Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00288)
| Name |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cell division protein kinase 8; Mediator complex subunit CDK8; Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit CDK8; Protein kinase K35
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CDK8
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr13:26254104-26405238[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MDYDFKVKLSSERERVEDLFEYEGCKVGRGTYGHVYKAKRKDGKDDKDYALKQIEGTGIS
MSACREIALLRELKHPNVISLQKVFLSHADRKVWLLFDYAEHDLWHIIKFHRASKANKKP VQLPRGMVKSLLYQILDGIHYLHANWVLHRDLKPANILVMGEGPERGRVKIADMGFARLF NSPLKPLADLDPVVVTFWYRAPELLLGARHYTKAIDIWAIGCIFAELLTSEPIFHCRQED IKTSNPYHHDQLDRIFNVMGFPADKDWEDIKKMPEHSTLMKDFRRNTYTNCSLIKYMEKH KVKPDSKAFHLLQKLLTMDPIKRITSEQAMQDPYFLEDPLPTSDVFAGCQIPYPKREFLT EEEPDDKGDKKNQQQQQGNNHTNGTGHPGNQDSSHTQGPPLKKVRVVPPTTTSGGLIMTS DYQRSNPHAAYPNPGPSTSQPQSSMGYSATSQQPPQYSHQTHRY Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in regulated gene transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional pre-initiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. Phosphorylates the CTD (C-terminal