Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00101)
| Name |
Ubiquitin-like protein ISG15 (ISG15)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Interferon-induced 15 kDa protein; Interferon-induced 17 kDa protein; IP17; Ubiquitin cross-reactive protein; hUCRP; G1P2; UCRP
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ISG15
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:1001138-1014540[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MGWDLTVKMLAGNEFQVSLSSSMSVSELKAQITQKIGVHAFQQRLAVHPSGVALQDRVPL
ASQGLGPGSTVLLVVDKCDEPLSILVRNNKGRSSTYEVRLTQTVAHLKQQVSGLEGVQDD LFWLTFEGKPLEDQLPLGEYGLKPLSTVFMNLRLRGGGTEPGGRS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Ubiquitin-like protein which plays a key role in the innate immune response to viral infection either via its conjugation to a target protein (ISGylation) or via its action as a free or unconjugated protein. ISGylation involves a cascade of enzymatic reactions involving E1, E2, and E3 enzymes which catalyze the conjugation of ISG15 to a lysine residue in the target protein. Its target proteins include IFIT1, MX1/MxA, PPM1B, UBE2L6, UBA7, CHMP5, CHMP2A, CHMP4B and CHMP6. Isgylation of the viral sensor IFIH1/MDA5 promotes IFIH1/MDA5 oligomerization and triggers activation of innate immunity against a range of viruses, including coronaviruses, flaviviruses and picornaviruses. Can also isgylate: EIF2AK2/PKR which results in its activation, DDX58/RIG-I which inhibits its function in antiviral signaling response, EIF4E2 which enhances its cap structure-binding activity and translation-inhibition activity, UBE2N and UBE2E1 which negatively regulates their activity, IRF3 which inhibits its ubiquitination and degradation and FLNB which prevents its ability to interact with the upstream activators of the JNK cascade thereby inhibiting IFNA-induced JNK signaling. Exhibits antiviral activity towards both DNA and RNA viruses, including influenza A, HIV-1 and Ebola virus. Restricts HIV-1 and ebola virus via disruption of viral budding. Inhibits the ubiquitination of HIV-1 Gag and host TSG101 and disrupts their interaction, thereby preventing assembly and release of virions from infected cells. Inhibits Ebola virus budding mediated by the VP40 protein by disrupting ubiquitin ligase activity of NEDD4 and its ability to ubiquitinate VP40. ISGylates influenza A virus NS1 protein which causes a loss of function of the protein and the inhibition of virus replication. The secreted form of ISG15 can: induce natural killer cell proliferation, act as a chemotactic factor for neutrophils and act as a IFN-gamma-inducing cytokine playing an essential role in antimycobacterial immunity. The secreted form acts through the integrin ITGAL/ITGB2 receptor to initiate activation of SRC family tyrosine kinases including LYN, HCK and FGR which leads to secretion of IFNG and IL10; the interaction is mediated by ITGAL.