Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00283)
| Name |
CD166 antigen (ALCAM)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ALCAM
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr3:105366909-105576900[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MESKGASSCRLLFCLLISATVFRPGLGWYTVNSAYGDTIIIPCRLDVPQNLMFGKWKYEK
PDGSPVFIAFRSSTKKSVQYDDVPEYKDRLNLSENYTLSISNARISDEKRFVCMLVTEDN VFEAPTIVKVFKQPSKPEIVSKALFLETEQLKKLGDCISEDSYPDGNITWYRNGKVLHPL EGAVVIIFKKEMDPVTQLYTMTSTLEYKTTKADIQMPFTCSVTYYGPSGQKTIHSEQAVF DIYYPTEQVTIQVLPPKNAIKEGDNITLKCLGNGNPPPEEFLFYLPGQPEGIRSSNTYTL TDVRRNATGDYKCSLIDKKSMIASTAITVHYLDLSLNPSGEVTRQIGDALPVSCTISASR NATVVWMKDNIRLRSSPSFSSLHYQDAGNYVCETALQEVEGLKKRESLTLIVEGKPQIKM TKKTDPSGLSKTIICHVEGFPKPAIQWTITGSGSVINQTEESPYINGRYYSKIIISPEEN VTLTCTAENQLERTVNSLNVSAISIPEHDEADEISDENREKVNDQAKLIVGIVVGLLLAA LVAGVVYWLYMKKSKTASKHVNKDLGNMEENKKLEENNHKTEA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Cell adhesion molecule that mediates both heterotypic cell-cell contacts via its interaction with CD6, as well as homotypic cell-cell contacts. Promotes T-cell activation and proliferation via its interactions with CD6. Contributes to the formation and maturation of the immunological synapse via its interactions with CD6. Mediates homotypic interactions with cells that express ALCAM. Acts as a ligand for the LILRB4 receptor, enhancing LILRB4-mediated inhibition of T cell proliferation. Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow. Mediates attachment of dendritic cells onto endothelial cells via homotypic interaction. Inhibits endothelial cell migration and promotes endothelial tube formation via homotypic interactions. Required for normal organization of the lymph vessel network. Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow. Plays a role in hematopoiesis; required for normal numbers of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Promotes in vitro osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Promotes neurite extension, axon growth and axon guidance; axons grow preferentially on surfaces that contain ALCAM. Mediates outgrowth and pathfinding for retinal ganglion cell axons.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Dual luciferase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR148a and miR152 reduce tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer via downregulating ALCAM. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.53E-11; Fold-change: 5.20E-01; Z-score: 4.64E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.13E-03; Fold-change: 5.79E-01; Z-score: 4.64E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
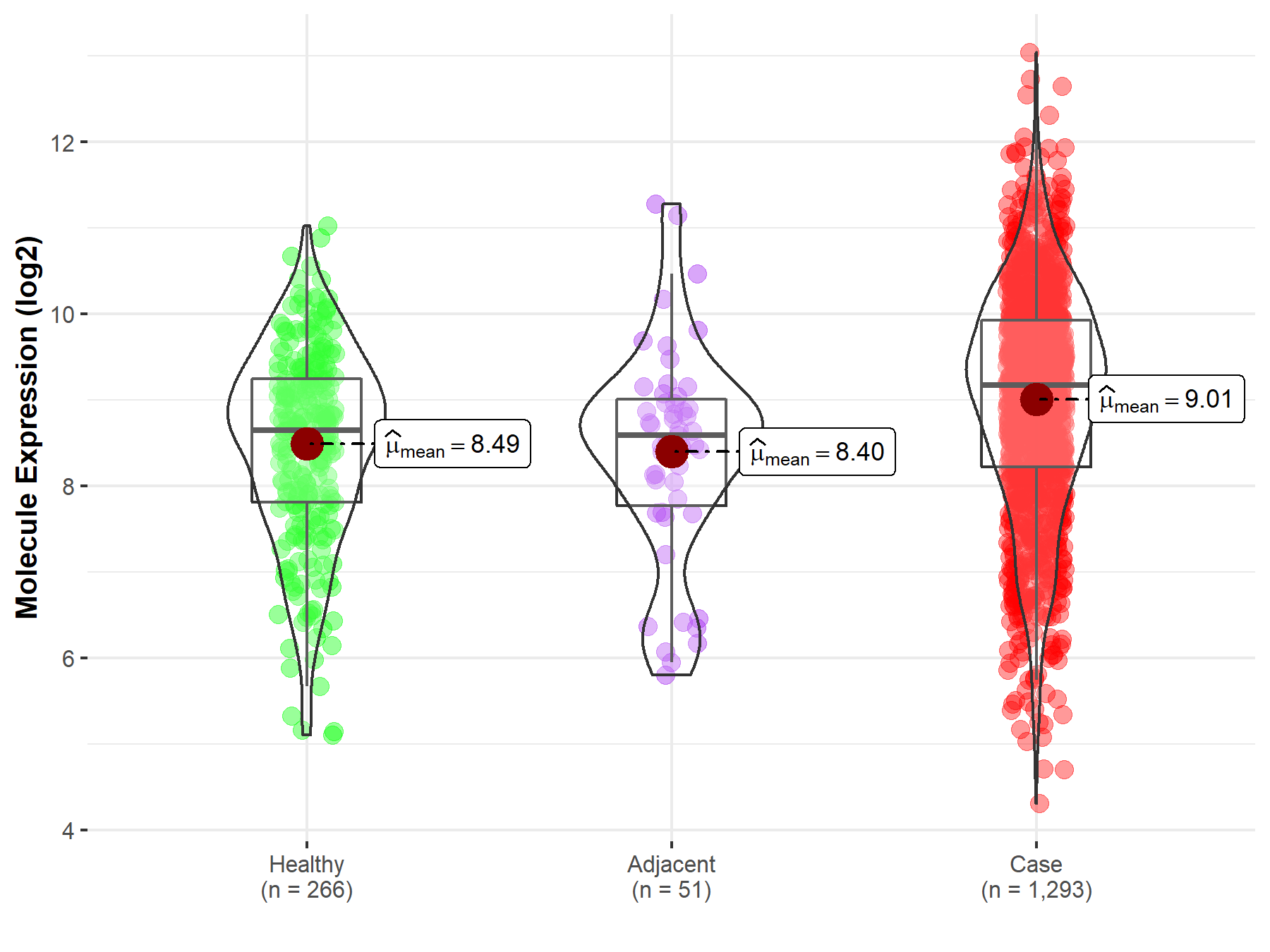
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

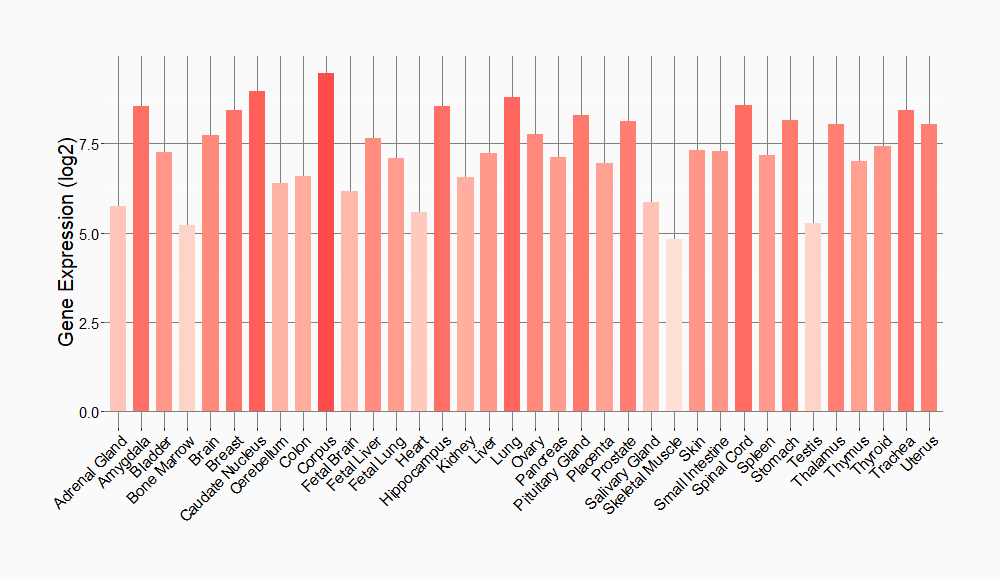
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
