Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00173)
| Name |
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src (SRC)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Proto-oncogene c-Src; pp60c-src; p60-Src; SRC1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SRC
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr20:37344685-37406050[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MGSNKSKPKDASQRRRSLEPAENVHGAGGGAFPASQTPSKPASADGHRGPSAAFAPAAAE
PKLFGGFNSSDTVTSPQRAGPLAGGVTTFVALYDYESRTETDLSFKKGERLQIVNNTEGD WWLAHSLSTGQTGYIPSNYVAPSDSIQAEEWYFGKITRRESERLLLNAENPRGTFLVRES ETTKGAYCLSVSDFDNAKGLNVKHYKIRKLDSGGFYITSRTQFNSLQQLVAYYSKHADGL CHRLTTVCPTSKPQTQGLAKDAWEIPRESLRLEVKLGQGCFGEVWMGTWNGTTRVAIKTL KPGTMSPEAFLQEAQVMKKLRHEKLVQLYAVVSEEPIYIVTEYMSKGSLLDFLKGETGKY LRLPQLVDMAAQIASGMAYVERMNYVHRDLRAANILVGENLVCKVADFGLARLIEDNEYT ARQGAKFPIKWTAPEAALYGRFTIKSDVWSFGILLTELTTKGRVPYPGMVNREVLDQVER GYRMPCPPECPESLHDLMCQCWRKEPEERPTFEYLQAFLEDYFTSTEPQYQPGENL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase which is activated following engagement of many different classes of cellular receptors including immune response receptors, integrins and other adhesion receptors, receptor protein tyrosine kinases, G protein-coupled receptors as well as cytokine receptors. Participates in signaling pathways that control a diverse spectrum of biological activities including gene transcription, immune response, cell adhesion, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, migration, and transformation. Due to functional redundancy between members of the SRC kinase family, identification of the specific role of each SRC kinase is very difficult. SRC appears to be one of the primary kinases activated following engagement of receptors and plays a role in the activation of other protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) families. Receptor clustering or dimerization leads to recruitment of SRC to the receptor complexes where it phosphorylates the tyrosine residues within the receptor cytoplasmic domains. Plays an important role in the regulation of cytoskeletal organization through phosphorylation of specific substrates such as AFAP1. Phosphorylation of AFAP1 allows the SRC SH2 domain to bind AFAP1 and to localize to actin filaments. Cytoskeletal reorganization is also controlled through the phosphorylation of cortactin (CTTN) (Probable). When cells adhere via focal adhesions to the extracellular matrix, signals are transmitted by integrins into the cell resulting in tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of focal adhesion proteins, including PTK2/FAK1 and paxillin (PXN). In addition to phosphorylating focal adhesion proteins, SRC is also active at the sites of cell-cell contact adherens junctions and phosphorylates substrates such as beta-catenin (CTNNB1), delta-catenin (CTNND1), and plakoglobin (JUP). Another type of cell-cell junction, the gap junction, is also a target for SRC, which phosphorylates connexin-43 (GJA1). SRC is implicated in regulation of pre-mRNA-processing and phosphorylates RNA-binding proteins such as KHDRBS1 (Probable). Also plays a role in PDGF-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of both STAT1 and STAT3, leading to increased DNA binding activity of these transcription factors. Involved in the RAS pathway through phosphorylation of RASA1 and RASGRF1. Plays a role in EGF-mediated calcium-activated chloride channel activation. Required for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) internalization through phosphorylation of clathrin heavy chain (CLTC and CLTCL1) at 'Tyr-1477'. Involved in beta-arrestin (ARRB1 and ARRB2) desensitization through phosphorylation and activation of GRK2, leading to beta-arrestin phosphorylation and internalization. Has a critical role in the stimulation of the CDK20/MAPK3 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by epidermal growth factor (Probable). Might be involved not only in mediating the transduction of mitogenic signals at the level of the plasma membrane but also in controlling progression through the cell cycle via interaction with regulatory proteins in the nucleus. Plays an important role in osteoclastic bone resorption in