Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00175)
| Name |
Tumor protein p53-inducible nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Stress-induced protein; p53-dependent damage-inducible nuclear protein 1; p53DINP1; P53DINP1; SIP
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
TP53INP1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:94925972-94949378[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MFQRLNKMFVGEVSSSSNQEPEFNEKEDDEWILVDFIDTCTGFSAEEEEEEEDISEESPT
EHPSVFSCLPASLECLADTSDSCFLQFESCPMEESWFITPPPCFTAGGLTTIKVETSPME NLLIEHPSMSVYAVHNSCPGLSEATRGTDELHSPSSPRVEAQNEMGQHIHCYVAALAAHT TFLEQPKSFRPSQWIKEHSERQPLNRNSLRRQNLTRDCHPRQVKHNGWVVHQPCPRQYNY Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic protein involved in cell stress response which acts as a dual regulator of transcription and autophagy. Acts as a positive regulator of autophagy. In response to cellular stress or activation of autophagy, relocates to autophagosomes where it interacts with autophagosome-associated proteins GABARAP, GABARAPL1/L2, MAP1LC3A/B/C and regulates autophagy. Acts as an antioxidant and plays a major role in p53/TP53-driven oxidative stress response. Possesses both a p53/TP53-independent intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulatory function and a p53/TP53-dependent transcription regulatory function. Positively regulates p53/TP53 and p73/TP73 and stimulates their capacity to induce apoptosis and regulate cell cycle. In response to double-strand DNA breaks, promotes p53/TP53 phosphorylation on 'Ser-46' and subsequent apoptosis. Acts as a tumor suppressor by inducing cell death by an autophagy and caspase-dependent mechanism. Can reduce cell migration by regulating the expression of SPARC.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-01 Fold-change: -1.23E-02 Z-score: -1.49E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | p73-mediated apoptosis signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| BT-549 | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | |
| MCF-10A | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-436 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0623 | |
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | |
