Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00430)
| Name |
I-kappa-B-kinase beta (IKKB)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
I-kappa-B-kinase beta; IKK-B; IKK-beta; IkBKB; I-kappa-B kinase 2; IKK2; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B inhibitor kinase beta; NFKBIKB; Serine/threonine protein kinase IKBKB; IKKB
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
IKBKB
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:42271302-42332460[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSWSPSLTTQTCGAWEMKERLGTGGFGNVIRWHNQETGEQIAIKQCRQELSPRNRERWCL
EIQIMRRLTHPNVVAARDVPEGMQNLAPNDLPLLAMEYCQGGDLRKYLNQFENCCGLREG AILTLLSDIASALRYLHENRIIHRDLKPENIVLQQGEQRLIHKIIDLGYAKELDQGSLCT SFVGTLQYLAPELLEQQKYTVTVDYWSFGTLAFECITGFRPFLPNWQPVQWHSKVRQKSE VDIVVSEDLNGTVKFSSSLPYPNNLNSVLAERLEKWLQLMLMWHPRQRGTDPTYGPNGCF KALDDILNLKLVHILNMVTGTIHTYPVTEDESLQSLKARIQQDTGIPEEDQELLQEAGLA LIPDKPATQCISDGKLNEGHTLDMDLVFLFDNSKITYETQISPRPQPESVSCILQEPKRN LAFFQLRKVWGQVWHSIQTLKEDCNRLQQGQRAAMMNLLRNNSCLSKMKNSMASMSQQLK AKLDFFKTSIQIDLEKYSEQTEFGITSDKLLLAWREMEQAVELCGRENEVKLLVERMMAL QTDIVDLQRSPMGRKQGGTLDDLEEQARELYRRLREKPRDQRTEGDSQEMVRLLLQAIQS FEKKVRVIYTQLSKTVVCKQKALELLPKVEEVVSLMNEDEKTVVRLQEKRQKELWNLLKI ACSKVRGPVSGSPDSMNASRLSQPGQLMSQPSTASNSLPEPAKKSEELVAEAHNLCTLLE NAIQDTVREQDQSFTALDWSWLQTEEEEHSCLEQAS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine kinase that plays an essential role in the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway which is activated by multiple stimuli such as inflammatory cytokines, bacterial or viral products, DNA damages or other cellular stresses. Acts as part of the canonical IKK complex in the conventional pathway of NF-kappa-B activation. Phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B on 2 critical serine residues. These modifications allow polyubiquitination of the inhibitors and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In turn, free NF-kappa-B is translocated into the nucleus and activates the transcription of hundreds of genes involved in immune response, growth control, or protection against apoptosis. In addition to the NF-kappa-B inhibitors, phosphorylates several other components of the signaling pathway including NEMO/IKBKG, NF-kappa-B subunits RELA and NFKB1, as well as IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKBKE. IKK-related kinase phosphorylations may prevent the overproduction of inflammatory mediators since they exert a negative regulation on canonical