Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00313)
| Name |
CX3C chemokine receptor 1 (CX3CR1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
C-X3-C CKR-1; CX3CR1; Beta chemokine receptor-like 1; CMK-BRL-1; CMK-BRL1; Fractalkine receptor; G-protein coupled receptor 13; V28; CMKBRL1; GPR13
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CX3CR1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr3:39263495-39281735[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MDQFPESVTENFEYDDLAEACYIGDIVVFGTVFLSIFYSVIFAIGLVGNLLVVFALTNSK
KPKSVTDIYLLNLALSDLLFVATLPFWTHYLINEKGLHNAMCKFTTAFFFIGFFGSIFFI TVISIDRYLAIVLAANSMNNRTVQHGVTISLGVWAAAILVAAPQFMFTKQKENECLGDYP EVLQEIWPVLRNVETNFLGFLLPLLIMSYCYFRIIQTLFSCKNHKKAKAIKLILLVVIVF FLFWTPYNVMIFLETLKLYDFFPSCDMRKDLRLALSVTETVAFSHCCLNPLIYAFAGEKF RRYLYHLYGKCLAVLCGRSVHVDFSSSESQRSRHGSVLSSNFTYHTSDGDALLLL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor for the C-X3-C chemokine fractalkine (CX3CL1) present on many early leukocyte cells; CX3CR1-CX3CL1 signaling exerts distinct functions in different tissue compartments, such as immune response, inflammation, cell adhesion and chemotaxis. CX3CR1-CX3CL1 signaling mediates cell migratory functions. Responsible for the recruitment of natural killer (NK) cells to inflamed tissues. Acts as a regulator of inflammation process leading to atherogenesis by mediating macrophage and monocyte recruitment to inflamed atherosclerotic plaques, promoting cell survival. Involved in airway inflammation by promoting interleukin 2-producing T helper (Th2) cell survival in inflamed lung. Involved in the migration of circulating monocytes to non-inflamed tissues, where they differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells. Acts as a negative regulator of angiogenesis, probably by promoting macrophage chemotaxis. Plays a key role in brain microglia by regulating inflammatory response in the central nervous system (CNS) and regulating synapse maturation. Required to restrain the microglial inflammatory response in the CNS and the resulting parenchymal damage in response to pathological stimuli. Involved in brain development by participating in synaptic pruning, a natural process during which brain microglia eliminates extra synapses during postnatal development. Synaptic pruning by microglia is required to promote the maturation of circuit connectivity during brain development. Acts as an important regulator of the gut microbiota by controlling immunity to intestinal bacteria and fungi. Expressed in lamina propria dendritic cells in the small intestine, which form transepithelial dendrites capable of taking up bacteria in order to provide defense against pathogenic bacteria. Required to initiate innate and adaptive immune responses against dissemination of commensal fungi (mycobiota) component of the gut: expressed in mononuclear phagocytes (MNPs) and acts by promoting induction of antifungal IgG antibodies response to confer protection against disseminated C.albicans or C.auris infection. Also acts as a receptor for C-C motif chemokine CCL26, inducing cell chemotaxis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.74E-47 Fold-change: -2.56E-01 Z-score: -1.79E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Calu3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0609 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| SPC-A1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6955 