| ZR-75-30 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1661 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
TUNEL assays | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-200a confers chemoresistance by antagonizing TP53INP1 and YAP1 in human breast cancer Inhibition of miR200a enhances gemcitabine chemosensitivity in resistance cancer cells. TP53INP1 and YAP1 are involved in the RNA damage-induced p73-mediated apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.90E-01 Fold-change: -6.41E-02 Z-score: -8.39E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Exosomal delivery of miR 155 5p may induce EMT and chemoresistant phenotypes from paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer cells to the sensitive cells, which may be mediated by GATA3 and TP53INP1 suppression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.59E-05 Fold-change: -9.30E-02 Z-score: -4.59E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | miR182/TP53INP1 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-182 levels are significantly increased in HCC patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Upregulated miR-182 inhibits TP53INP1 expression, which results in sequent cisplatin resistance. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.90E-01; Fold-change: -4.33E-01; Z-score: -9.50E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.89E-01; Fold-change: 2.82E-03; Z-score: 6.27E-03 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.59E-05; Fold-change: -5.04E-01; Z-score: -9.56E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.35E-01; Fold-change: -8.89E-02; Z-score: -2.25E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 8.31E-01; Fold-change: -1.12E-01; Z-score: -9.41E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
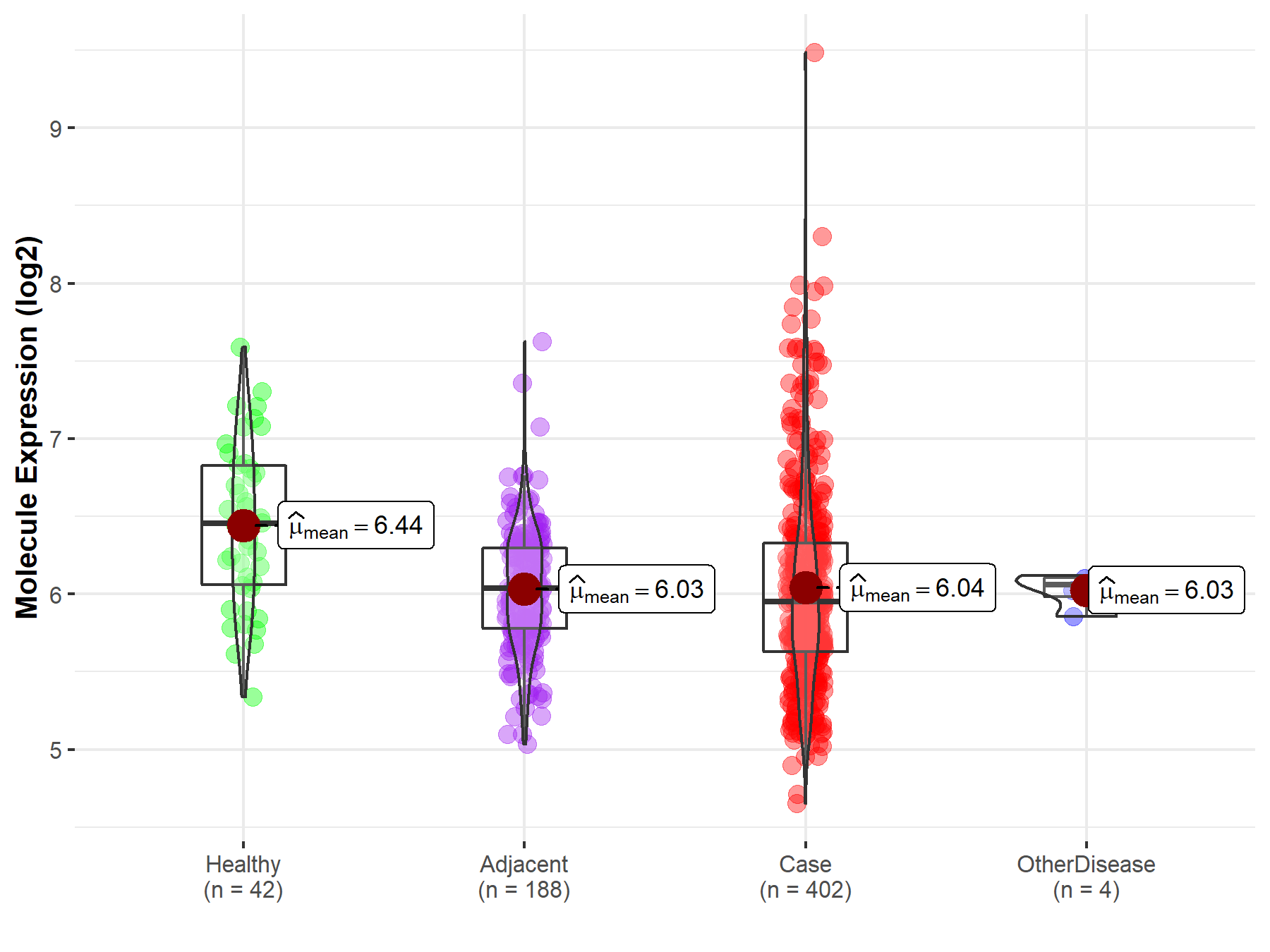
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-01; Fold-change: -8.93E-02; Z-score: -1.90E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.85E-02; Fold-change: -1.81E-01; Z-score: -4.66E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
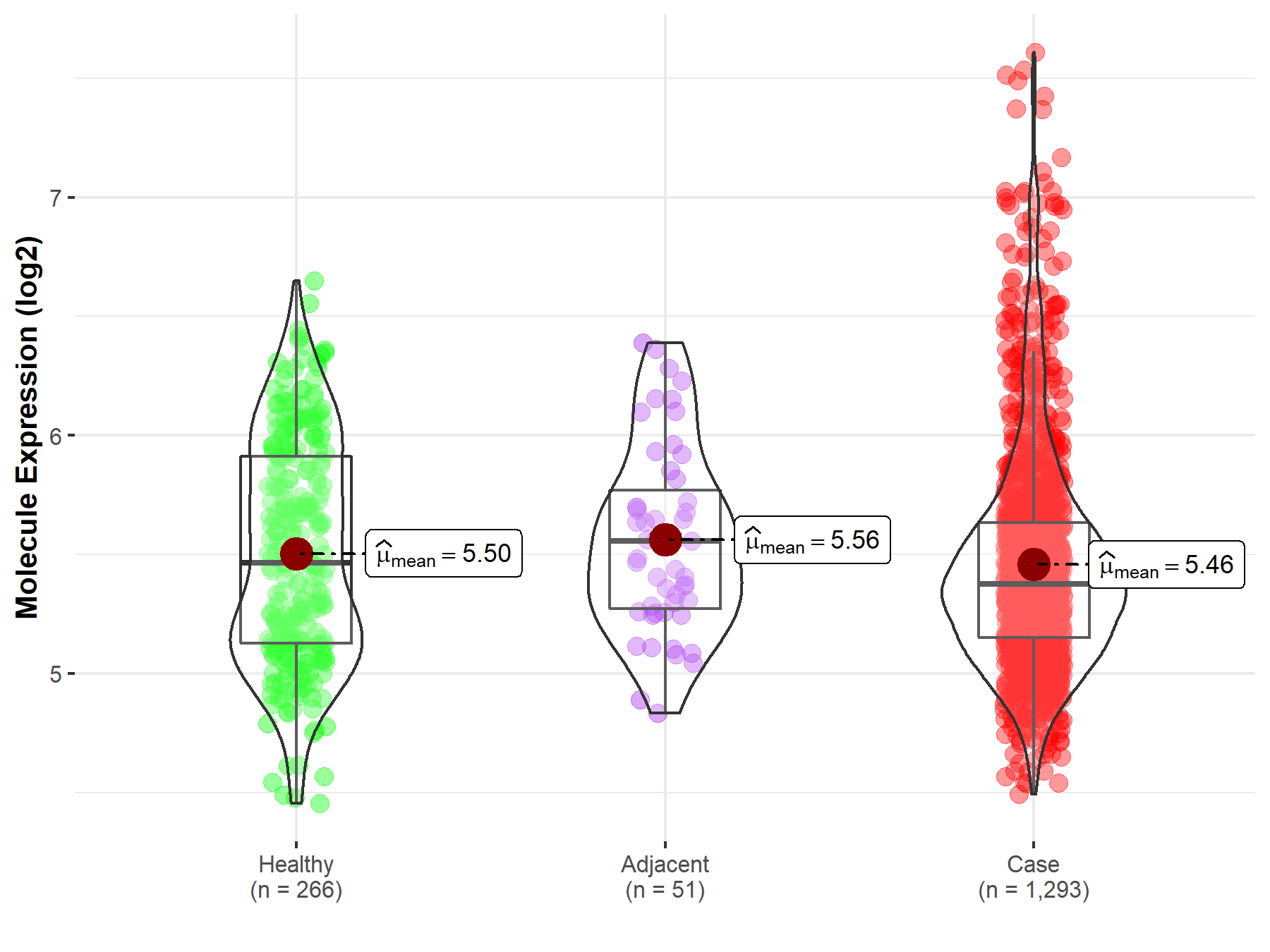
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
