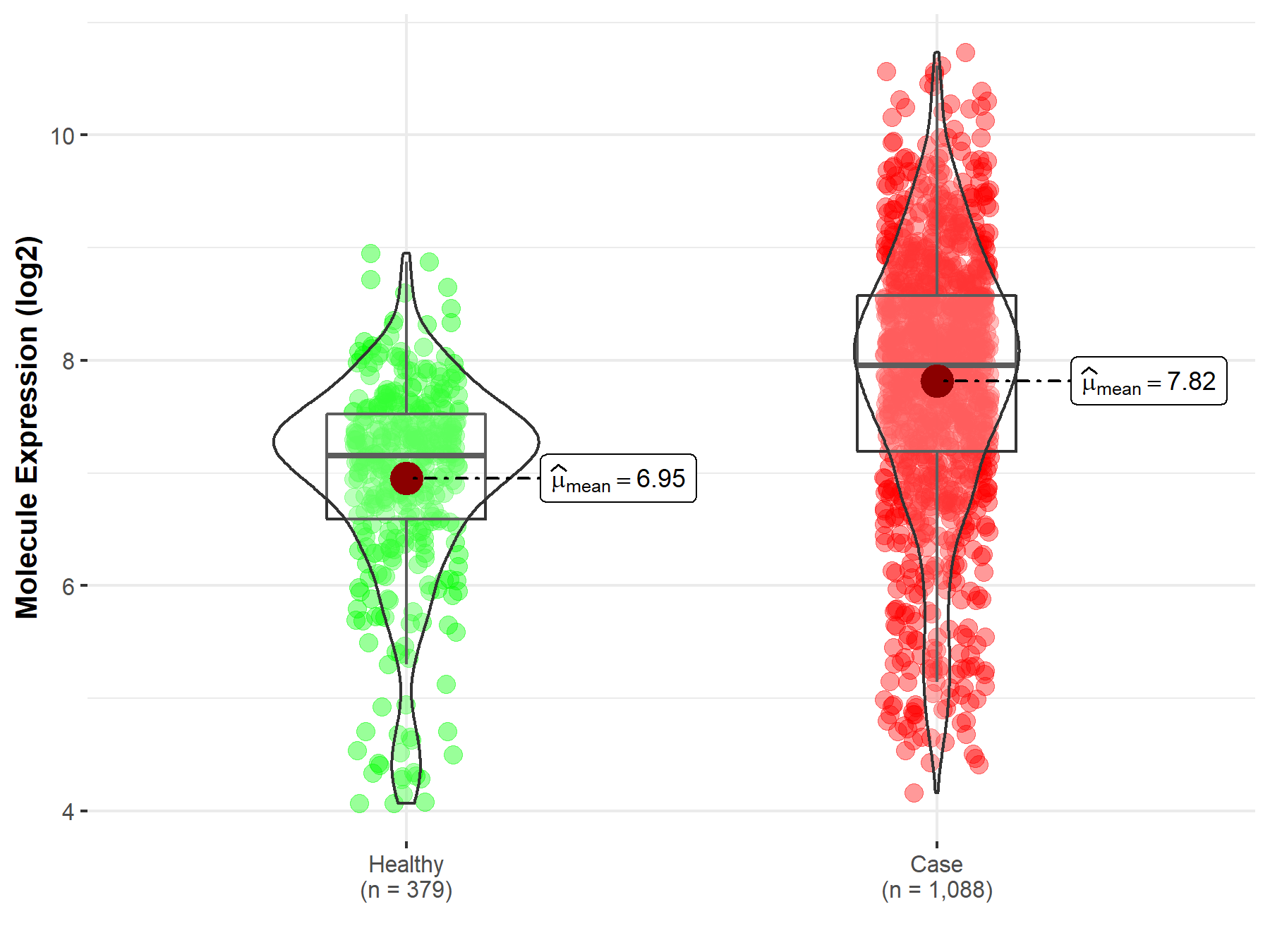
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.85E-01; Fold-change: 1.04E+00; Z-score: 9.46E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.14E-04; Fold-change: 1.08E+00; Z-score: 1.43E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
