Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00284)
| Name |
Extracellular matrix receptor III (CD44)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CD44
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr11:35138882-35232402[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MDKFWWHAAWGLCLVPLSLAQIDLNITCRFAGVFHVEKNGRYSISRTEAADLCKAFNSTL
PTMAQMEKALSIGFETCRYGFIEGHVVIPRIHPNSICAANNTGVYILTSNTSQYDTYCFN ASAPPEEDCTSVTDLPNAFDGPITITIVNRDGTRYVQKGEYRTNPEDIYPSNPTDDDVSS GSSSERSSTSGGYIFYTFSTVHPIPDEDSPWITDSTDRIPATTLMSTSATATETATKRQE TWDWFSWLFLPSESKNHLHTTTQMAGTSSNTISAGWEPNEENEDERDRHLSFSGSGIDDD EDFISSTISTTPRAFDHTKQNQDWTQWNPSHSNPEVLLQTTTRMTDVDRNGTTAYEGNWN PEAHPPLIHHEHHEEEETPHSTSTIQATPSSTTEETATQKEQWFGNRWHEGYRQTPKEDS HSTTGTAAASAHTSHPMQGRTTPSPEDSSWTDFFNPISHPMGRGHQAGRRMDMDSSHSIT LQPTANPNTGLVEDLDRTGPLSMTTQQSNSQSFSTSHEGLEEDKDHPTTSTLTSSNRNDV TGGRRDPNHSEGSTTLLEGYTSHYPHTKESRTFIPVTSAKTGSFGVTAVTVGDSNSNVNR SLSGDQDTFHPSGGSHTTHGSESDGHSHGSQEGGANTTSGPIRTPQIPEWLIILASLLAL ALILAVCIAVNSRRRCGQKKKLVINSGNGAVEDRKPSGLNGEASKSQEMVHLVNKESSET PDQFMTADETRNLQNVDMKIGV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Cell-surface receptor that plays a role in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration, helping them to sense and respond to changes in the tissue microenvironment. Participates thereby in a wide variety of cellular functions including the activation, recirculation and homing of T-lymphocytes, hematopoiesis, inflammation and response to bacterial infection. Engages, through its ectodomain, extracellular matrix components such as hyaluronan/HA, collagen, growth factors, cytokines or proteases and serves as a platform for signal transduction by assembling, via its cytoplasmic domain, protein complexes containing receptor kinases and membrane proteases. Such effectors include PKN2, the RhoGTPases RAC1 and RHOA, Rho-kinases and phospholipase C that coordinate signaling pathways promoting calcium mobilization and actin-mediated cytoskeleton reorganization essential for cell migration and adhesion.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.11E-07 Fold-change: -3.65E-01 Z-score: -5.35E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| HLE cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1281 | |