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| NCI-H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| D6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LAX cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LTEP-2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6929 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR296-3p inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation, enhance the drug resistance, and apoptosis. Data of luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that the CX3CR1 gene was a direct regulator of tumorsuppressive miR296-3p. Moreover, overexpressed CX3CR1 was confirmed in NSCLC clinical specimens. Inhibition of CX3CR1 could inhibit cancer cellular survival and increase chemotherapy sensitivity. There was a negative relationship between miR296-3p and CX3CR1 expression in NSCLC tissues. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Calu3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0609 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| SPC-A1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6955 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| NCI-H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| D6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LAX cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LTEP-2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6929 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR296-3p inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation, enhance the drug resistance, and apoptosis. Data of luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that the CX3CR1 gene was a direct regulator of tumorsuppressive miR296-3p. Moreover, overexpressed CX3CR1 was confirmed in NSCLC clinical specimens. Inhibition of CX3CR1 could inhibit cancer cellular survival and increase chemotherapy sensitivity. There was a negative relationship between miR296-3p and CX3CR1 expression in NSCLC tissues. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Calu3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0609 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| SPC-A1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6955 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| NCI-H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| D6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LAX cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LTEP-2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6929 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR296-3p inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation, enhance the drug resistance, and apoptosis. Data of luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that the CX3CR1 gene was a direct regulator of tumorsuppressive miR296-3p. Moreover, overexpressed CX3CR1 was confirmed in NSCLC clinical specimens. Inhibition of CX3CR1 could inhibit cancer cellular survival and increase chemotherapy sensitivity. There was a negative relationship between miR296-3p and CX3CR1 expression in NSCLC tissues. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.74E-47; Fold-change: -1.12E+00; Z-score: -1.57E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 9.55E-42; Fold-change: -1.26E+00; Z-score: -2.04E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
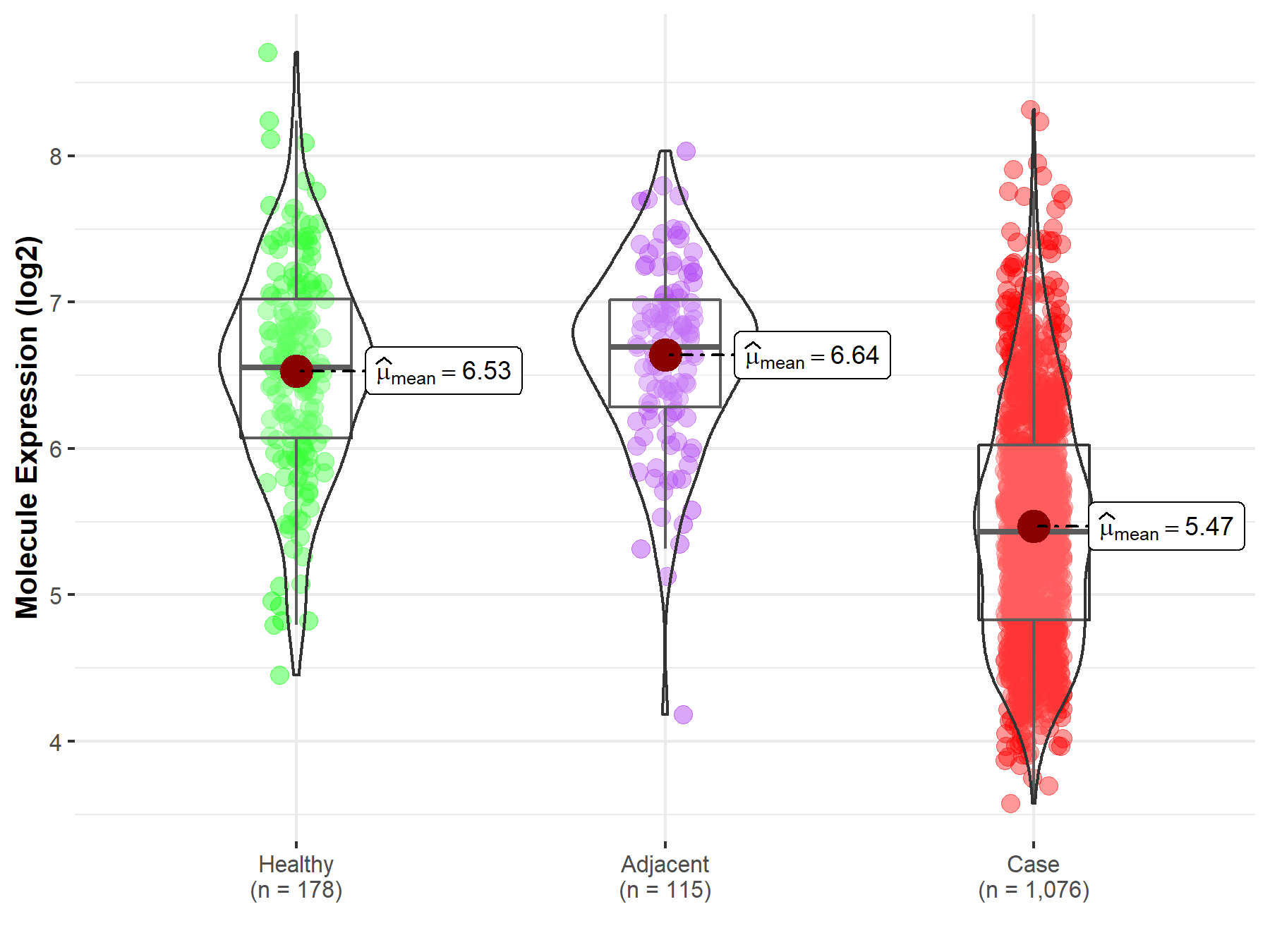
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
