Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00188)
| Name |
Tripartite motif-containing protein 16 (TRIM16)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM16; Estrogen-responsive B box protein; EBBP
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
TRIM16
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr17:15627960-15684311[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAELDLMAPGPLPRATAQPPAPLSPDSGSPSPDSGSASPVEEEDVGSSEKLGRETEEQDS
DSAEQGDPAGEGKEVLCDFCLDDTRRVKAVKSCLTCMVNYCEEHLQPHQVNIKLQSHLLT EPVKDHNWRYCPAHHSPLSAFCCPDQQCICQDCCQEHSGHTIVSLDAARRDKEAELQCTQ LDLERKLKLNENAISRLQANQKSVLVSVSEVKAVAEMQFGELLAAVRKAQANVMLFLEEK EQAALSQANGIKAHLEYRSAEMEKSKQELERMAAISNTVQFLEEYCKFKNTEDITFPSVY VGLKDKLSGIRKVITESTVHLIQLLENYKKKLQEFSKEEEYDIRTQVSAVVQRKYWTSKP EPSTREQFLQYAYDITFDPDTAHKYLRLQEENRKVTNTTPWEHPYPDLPSRFLHWRQVLS QQSLYLHRYYFEVEIFGAGTYVGLTCKGIDRKGEERNSCISGNNFSWSLQWNGKEFTAWY SDMETPLKAGPFRRLGVYIDFPGGILSFYGVEYDTMTLVHKFACKFSEPVYAAFWLSKKE NAIRIVDLGEEPEKPAPSLVGTAP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays an essential role in the organization of autophagic response and ubiquitination upon lysosomal and phagosomal damages. Plays a role in the stress-induced biogenesis and degradation of protein aggresomes by regulating the p62-KEAP1-NRF2 signaling and particularly by modulating the ubiquitination levels and thus