Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00287)
| Name |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cell division protein kinase 2; p33 protein kinase; CDKN2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CDK2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr12:55966781-55972789[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MENFQKVEKIGEGTYGVVYKARNKLTGEVVALKKIRLDTETEGVPSTAIREISLLKELNH
PNIVKLLDVIHTENKLYLVFEFLHQDLKKFMDASALTGIPLPLIKSYLFQLLQGLAFCHS HRVLHRDLKPQNLLINTEGAIKLADFGLARAFGVPVRTYTHEVVTLWYRAPEILLGCKYY STAVDIWSLGCIFAEMVTRRALFPGDSEIDQLFRIFRTLGTPDEVVWPGVTSMPDYKPSF PKWARQDFSKVVPPLDEDGRSLLSQMLHYDPNKRISAKAALAHPFFQDVTKPVPHLRL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the control of the cell cycle; essential for meiosis, but dispensable for mitosis. Phosphorylates CTNNB1, USP37, p53/TP53, NPM1, CDK7, RB1, BRCA2, MYC, NPAT, EZH2. Triggers duplication of centrosomes and DNA. Acts at the G1-S transition to promote the E2F transcriptional program and the initiation of DNA synthesis, and modulates G2 progression; controls the timing of entry into mitosis/meiosis by controlling the subsequent activation of cyclin B/CDK1 by phosphorylation, and coordinates the activation of cyclin B/CDK1 at the centrosome and in the nucleus. Crucial role in orchestrating a fine balance between cellular proliferation, cell death, and DNA repair in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). Activity of CDK2 is maximal during S phase and G2; activated by interaction with cyclin E during the early stages of DNA synthesis to permit G1-S transition, and subsequently activated by cyclin A2 (cyclin A1 in germ cells) during the late stages of DNA replication to drive the transition from S phase to mitosis, the G2 phase. EZH2 phosphorylation promotes H3K27me3 maintenance and epigenetic gene silencing. Phosphorylates CABLES1. Cyclin E/CDK2 prevents oxidative stress-mediated Ras-induced senescence by phosphorylating MYC. Involved in G1-S phase DNA damage checkpoint that prevents cells with