Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00517)
| Name |
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 (MSH2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
hMSH2; MutS protein homolog 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MSH2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:47403067-47663146[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAVQPKETLQLESAAEVGFVRFFQGMPEKPTTTVRLFDRGDFYTAHGEDALLAAREVFKT
QGVIKYMGPAGAKNLQSVVLSKMNFESFVKDLLLVRQYRVEVYKNRAGNKASKENDWYLA YKASPGNLSQFEDILFGNNDMSASIGVVGVKMSAVDGQRQVGVGYVDSIQRKLGLCEFPD NDQFSNLEALLIQIGPKECVLPGGETAGDMGKLRQIIQRGGILITERKKADFSTKDIYQD LNRLLKGKKGEQMNSAVLPEMENQVAVSSLSAVIKFLELLSDDSNFGQFELTTFDFSQYM KLDIAAVRALNLFQGSVEDTTGSQSLAALLNKCKTPQGQRLVNQWIKQPLMDKNRIEERL NLVEAFVEDAELRQTLQEDLLRRFPDLNRLAKKFQRQAANLQDCYRLYQGINQLPNVIQA LEKHEGKHQKLLLAVFVTPLTDLRSDFSKFQEMIETTLDMDQVENHEFLVKPSFDPNLSE LREIMNDLEKKMQSTLISAARDLGLDPGKQIKLDSSAQFGYYFRVTCKEEKVLRNNKNFS TVDIQKNGVKFTNSKLTSLNEEYTKNKTEYEEAQDAIVKEIVNISSGYVEPMQTLNDVLA QLDAVVSFAHVSNGAPVPYVRPAILEKGQGRIILKASRHACVEVQDEIAFIPNDVYFEKD KQMFHIITGPNMGGKSTYIRQTGVIVLMAQIGCFVPCESAEVSIVDCILARVGAGDSQLK GVSTFMAEMLETASILRSATKDSLIIIDELGRGTSTYDGFGLAWAISEYIATKIGAFCMF ATHFHELTALANQIPTVNNLHVTALTTEETLTMLYQVKKGVCDQSFGIHVAELANFPKHV IECAKQKALELEEFQYIGESQGYDIMEPAAKKCYLEREQGEKIIQEFLSKVKQMPFTEMS EENITIKLKQLKAEVIAKNNSFVNEIISRIKVTT Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Component of the post-replicative DNA mismatch repair system (MMR). Forms two different heterodimers: MutS alpha (MSH2-MSH6 heterodimer) and MutS beta (MSH2-MSH3 heterodimer) which binds to DNA mismatches thereby initiating DNA