Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00464)
| Name |
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 (RPS6KB1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
S6K-beta-1; S6K1; 70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1; P70S6K1; p70-S6K 1; Ribosomal protein S6 kinase I; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 14A; p70 ribosomal S6 kinase alpha; p70 S6 kinase alpha; p70 S6K-alpha; p70 S6KA; STK14A
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
RPS6KB1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr17:59893046-59950574[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MRRRRRRDGFYPAPDFRDREAEDMAGVFDIDLDQPEDAGSEDELEEGGQLNESMDHGGVG
PYELGMEHCEKFEISETSVNRGPEKIRPECFELLRVLGKGGYGKVFQVRKVTGANTGKIF AMKVLKKAMIVRNAKDTAHTKAERNILEEVKHPFIVDLIYAFQTGGKLYLILEYLSGGEL FMQLEREGIFMEDTACFYLAEISMALGHLHQKGIIYRDLKPENIMLNHQGHVKLTDFGLC KESIHDGTVTHTFCGTIEYMAPEILMRSGHNRAVDWWSLGALMYDMLTGAPPFTGENRKK TIDKILKCKLNLPPYLTQEARDLLKKLLKRNAASRLGAGPGDAGEVQAHPFFRHINWEEL LARKVEPPFKPLLQSEEDVSQFDSKFTRQTPVDSPDDSTLSESANQVFLGFTYVAPSVLE SVKEKFSFEPKIRSPRRFIGSPRTPVSPVKFSPGDFWGRGASASTANPQTPVEYPMETSG IEQMDVTMSGEASAPLPIRQPNSGPYKKQAFPMISKRPEHLRMNL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of mTOR signaling in response to growth factors and nutrients to promote cell proliferation, cell growth and cell cycle progression. Regulates protein synthesis through phosphorylation of EIF4B, RPS6 and EEF2K, and contributes to cell survival by repressing the pro-apoptotic function of BAD. Under conditions of nutrient depletion, the inactive form associates with the EIF3 translation initiation complex. Upon mitogenic stimulation, phosphorylation by the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) leads to dissociation from the EIF3 complex and activation. The active form then phosphorylates and activates several substrates in the pre-initiation complex, including the EIF2B complex and the cap-binding complex component EIF4B. Also controls translation initiation by phosphorylating a negative regulator of EIF4A, PDCD4, targeting it for ubiquitination and subsequent proteolysis. Promotes initiation of the pioneer round of protein synthesis by phosphorylating POLDIP3/SKAR. In response to IGF1, activates translation elongation by phosphorylating EEF2 kinase (EEF2K), which leads to its inhibition and thus activation of EEF2. Also plays a role in feedback regulation of mTORC2 by mTORC1 by phosphorylating RICTOR, resulting in the inhibition of mTORC2 and AKT1 signaling. Mediates cell survival by phosphorylating the pro-apoptotic protein BAD and suppressing its pro-apoptotic function. Phosphorylates mitochondrial URI1 leading to dissociation of a URI1-PPP1CC complex. The free mitochondrial PPP1CC can then dephosphorylate RPS6KB1 at Thr-412, which is proposed to be a negative feedback mechanism for the RPS6KB1 anti-apoptotic function. Mediates TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance by phosphorylating IRS1 at multiple serine residues, resulting in accelerated degradation of IRS1. In cells lacking functional TSC1-2 complex, constitutively phosphorylates and inhibits GSK3B. May be involved in cytoskeletal rearrangement through binding to neurabin. Phosphorylates and activates the pyrimidine biosynthesis enzyme CAD, downstream of MTOR. Following activation by mTORC1, phosphorylates EPRS and thereby plays a key role in fatty acid uptake by adipocytes and also most probably in interferon-gamma-induced translation inhibition.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.4] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.4] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.88E-02 Fold-change: -4.06E-02 Z-score: -2.54E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | BxPC-3 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0186 |
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0480 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Transwell migration assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miRNA-145 increases therapeutic sensibility to gemcitabine treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells, miR145 negatively regulated p70S6k1 expression at the posttranscriptional level in colon cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor [ICD-11: 2C10.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor [ICD-11: 2C10.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Everolimus | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| CXCR4-CXCL12-CXCR7 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04061 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A498 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1056 |
| SN12C cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1705 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | When the CXCR4-CXCL12-CXCR7 pathway is activated through CXCL12 in human renal cancer cells were, SN12C and A498, CXCL12 induced the mTOR targets p-P70S6K and p-4EBP1.The combination therapy of mTOR inhibitors with the CXCR4-CXCL12-CXCR7 axis inhibitors in renal cancer tumors could overcome the Everolimus resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04150 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| DLD1 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0248 | |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |
| HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpressed RP11-708H21.4 suppresses CRC cell proliferation through inducing G1 arrest. Moreover, up-regulation of RP11-708H21.4 inhibits cell migration and invasion, causes cell apoptosis, and enhances 5-FU sensitivity of CRC cells. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.88E-02; Fold-change: -1.36E-01; Z-score: -4.31E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.42E-03; Fold-change: 2.30E-01; Z-score: 6.66E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

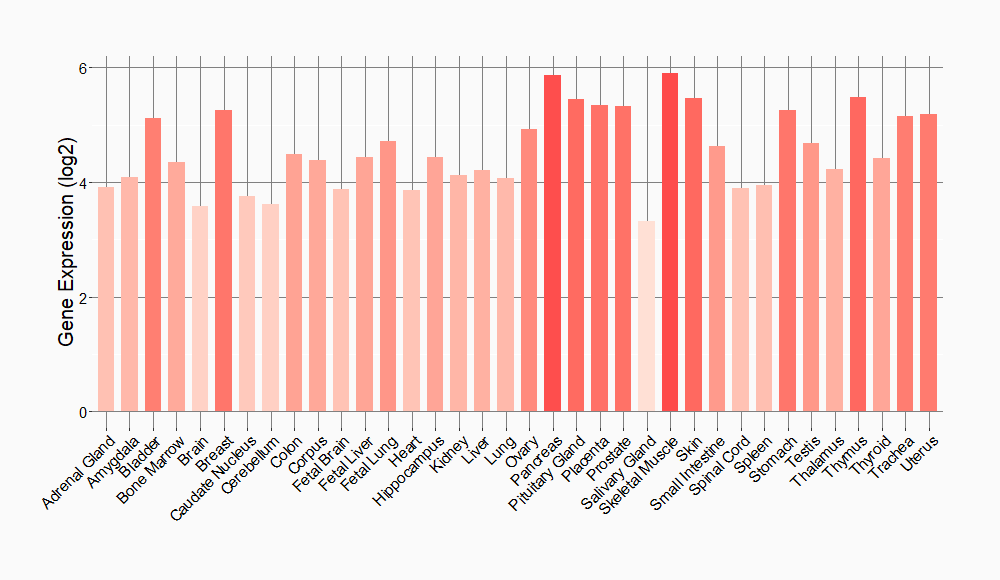
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