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | TRAIL | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.21E-01 Fold-change: -7.00E-03 Z-score: -9.97E-02 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| HLCZ01 cells | Hepatoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1J92 | |
| LH86 cells | Hepatoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8889 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-138 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through interferon-stimulated gene 15 downregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. | |||
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Irinotecan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF+kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04218 | |
| In Vitro Model | DLD-1 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0248 |
| SW-480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 | |
| RkO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0504 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay; qRT-PCR; Immunofluorescence staining assay; Reporter Gene assay; RNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell cytotoxicity assay; Tumorigenicity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Our data suggest that irinotecan upregulates various oncogenes, proliferative pathways, and metastatic markers, which may compromise its efficacy. SN38 induces p53-independent CDKIs and regulates cancer cell growth. OPN silencing regulates the SN38-mediated increase in PD-L1. Inhibition of non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling by QNZ results in the regulation of SN38-induced survivin and ISG15 (Figure 7). The targeting of OPN, PD-L1, ISG15, and NF-kappaB pathways may elevate irinotecan potency and lead to its combination with immunomodulatory therapies for CRC prognostic strategies. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.66E-06; Fold-change: 5.21E-01; Z-score: 5.92E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.13E-02; Fold-change: 4.81E-01; Z-score: 3.51E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 6.68E-01; Fold-change: -2.41E-01; Z-score: -2.45E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
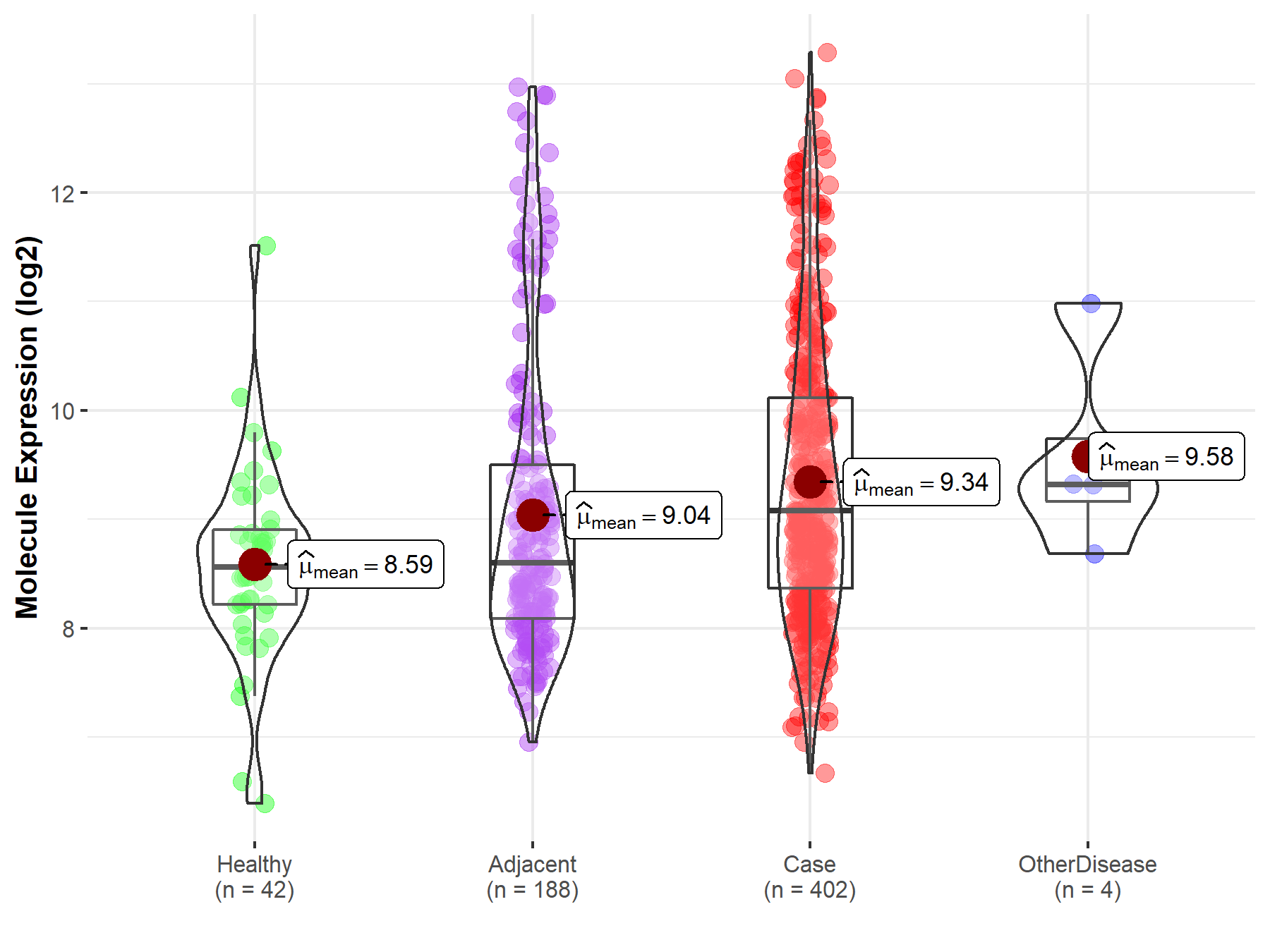
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

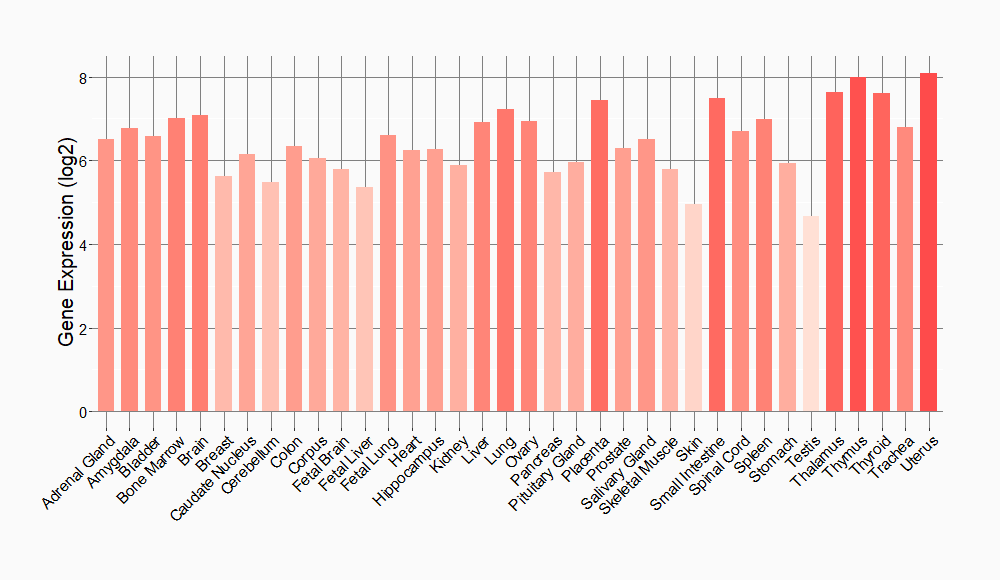
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