IKKs. Phosphorylates FOXO3, mediating the TNF-dependent inactivation of this pro-apoptotic transcription factor. Also phosphorylates other substrates including NCOA3, BCL10 and IRS1. Within the nucleus, acts as an adapter protein for NFKBIA degradation in UV-induced NF-kappa-B activation. Phosphorylates RIPK1 at 'Ser-25' which represses its kinase activity and consequently prevents TNF-mediated RIPK1-dependent cell death. Phosphorylates the C-terminus of IRF5, stimulating IRF5 homodimerization and translocation into the nucleus.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.19E-03 Fold-change: 4.24E-02 Z-score: 3.17E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04064 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BEL-7402 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5492 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| HCCLM3 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6832 | |
| BEL-7404 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6568 | |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| PLC cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RIP assay; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Silencing the expression of miR-16 induced the chemoresistance in HCC by target IkBkB via NF-kB signaling pathway. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Ectopic expression of miR-16 promoted Taxol-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, IkBkB was identified to be a direct target of miR-16, restoring the expression of IkBkB counteracted miR-16-mediated Taxol sensitivity. Moreover, miR-16 was highly expressed in Taxol-sensitive breast cancer patients and negatively associated with T stages, whereas IkBkB was lowly expressed in Taxol-sensitive breast cancer and positively correlated with T, N and clinical stages. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.19E-03; Fold-change: 1.69E-01; Z-score: 5.48E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.90E-02; Fold-change: 1.67E-02; Z-score: 5.22E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 8.29E-01; Fold-change: -6.88E-02; Z-score: -7.27E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
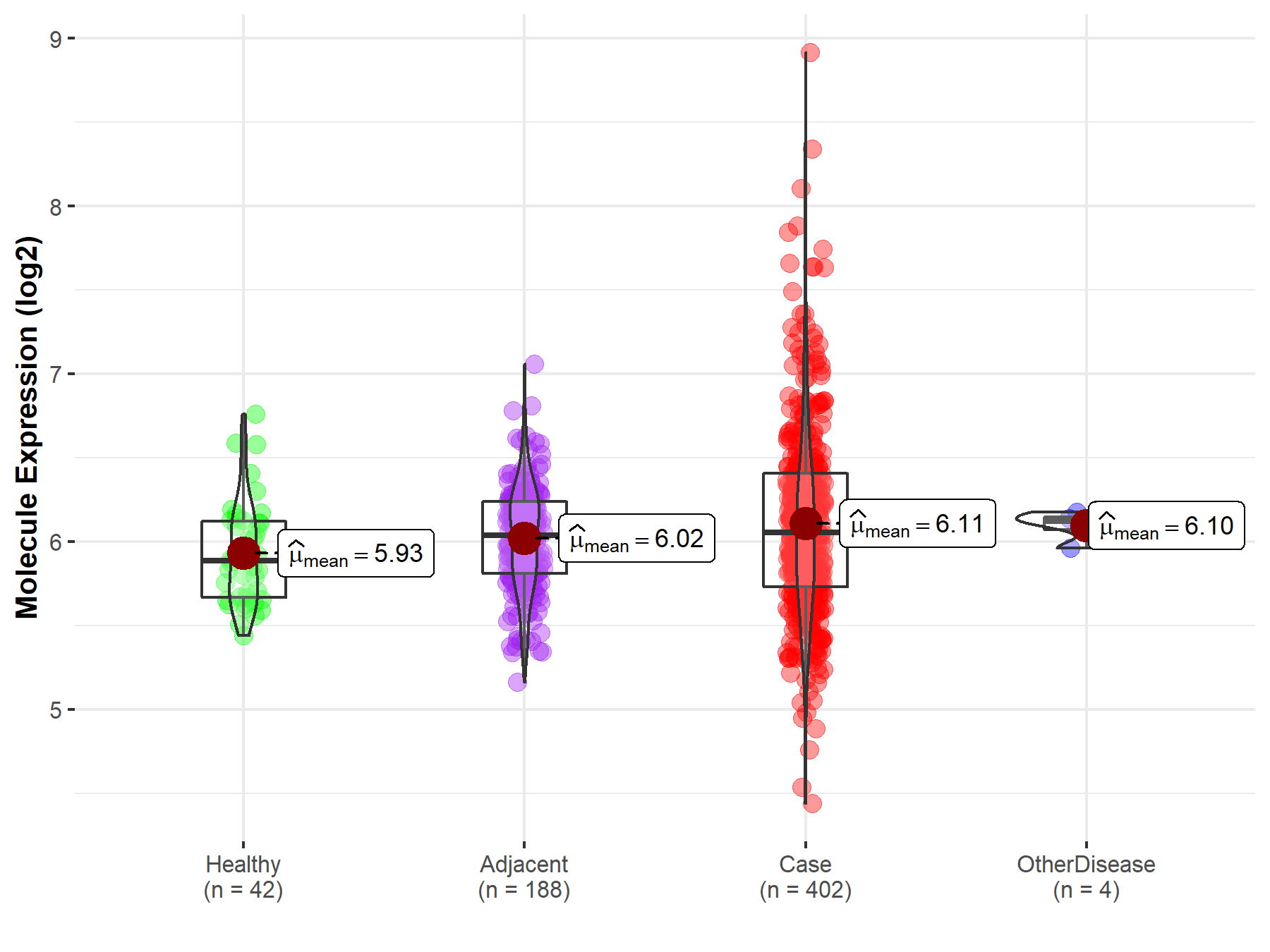
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.01E-57; Fold-change: 6.32E-01; Z-score: 1.22E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.68E-05; Fold-change: 4.34E-01; Z-score: 6.36E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