domain) of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAp II), which may inhibit the formation of a transcription initiation complex. Phosphorylates CCNH leading to down-regulation of the TFIIH complex and transcriptional repression. Recruited through interaction with MAML1 to hyperphosphorylate the intracellular domain of NOTCH, leading to its degradation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.61E-08 Fold-change: 5.12E-02 Z-score: 5.77E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| miR141-3p/CDk8 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05206 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-141-3p could restore the sensitivity to trastuzumab in breast cancer cells by repressing CDk8, which might regulate the phosphorylation levels of SMAD2/SMAD3 via TGF-beta. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The A549 cells transfected with miR-107 mimics were significantly more sensitive to the therapy of cisplatin than control cells. A549 cells Transfected with miR-107 mimics showed a decreased CDk8 protein expression. Down-regulation of CDk8 expression by siRNAs, A549 cells became more sensitive to the therapy of cisplatin. In addition, the (+) growth-inhibitory effect by the miR-107 mimic transfection was (+) after the addition of CDk8 siRNA. The present study provides the first evidence that miR-107 plays a key role in cisplatin resistance by targeting the CDk8 protein in NSCLC cell lines, suggesting that miR-107 can be used to predict a patient's response to chemotherapy as well as serve as a novel potential maker for NSCLC therapy. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.08E-37; Fold-change: 3.87E-01; Z-score: 1.30E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.40E-11; Fold-change: 2.53E-01; Z-score: 5.63E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
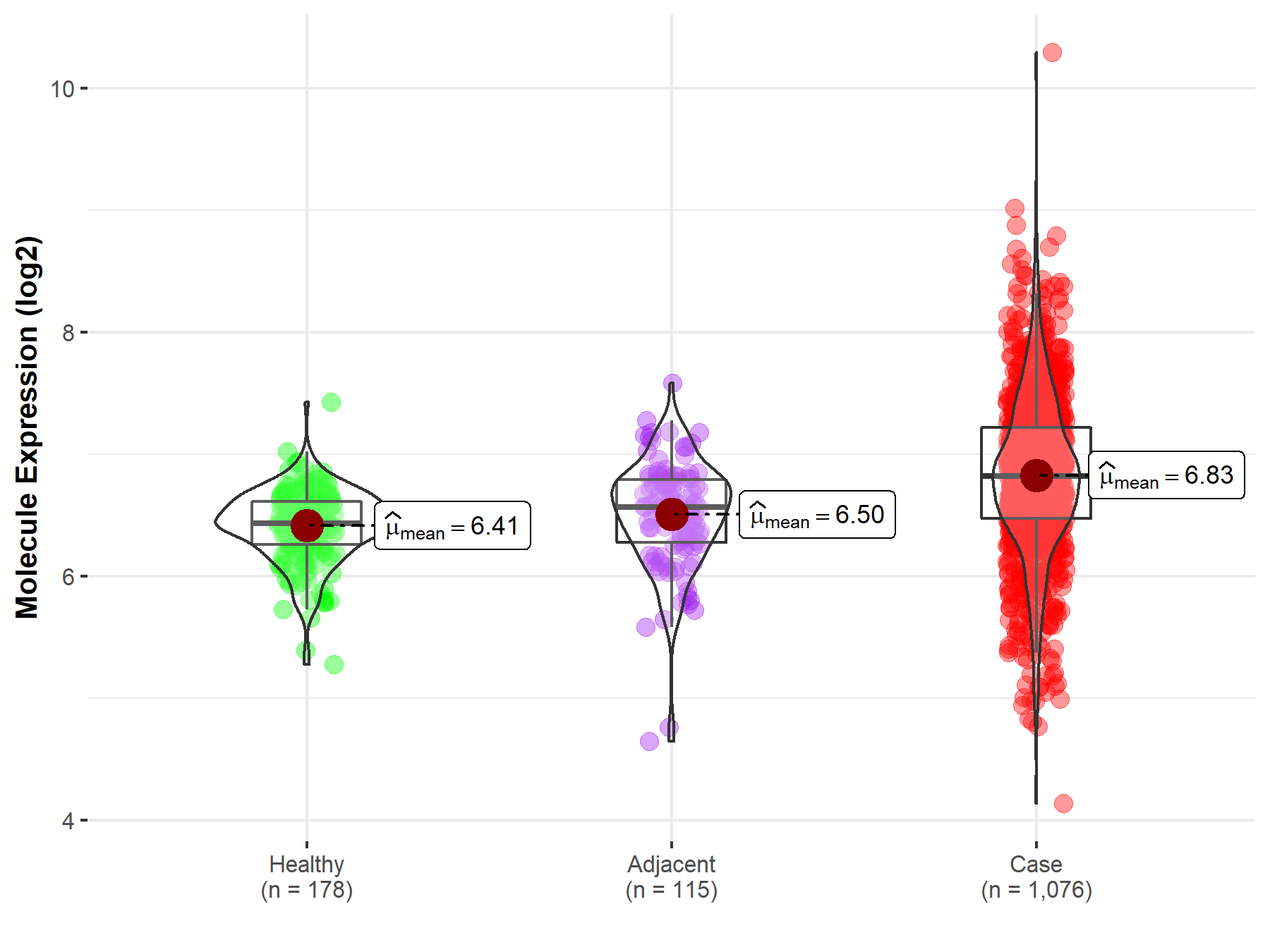
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.61E-08; Fold-change: 1.03E-01; Z-score: 1.63E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.90E-04; Fold-change: 2.47E-01; Z-score: 4.06E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
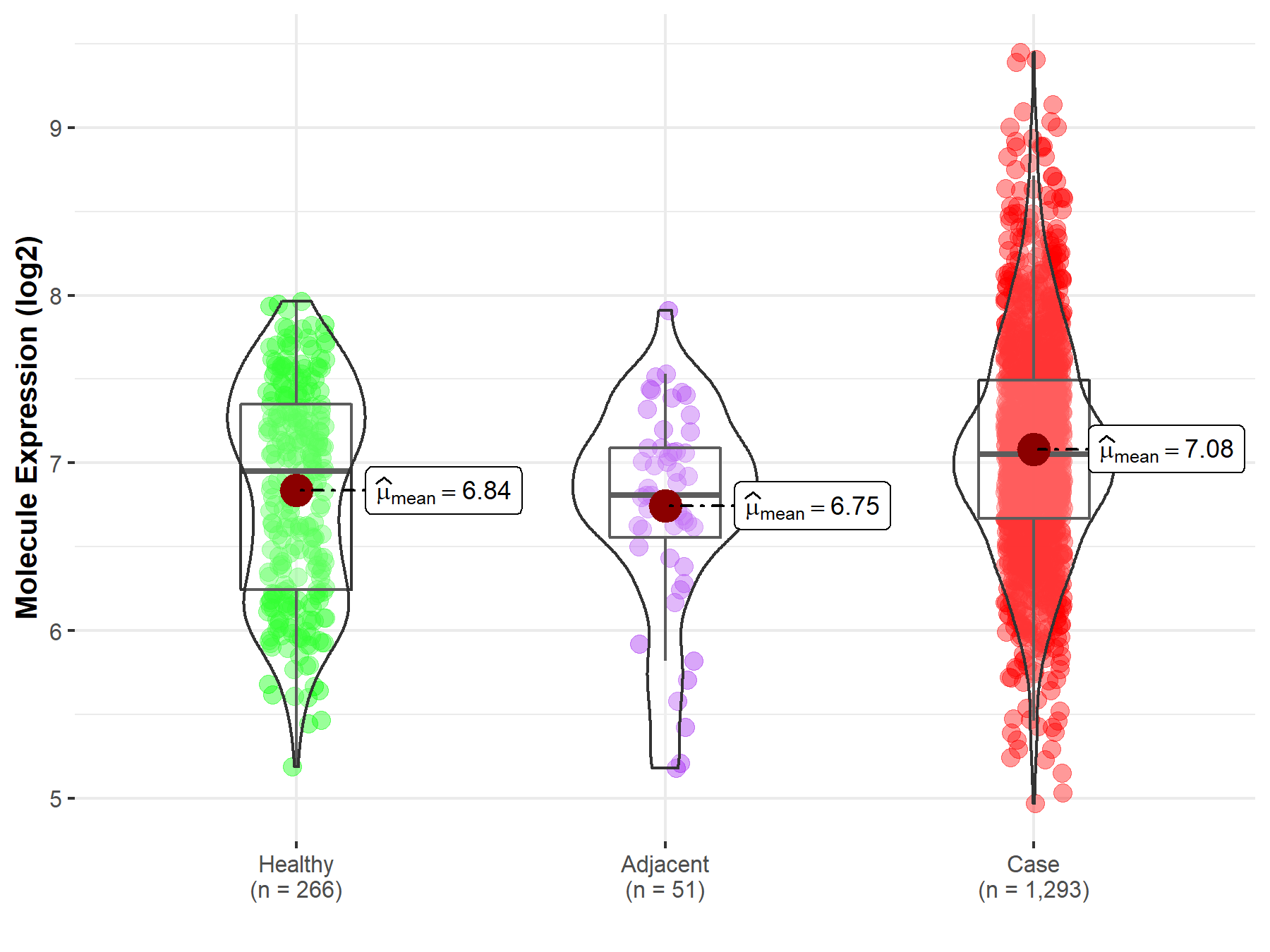
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

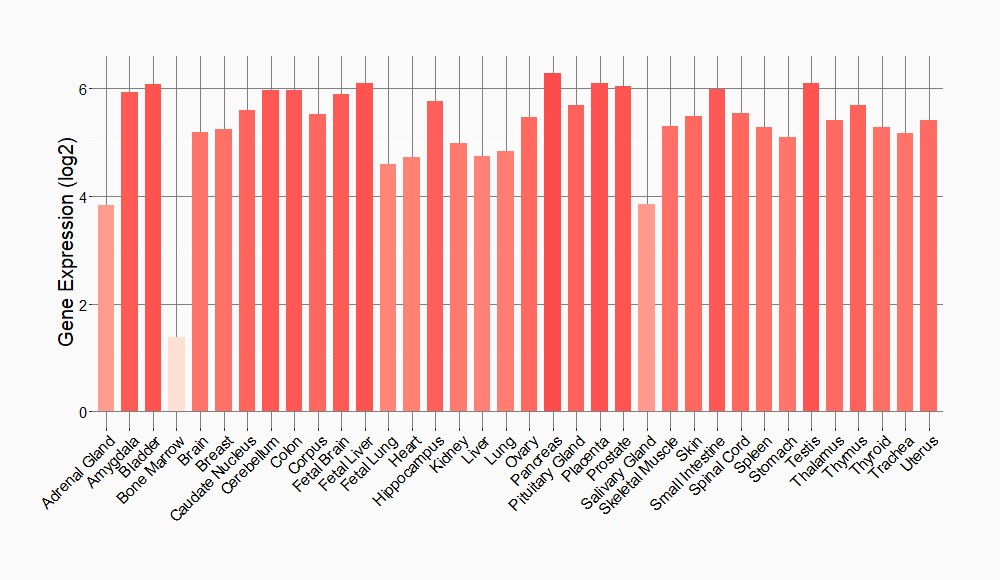
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