stability of NRF2. Acts as a scaffold protein and facilitates autophagic degradation of protein aggregates by interacting with p62/SQSTM, ATG16L1 and LC3B/MAP1LC3B. In turn, protects the cell against oxidative stress-induced cell death as a consequence of endomembrane damage.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.34E-02 Fold-change: -1.04E-01 Z-score: -2.04E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04630 | ||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| H4006 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| NCI-H1650 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1483 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual-Luciferase activity assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR135 acted as a tumor promoter, and its suppression could improve sensitivity to gefitinib by targeting TRIM16 and inhibition of the JAk/STAT pathway. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.27E-16; Fold-change: 1.14E-01; Z-score: 2.27E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.90E-03; Fold-change: -9.95E-02; Z-score: -1.63E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
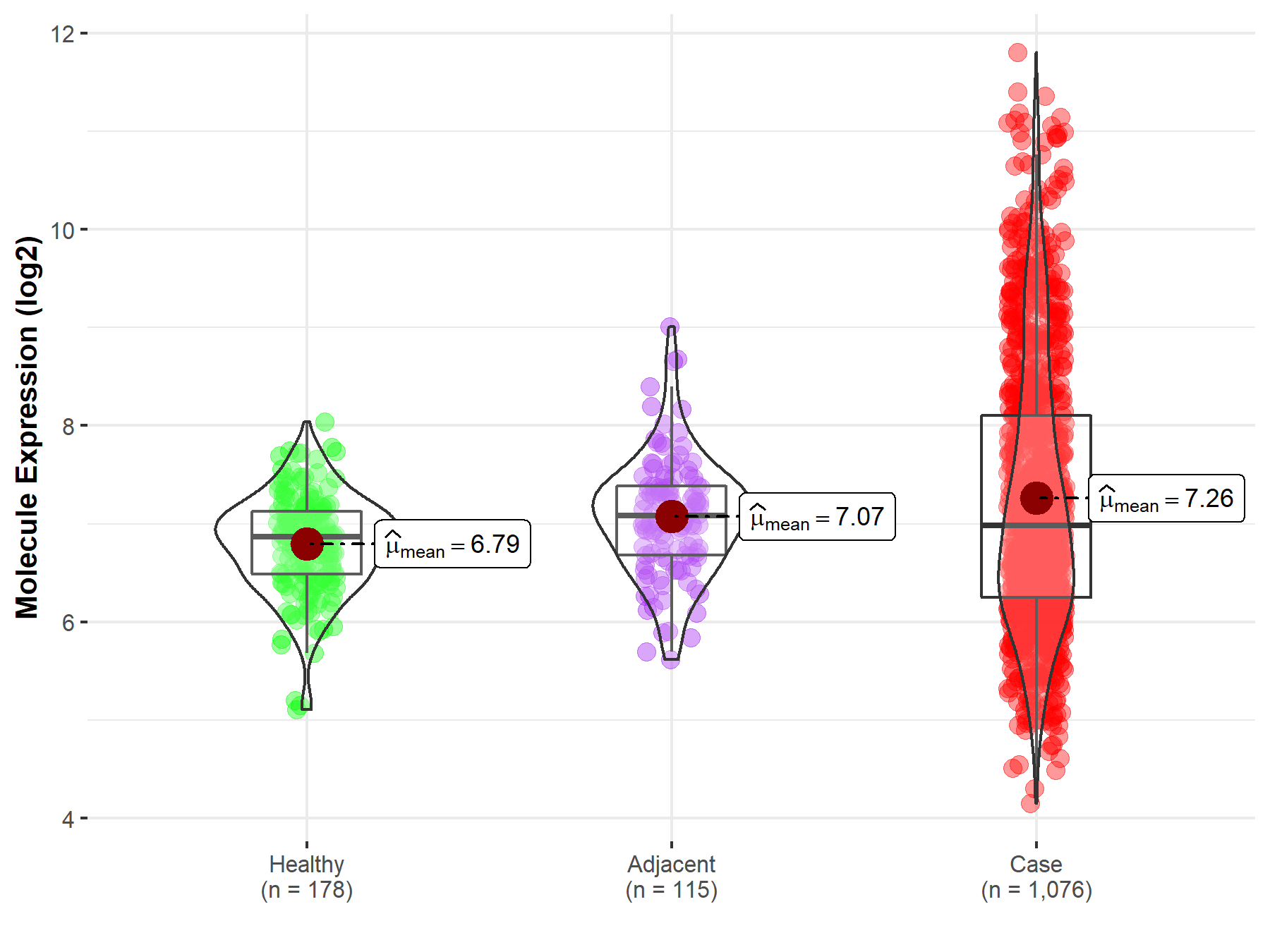
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

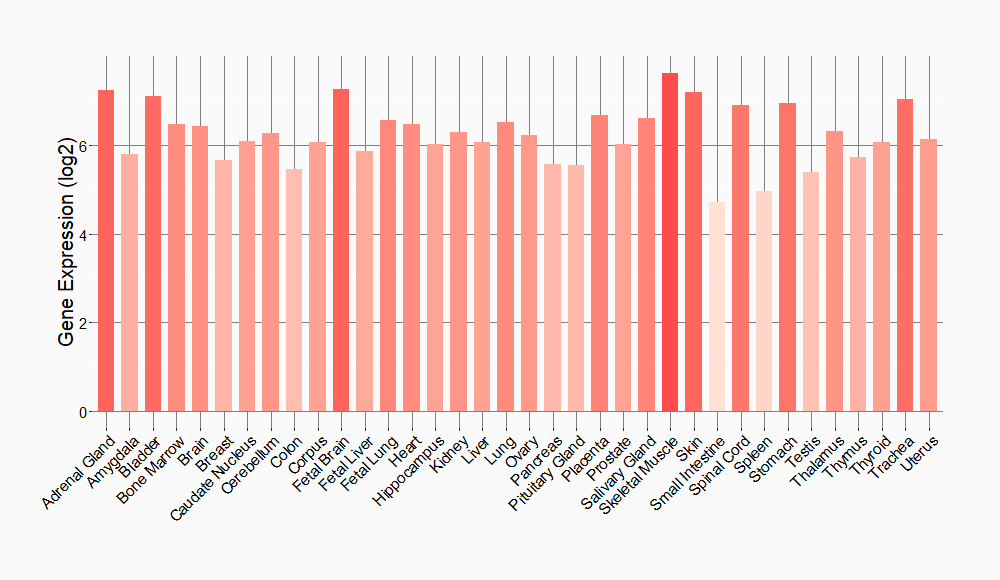
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