repair. When bound, heterodimers bend the DNA helix and shields approximately 20 base pairs. MutS alpha recognizes single base mismatches and dinucleotide insertion-deletion loops (IDL) in the DNA. MutS beta recognizes larger insertion-deletion loops up to 13 nucleotides long. After mismatch binding, MutS alpha or beta forms a ternary complex with the MutL alpha heterodimer, which is thought to be responsible for directing the downstream MMR events, including strand discrimination, excision, and resynthesis. Recruits DNA helicase MCM9 to chromatin which unwinds the mismatch containing DNA strand. ATP binding and hydrolysis play a pivotal role in mismatch repair functions. The ATPase activity associated with MutS alpha regulates binding similar to a molecular switch: mismatched DNA provokes ADP-->ATP exchange, resulting in a discernible conformational transition that converts MutS alpha into a sliding clamp capable of hydrolysis-independent diffusion along the DNA backbone. This transition is crucial for mismatch repair. MutS alpha may also play a role in DNA homologous recombination repair. In melanocytes may modulate both UV-B-induced cell cycle regulation and apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NCk1-AS1 downregulation and miR-134-5p upregulation suppress the expression of MSH2 and reduce cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| HT-29/5-FU cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0I27 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 targeted the human mutS homolog2 (hMSH2), and indirectly regulated the expression of thymidine phosphorylase (TP) and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD). These results demonstrate that miR-21 may play an important role in the 5-FU resistance of colon cancer cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| COLO 320DM cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0219 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
FACS analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mismatch repair (MMR) system is involved in DNA damage recognition and repair. Human mutS homolog 2 (hMSH2) and human mutL homolog 1 (hMLH1) function as core MMR proteins and form heterodimers with protein homologs hMSH3 or hMSH6 and hMLH3 or hPMS2, respectively. Colorectal tumors that express a high level of miR-21 display reduced hMSH2 protein expression. Cells that overproduce miR-21 exhibit significantly reduced 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) -induced G2/M damage arrest and apoptosis that is characteristic of defects in the core MMR component. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.20E-36; Fold-change: 7.28E-01; Z-score: 1.39E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.12E-27; Fold-change: 8.34E-01; Z-score: 1.23E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
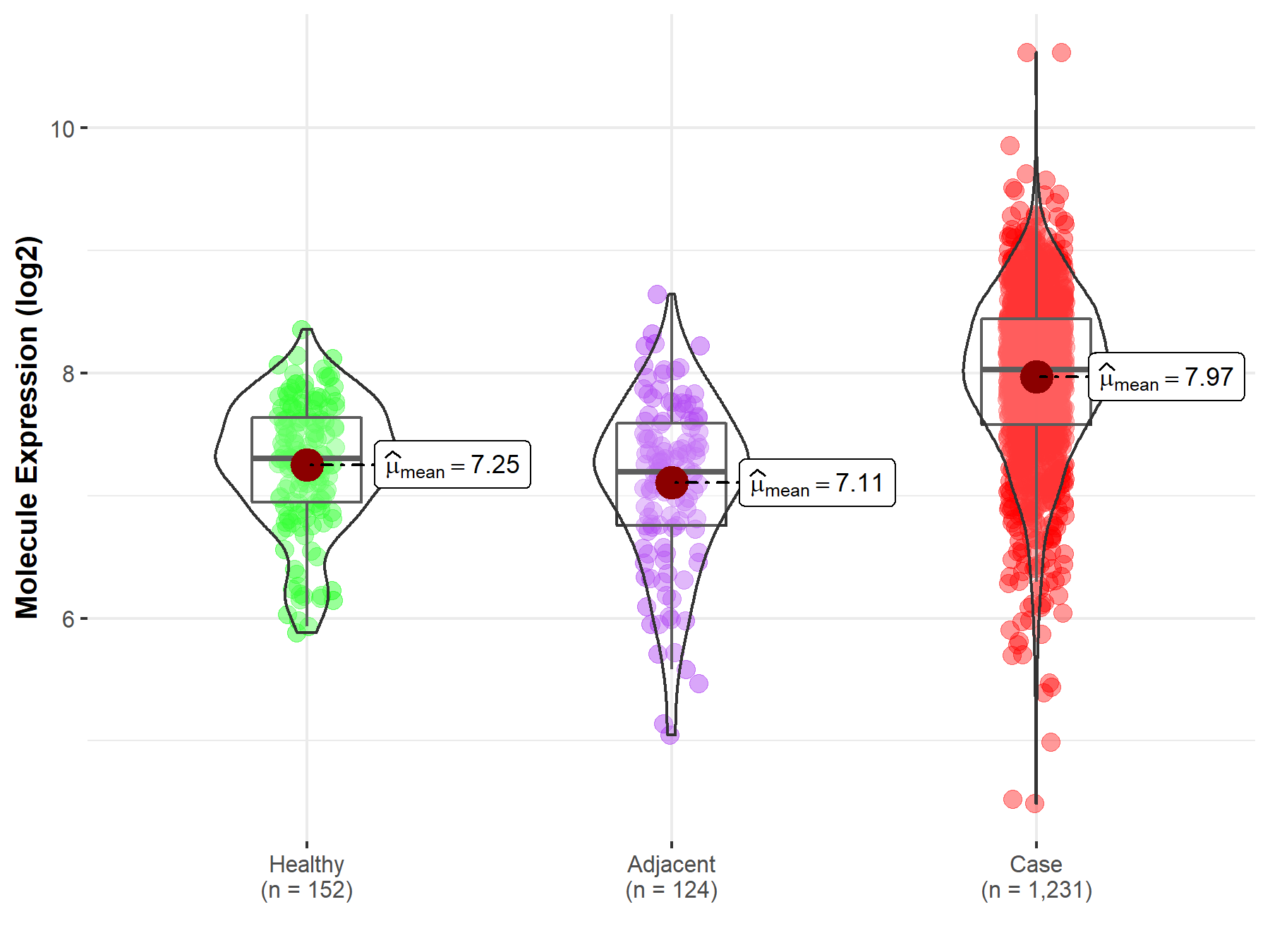
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.33E-04; Fold-change: 7.34E-01; Z-score: 1.15E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
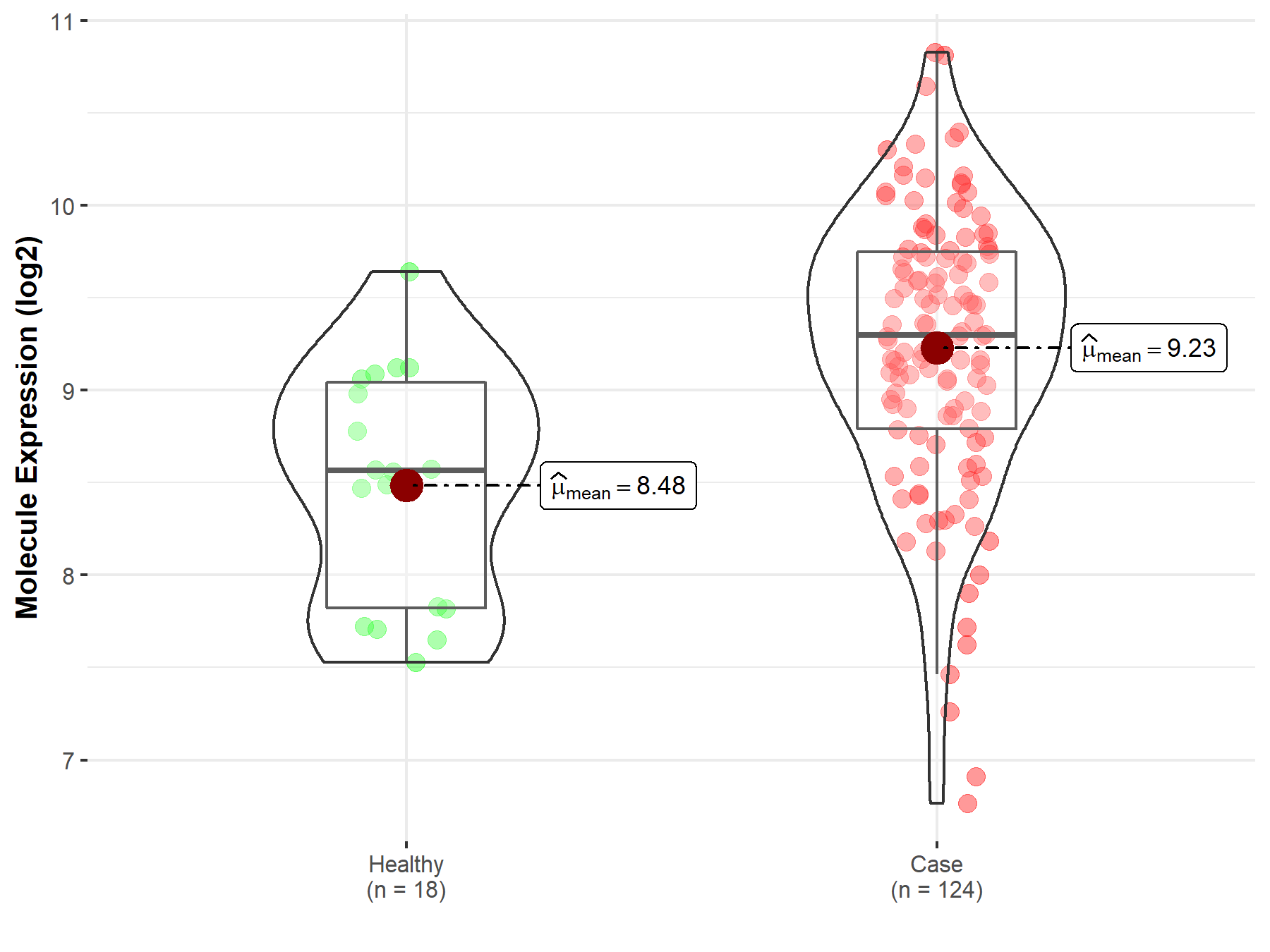
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

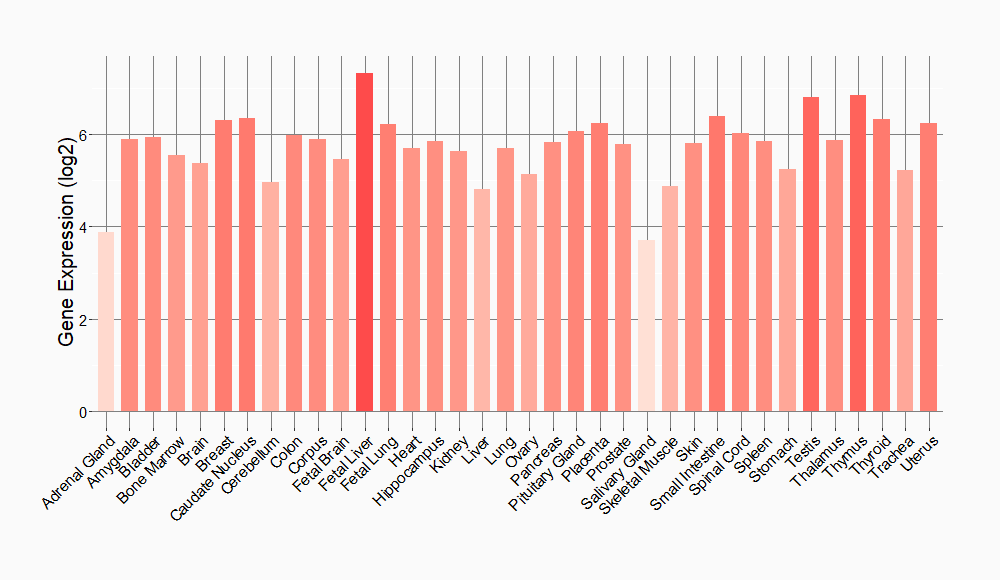
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