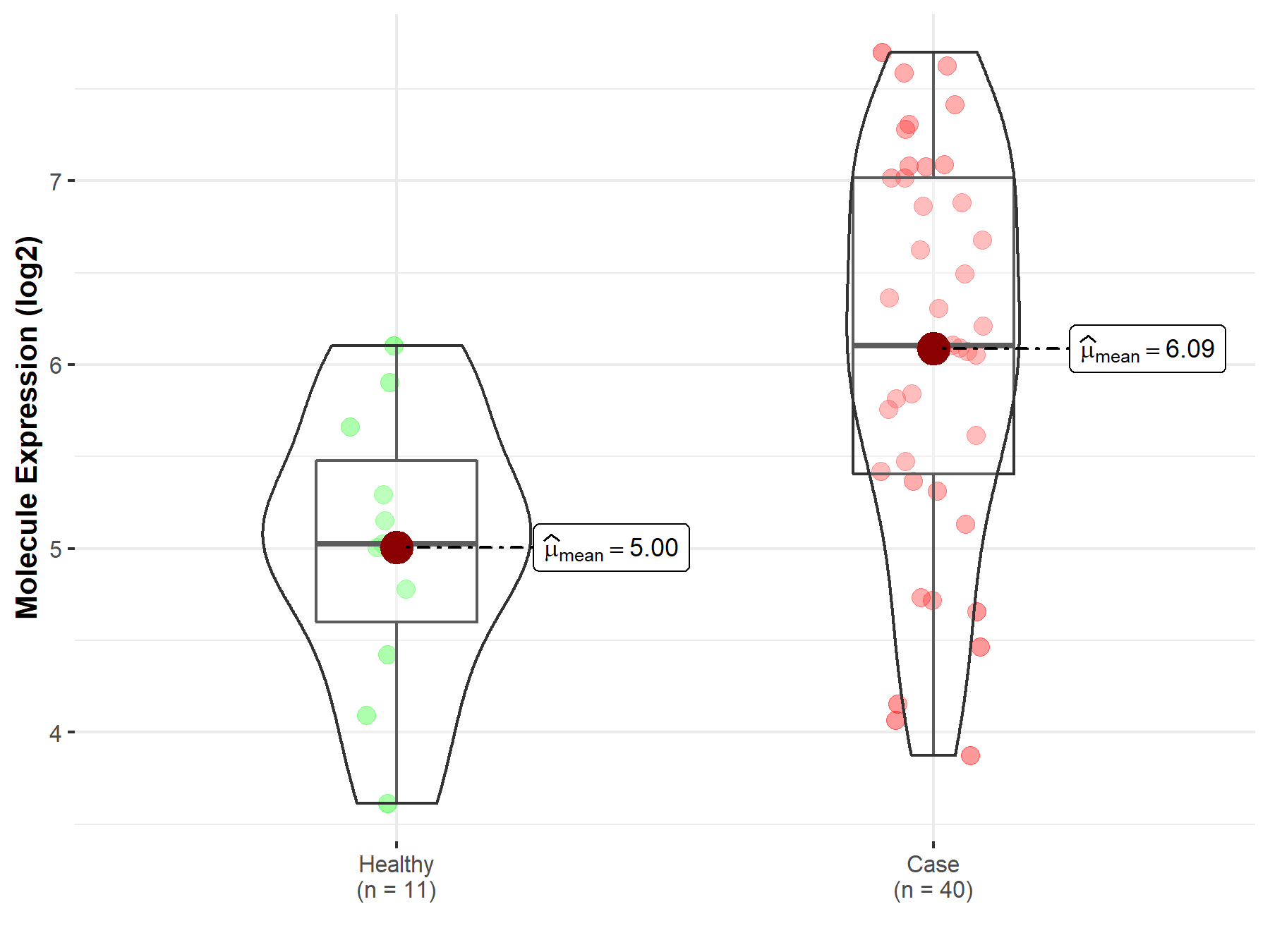
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-06; Fold-change: 2.19E+00; Z-score: 3.56E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
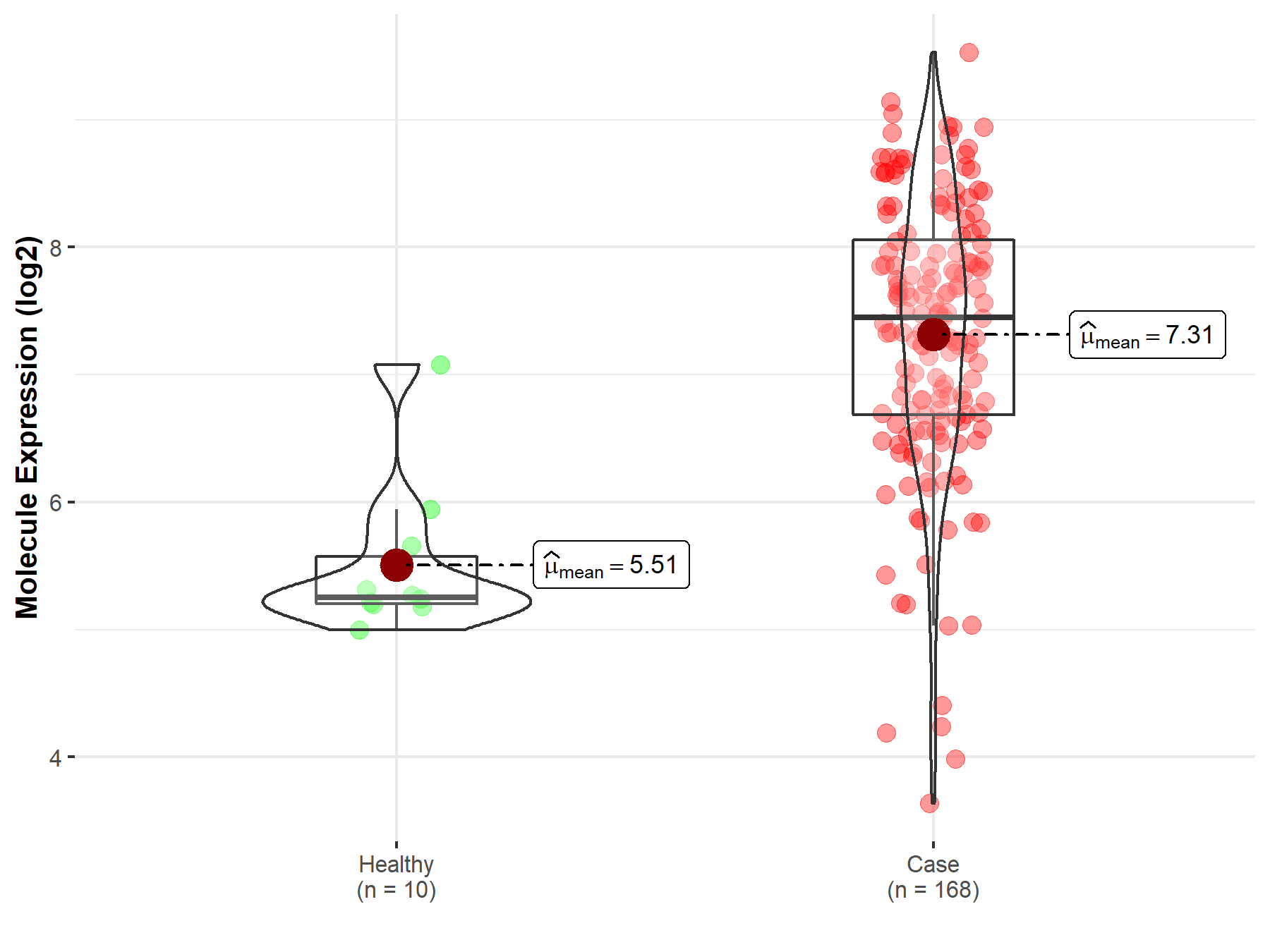