damaged DNA from initiating mitosis; regulates homologous recombination-dependent repair by phosphorylating BRCA2, this phosphorylation is low in S phase when recombination is active, but increases as cells progress towards mitosis. In response to DNA damage, double-strand break repair by homologous recombination a reduction of CDK2-mediated BRCA2 phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of RB1 disturbs its interaction with E2F1. NPM1 phosphorylation by cyclin E/CDK2 promotes its dissociates from unduplicated centrosomes, thus initiating centrosome duplication. Cyclin E/CDK2-mediated phosphorylation of NPAT at G1-S transition and until prophase stimulates the NPAT-mediated activation of histone gene transcription during S phase. Required for vitamin D-mediated growth inhibition by being itself inactivated. Involved in the nitric oxide- (NO) mediated signaling in a nitrosylation/activation-dependent manner. USP37 is activated by phosphorylation and thus triggers G1-S transition. CTNNB1 phosphorylation regulates insulin internalization. Phosphorylates FOXP3 and negatively regulates its transcriptional activity and protein stability. Phosphorylates CDK2AP2. Phosphorylates ERCC6 which is essential for its chromatin remodeling activity at DNA double-strand breaks.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| HeLa/DDP cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C869 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; EdU assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | UCA1 suppressed apoptosis by downregulating caspase 3 and upregulating CDk2, whereas enhanced cell proliferation by increased level of survivin and decreased level of p21. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.22E-07; Fold-change: 2.53E-01; Z-score: 7.45E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
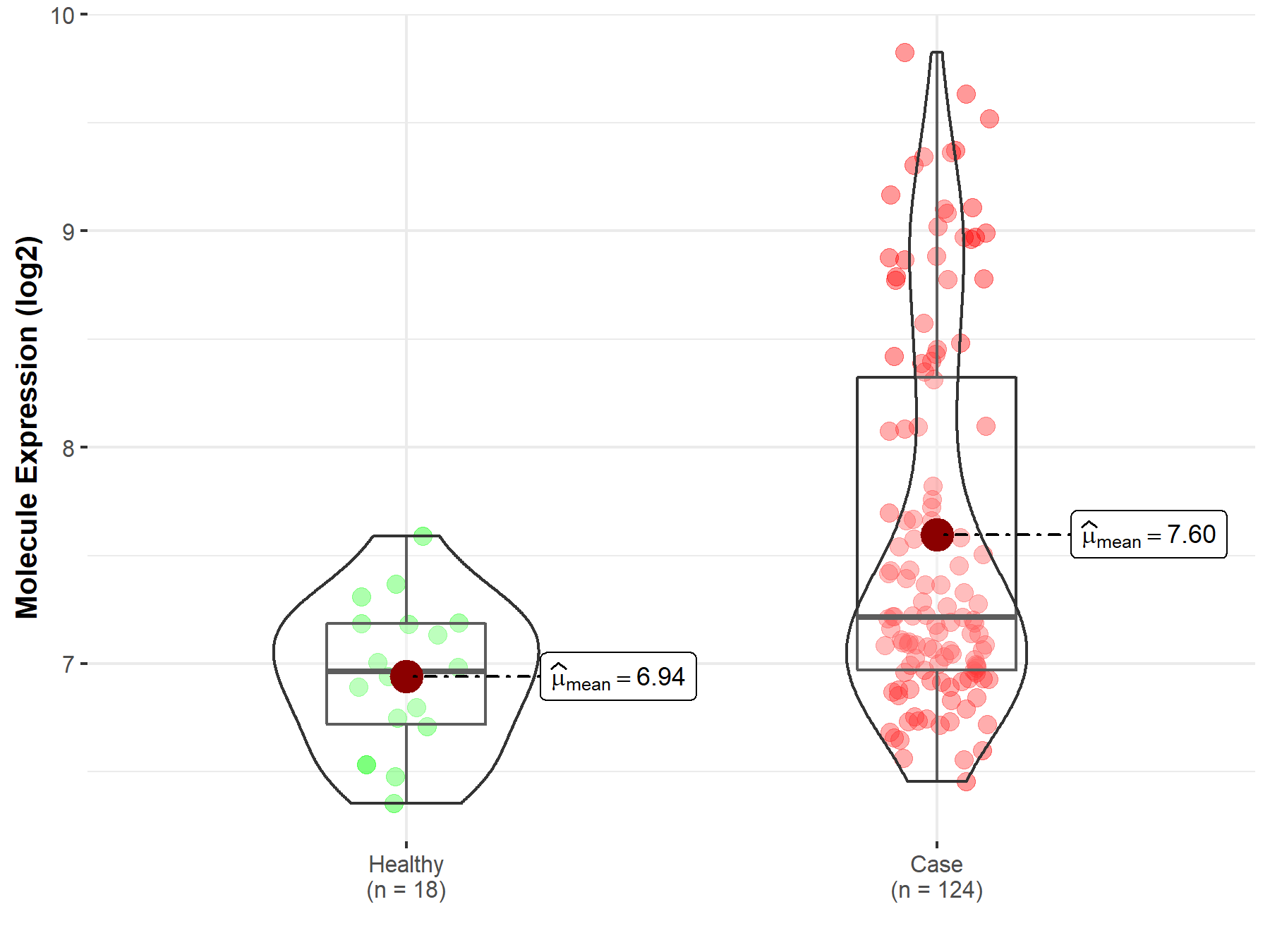
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

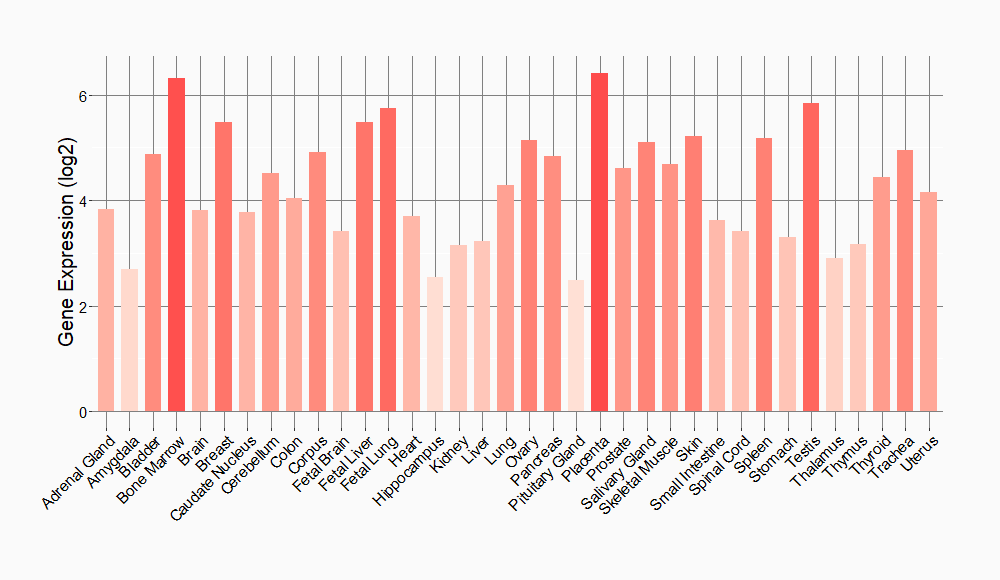
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