conjunction with PTK2B/PYK2. Both the formation of a SRC-PTK2B/PYK2 complex and SRC kinase activity are necessary for this function. Recruited to activated integrins by PTK2B/PYK2, thereby phosphorylating CBL, which in turn induces the activation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the cell membrane in a signaling pathway that is critical for osteoclast function. Promotes energy production in osteoclasts by activating mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase. Phosphorylates DDR2 on tyrosine residues, thereby promoting its subsequent autophosphorylation. Phosphorylates RUNX3 and COX2 on tyrosine residues, TNK2 on 'Tyr-284' and CBL on 'Tyr-731'. Enhances DDX58/RIG-I-elicited antiviral signaling. Phosphorylates PDPK1 at 'Tyr-9', 'Tyr-373' and 'Tyr-376'. Phosphorylates BCAR1 at 'Tyr-128'. Phosphorylates CBLC at multiple tyrosine residues, phosphorylation at 'Tyr-341' activates CBLC E3 activity. Involved in anchorage-independent cell growth. Required for podosome formation. Mediates IL6 signaling by activating YAP1-NOTCH pathway to induce inflammation-induced epithelial regeneration.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.61E-01 Fold-change: -3.44E-02 Z-score: -1.17E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BxPC-3 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0186 |
| MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0480 | |
| Capan-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0237 | |
| AsPC-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0152 | |
| SW1990 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1723 | |
| Su.86.86 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3881 | |
| In Vivo Model | Engrafted tumor mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; qRT-PCR; IHC analyses | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SRC inhibition leads to improved efficacy of gemcitabine in PC cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chondrosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B50.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Chondrosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B50.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Src/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04917 | |
| In Vitro Model | CH-2879 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9921 |
| OUMS-27 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3090 | |
| SW1353 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0543 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Transwell invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Src kinase is a direct target of miR23b in chondrosarcoma cells, overexpression of miR23b suppresses Src-Akt pathway, leading to the sensitization of cisplatin resistant chondrosarcoma cells to cisplatin. | |||
| Disease Class: Gallbladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C13.0] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gallbladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C13.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | miR31/Src/AKT/Bax/BCL2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05206 | |
| In Vitro Model | GBC-SD cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6903 |
| NOZ cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3079 | |
| GBC-SD/DDP cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6903 | |
| NOZ/DDP cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3079 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony forming assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR31 regulates the cisplatin resistance by targeting Src in gallbladder cancer The Src/Akt/Bax/Bcl-2 signaling cascade could be activated in the miR31-downregulated DDP-resistant GBC cells, and downregulation of Src sensitized the miR31 expressing GBC cells to DDP. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.61E-01; Fold-change: -9.19E-02; Z-score: -2.18E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.61E-06; Fold-change: -3.28E-01; Z-score: -8.30E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

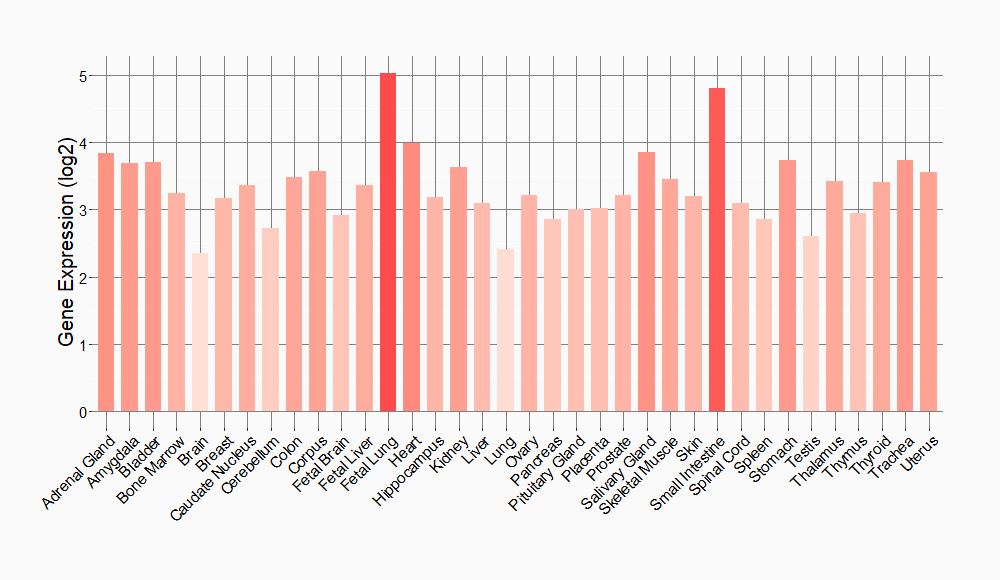
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