| HLF cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2947 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | There is an inverse correlation between the expression of miR-199a-3p and CD44 protein. Transfection of miR-199a-3p into SNU449 cells reduced in vitro invasion and sensitized the cells to doxorubicin. Inhibition of CD44 in CD44+ HCC cell lines using antisense oligonucleotides increased apoptosis, enhanced chemosensitivity, reduced tumorigensis and invasion. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 |
| KHOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2546 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CD44 was overexpressed in metastatic and recurrent osteosarcoma as compared with primary tumors. Higher expression of CD44 was found in both patients with shorter survival and patients who exhibited unfavorable response to chemotherapy before surgical resection. Additionally, the 3'-untranslated region of CD44 mRNA was the direct target of microRNA-199a-3p (miR-199a-3p). Overexpression of miR-199a-3p significantly inhibited CD44 expression in osteosarcoma cells. miR-199a-3p is One of the most dramatically decreased miRs in osteosarcoma cells and tumor tissues as compared with normal osteoblast cells. Transfection of miR-199a-3p significantly increased the drug sensitivity through down-regulation of CD44 in osteosarcoma cells. Taken together, these results suggest that the CD44-miR-199a-3p axis plays an important role in the development of metastasis, recurrence, and drug resistance of osteosarcoma. Developing strategies to target CD44 may improve the clinical outcome of osteosarcoma. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | CD44+/CD117+ ovarian CICs cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CD44 plays an important role in cellular adhesion, lymphocyte activation/migration, tumorigenesis, and the formation of metastases, endogenous mature miR-199a may prevent the growth of human ovarian CICs via decreasing the expression of CD44. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Leiomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B58.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leiomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B58.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Spheroid formation | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SK-UT-1 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0533 |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c-nu female mice | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; Transwell migration and invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression levels of CSC-related markers in CD133+ subpopulation derived from SK-UT-1 cells, Western blotting was employed to detect the expression levels of CD44, ALDH1, BMI1, and Nanog. Expectedly, researchers found that CD133+subpopulation had higher expression levels of CD44, ALDH1, BMI1, and Nanog compared with those of CD133 subpopulation. Collectively, the above-mentioned results suggested that CD133+ subpopulation derived from SK-UT-1 cells possessed capabilities of resistance to apoptosis after treatment with DXR, as well as stemness feature of cancer stem-like cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Leiomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B58.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leiomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B58.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Spheroid formation | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SK-UT-1 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0533 |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c-nu female mice | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; Transwell migration and invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression levels of CSC-related markers in CD133+ subpopulation derived from SK-UT-1 cells, Western blotting was employed to detect the expression levels of CD44, ALDH1, BMI1, and Nanog. Expectedly, researchers found that CD133+subpopulation had higher expression levels of CD44, ALDH1, BMI1, and Nanog compared with those of CD133 subpopulation. Collectively, the above-mentioned results suggested that CD133+ subpopulation derived from SK-UT-1 cells possessed capabilities of resistance to apoptosis after treatment with DXR, as well as stemness feature of cancer stem-like cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.62E-01 Fold-change: 1.66E-01 Z-score: 1.54E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-145 exerts tumor-suppressive and chemo-resistance lowering effects by targeting CD44 in gastric cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-145 exerts tumor-suppressive and chemo-resistance lowering effects by targeting CD44 in gastric cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | 5637 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0126 |
| J82 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0359 | |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HT1376 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1292 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumorigenicity in nude mice | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cisplatin-based chemotherapy induced demethylation of miR-34a promoter and increased miR-34a expression, which in turn sensitized MIBC cells to cisplatin and decreased the tumorigenicity and proliferation of cancer cells that by reducing the production of CD44. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | CD44+/CD117+ ovarian CICs cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CD44 plays an important role in cellular adhesion, lymphocyte activation/migration, tumorigenesis, and the formation of metastases, endogenous mature miR-199a may prevent the growth of human ovarian CICs via decreasing the expression of CD44. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | CD44+/CD117+ ovarian CICs cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CD44 plays an important role in cellular adhesion, lymphocyte activation/migration, tumorigenesis, and the formation of metastases, endogenous mature miR-199a may prevent the growth of human ovarian CICs via decreasing the expression of CD44. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | GES-1 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EQ22 |
| SGC7901/VCR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU58 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Wound healing and transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR647 sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy in vivo by reducing the expression levels of ANk2, FAk, MMP2, MMP12, CD44 and SNAIL1. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.62E-01; Fold-change: 8.01E-01; Z-score: 8.18E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 9.88E-03; Fold-change: 3.04E-01; Z-score: 4.17E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
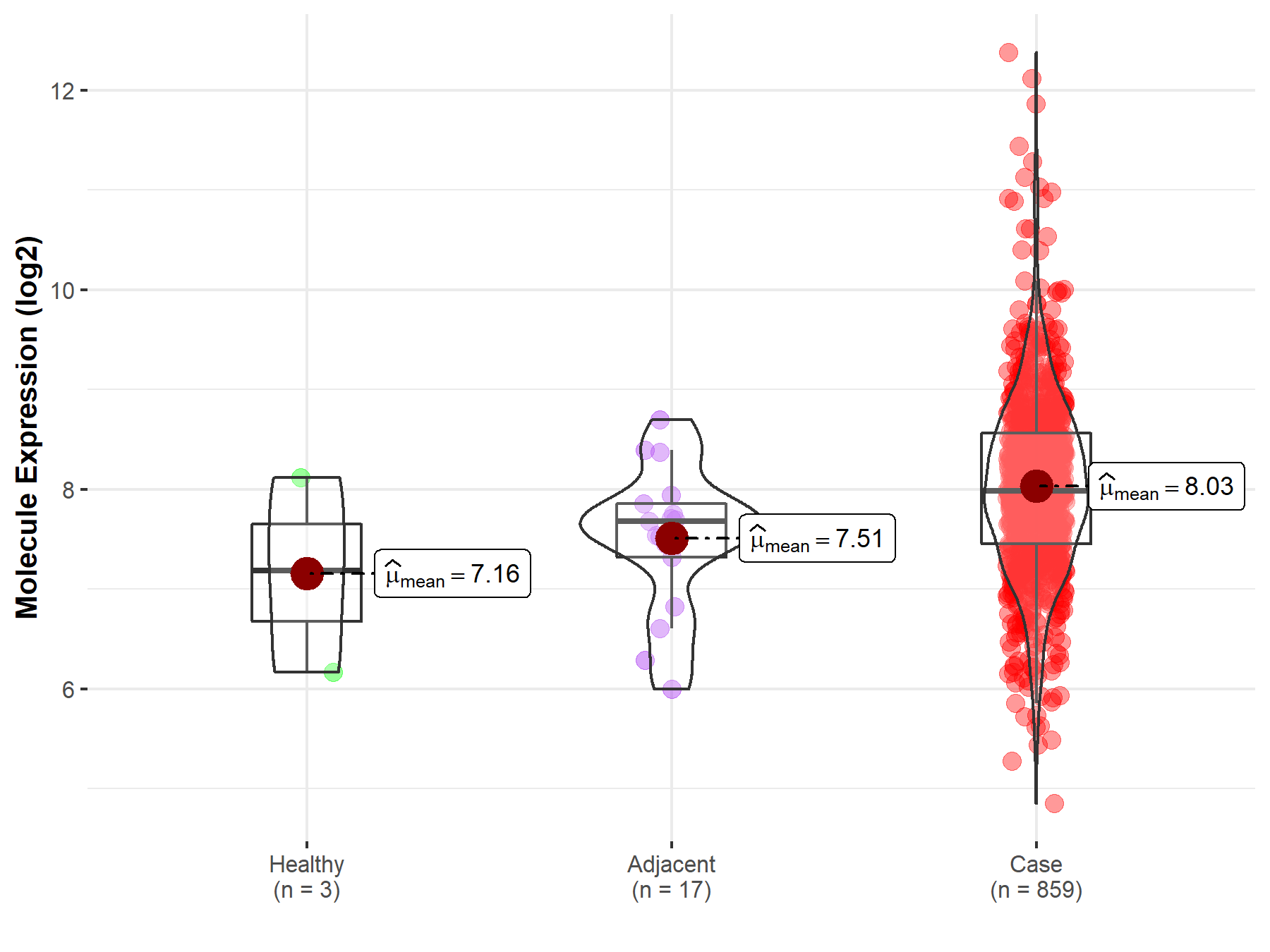
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.17E-06; Fold-change: 2.17E-01; Z-score: 5.12E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.39E-03; Fold-change: -3.65E-02; Z-score: -6.87E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 3.89E-01; Fold-change: -1.01E-01; Z-score: -2.71E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
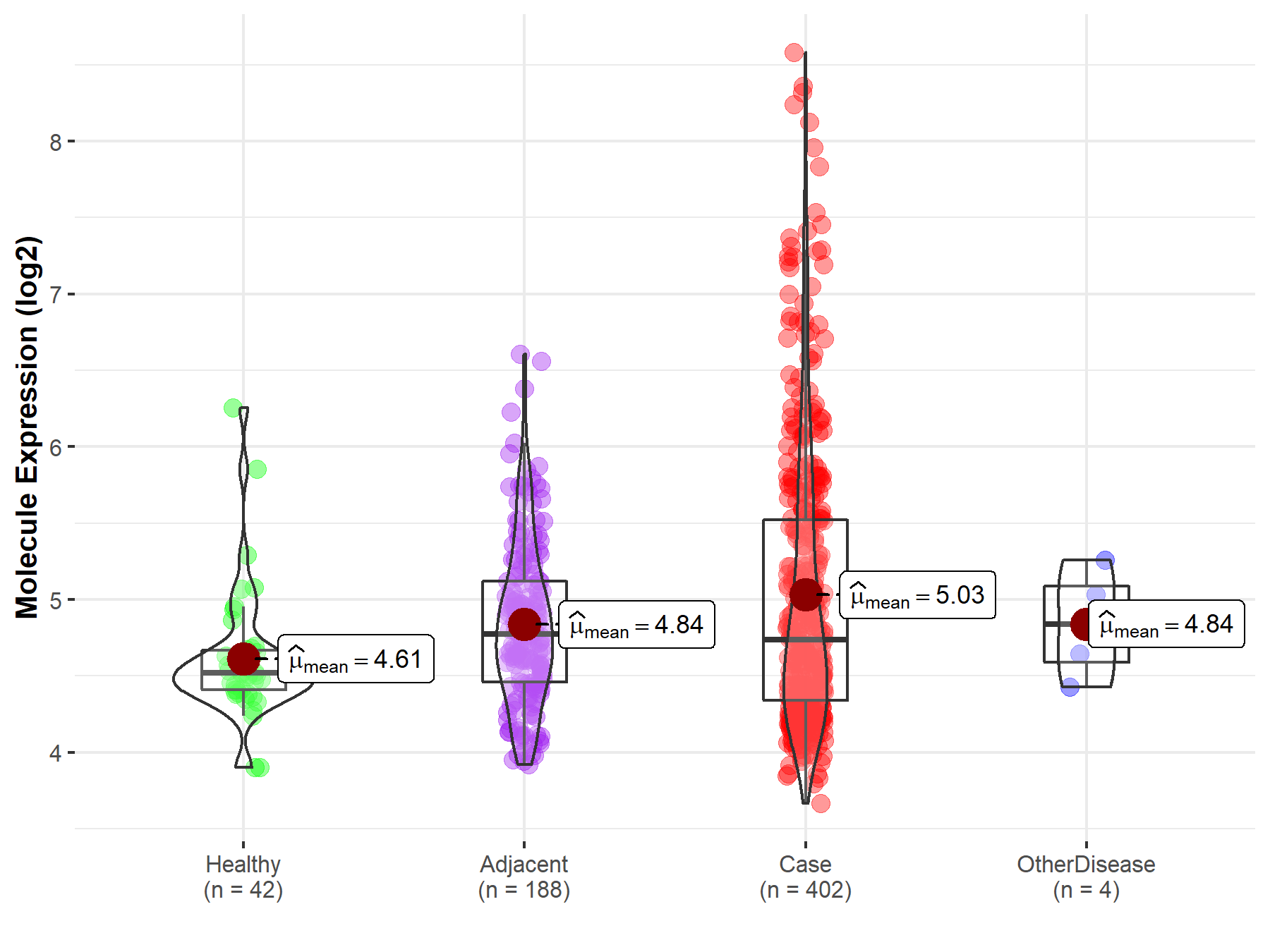
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.65E-02; Fold-change: 1.04E+00; Z-score: 1.22E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.31E-02; Fold-change: 2.33E-02; Z-score: 1.15E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
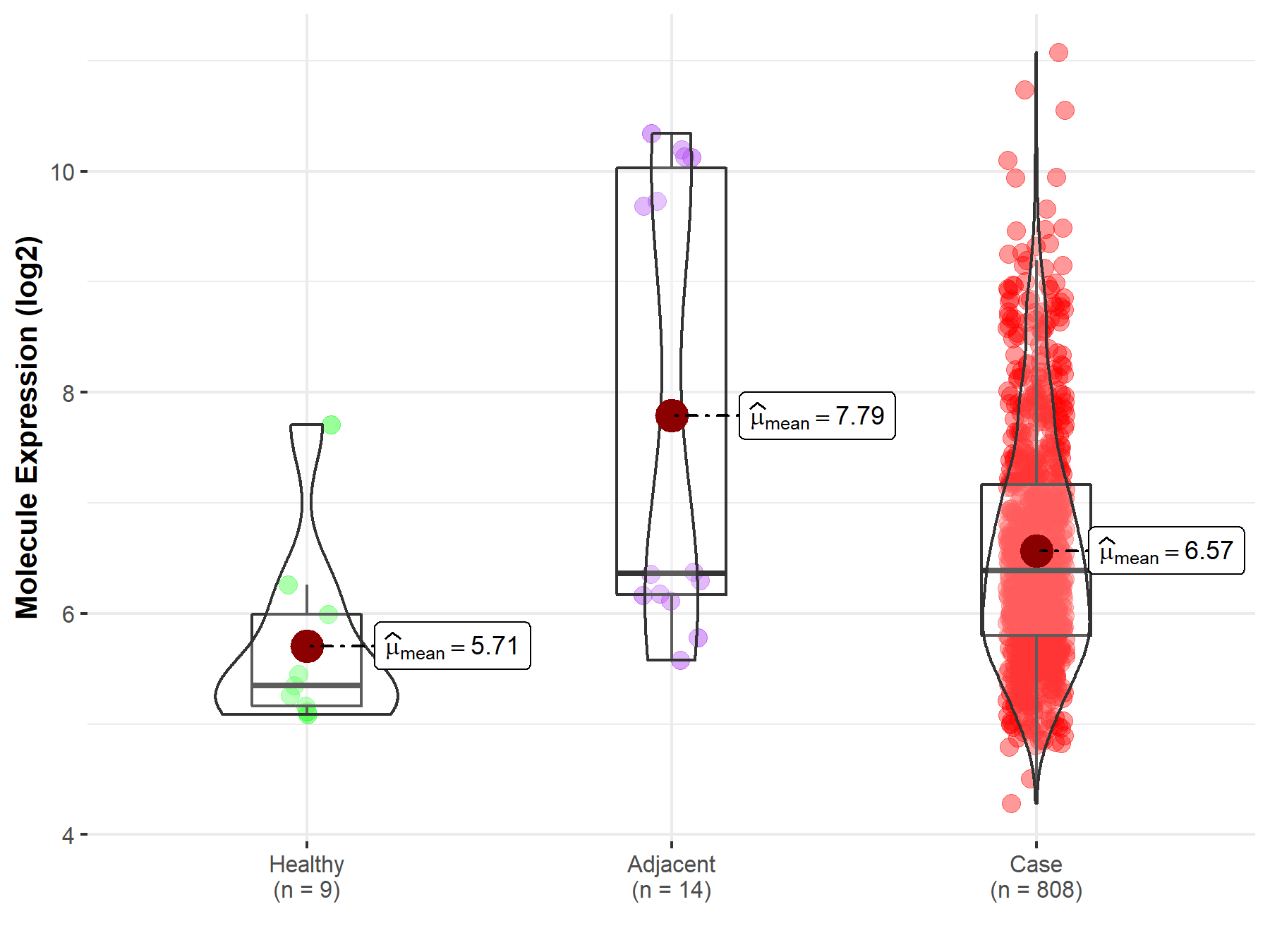
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.32E-05; Fold-change: -6.87E-01; Z-score: -3.49E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

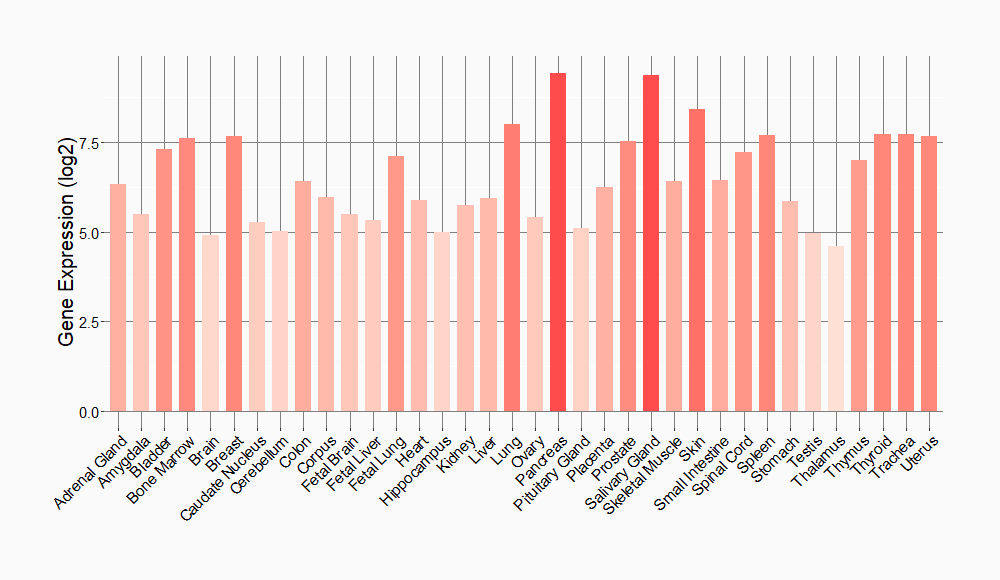
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
