Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00203)
| Name |
Mth938 domain-containing protein (AAMDC)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Adipogenesis associated Mth938 domain-containing protein; C11orf67; PTD015
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
AAMDC
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr11:77821109-77918432[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MTSPEIASLSWGQMKVKGSNTTYKDCKVWPGGSRTWDWRETGTEHSPGVQPADVKEVVEK
GVQTLVIGRGMSEALKVPSSTVEYLKKHGIDVRVLQTEQAVKEYNALVAQGVRVGGVFHS TC Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
May play a role in preadipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Everolimus | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| BT549 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | |
| MCF-12A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3744 | |
| SUM159 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5423 | |
| SUM44PE cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3424 | |
| SUM52PE cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3425 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/cJ Foxn1/Arc nude mice xenografts model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo 2.0 luminescence assay protocol assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High AAMDC expression is associated with sensitization to dactolisib and everolimus, and these PI3k-mTOR inhibitors exhibit synergistic interactions with anti-estrogens in IntClust2 models. Ectopic AAMDC expression is sufficient to activate AkT signaling, resulting in estrogen-independent tumor growth. Thus, AAMDC-overexpressing tumors may be sensitive to PI3k-mTORC1 blockers in combination with anti-estrogens. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.20E-04; Fold-change: -1.60E-01; Z-score: -2.73E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.77E-03; Fold-change: -2.50E-01; Z-score: -6.95E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
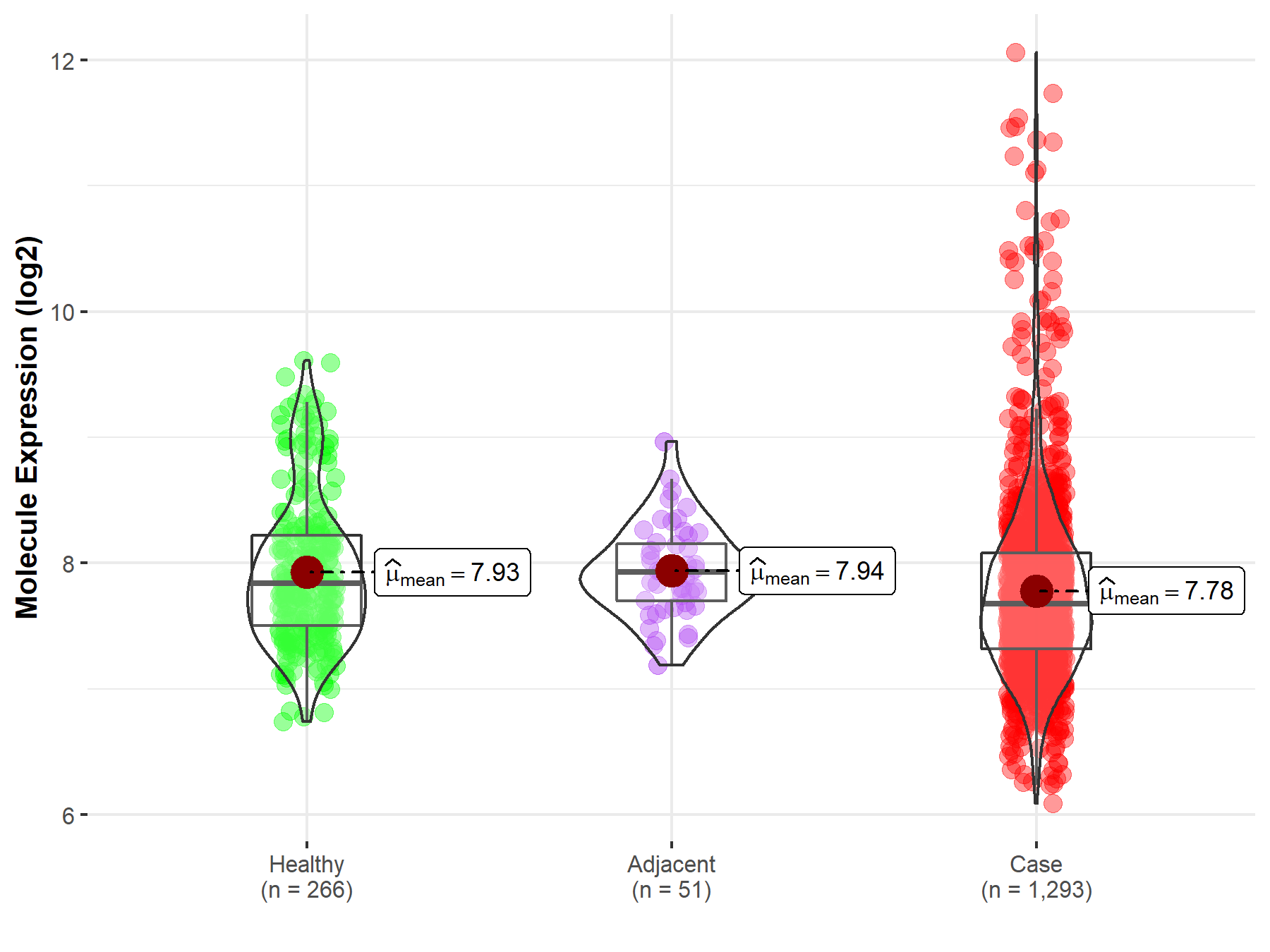
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