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.79E-03; Fold-change: 6.83E-01; Z-score: 9.15E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary gonadotrope tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.40E-02; Fold-change: 1.29E+00; Z-score: 2.21E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
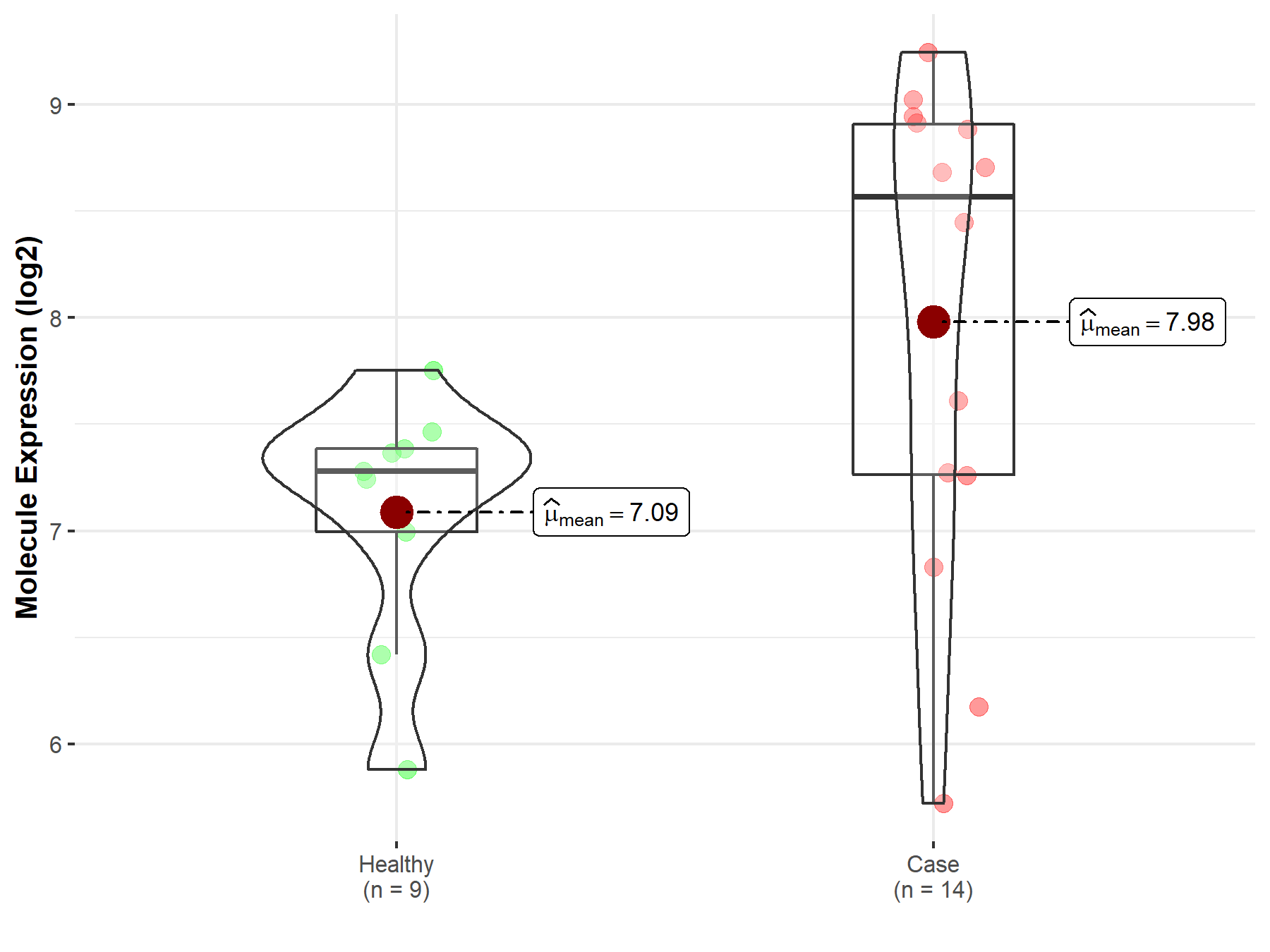
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
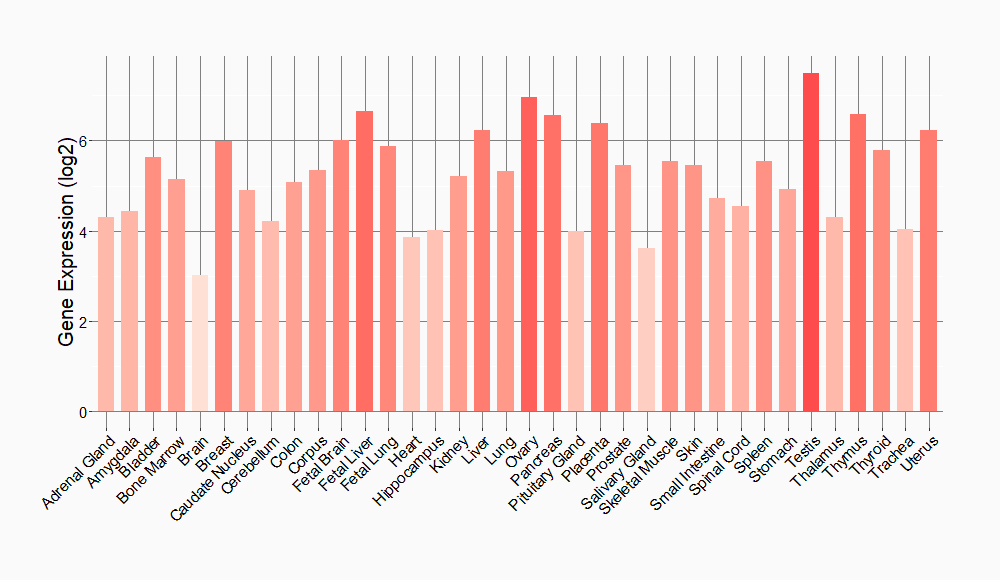
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
