Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00081)
| Name |
Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1 (HEY1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cardiovascular helix-loop-helix factor 2; CHF-2; Class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 31; bHLHb31; HES-related repressor protein 1; Hairy and enhancer of split-related protein 1; HESR-1; Hairy-related transcription factor 1; HRT-1; hHRT1; BHLHB31; CHF2; HERP2; HESR1; HRT1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
HEY1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:79762371-79767857[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MKRAHPEYSSSDSELDETIEVEKESADENGNLSSALGSMSPTTSSQILARKRRRGIIEKR
RRDRINNSLSELRRLVPSAFEKQGSAKLEKAEILQMTVDHLKMLHTAGGKGYFDAHALAM DYRSLGFRECLAEVARYLSIIEGLDASDPLRVRLVSHLNNYASQREAASGAHAGLGHIPW GTVFGHHPHIAHPLLLPQNGHGNAGTTASPTEPHHQGRLGSAHPEAPALRAPPSGSLGPV LPVVTSASKLSPPLLSSVASLSAFPFSFGSFHLLSPNALSPSAPTQAANLGKPYRPWGTE IGAF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Transcriptional repressor which binds preferentially to the canonical E box sequence 5'-CACGTG-3'. Downstream effector of Notch signaling required for cardiovascular development. Specifically required for the Notch-induced endocardial epithelial to mesenchymal transition, which is itself criticial for cardiac valve and septum development. May be required in conjunction with HEY2 to specify arterial cell fate or identity. Promotes maintenance of neuronal precursor cells and glial versus neuronal fate specification. Represses transcription by the cardiac transcriptional activators GATA4 and GATA6 and by the neuronal bHLH factors ASCL1/MASH1 and NEUROD4/MATH3. Involved in the regulation of liver cancer cells self-renewal.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.86E-37 Fold-change: -1.22E-01 Z-score: -1.41E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt2/Beta-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| KPL-4 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5310 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RIP assay; ChIP assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long non-coding RNA LINC00968 attenuates drug resistance of breast cancer cells through inhibiting the Wnt2/beta-catenin signaling pathway by regulating WNT2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt2/Beta-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| KPL-4 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5310 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RIP assay; ChIP assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long non-coding RNA LINC00968 attenuates drug (Doxorubicin; Vincristine; Taxol) resistance of breast cancer cells through inhibiting the Wnt2/beta-catenin signaling pathway by regulating WNT2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt2/Beta-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| KPL-4 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5310 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RIP assay; ChIP assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long non-coding RNA LINC00968 attenuates drug resistance of breast cancer cells through inhibiting the Wnt2/beta-catenin signaling pathway by regulating WNT2. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.86E-37; Fold-change: -7.87E-01; Z-score: -1.06E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.92E-09; Fold-change: -7.89E-01; Z-score: -1.04E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
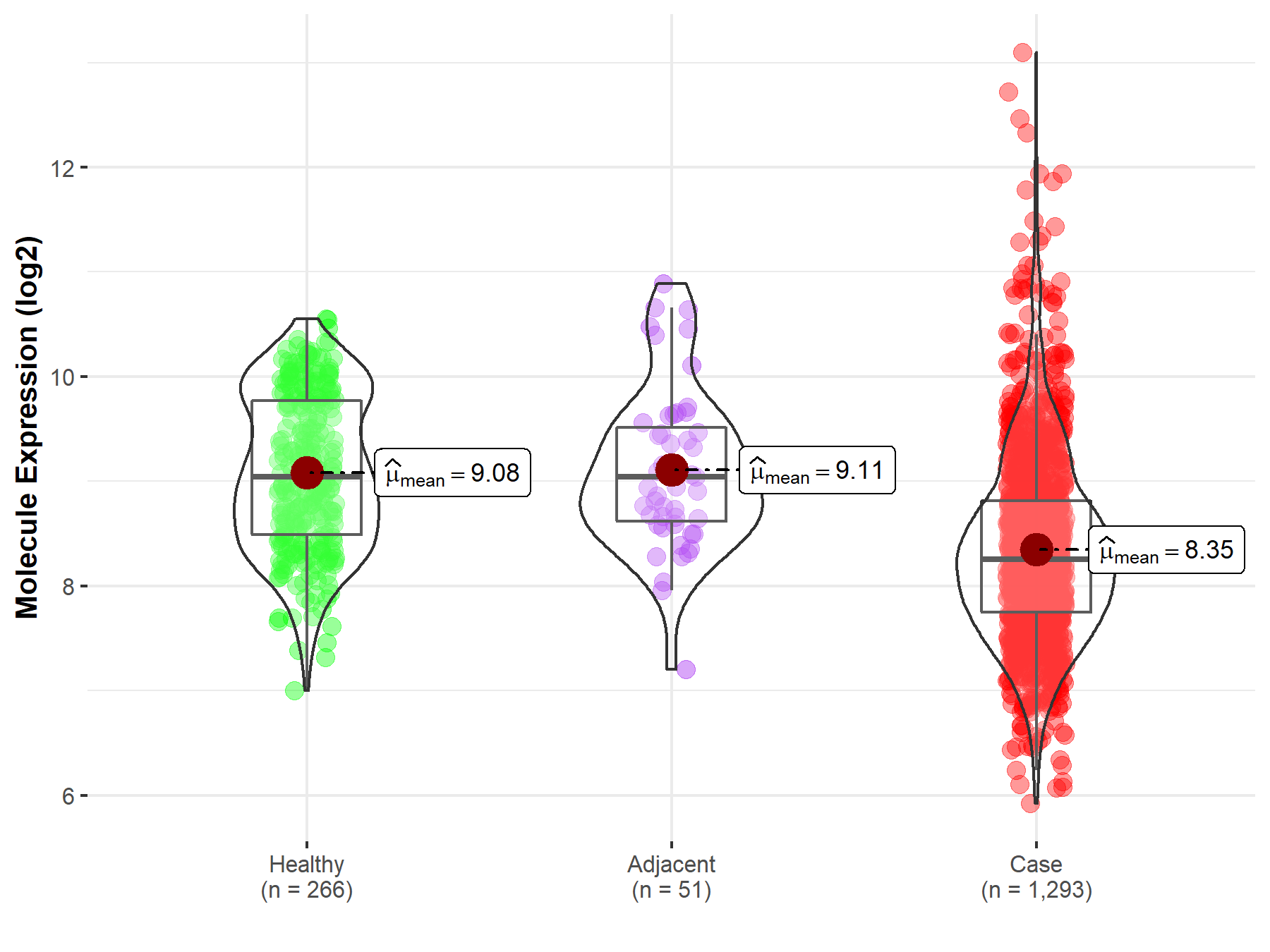
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

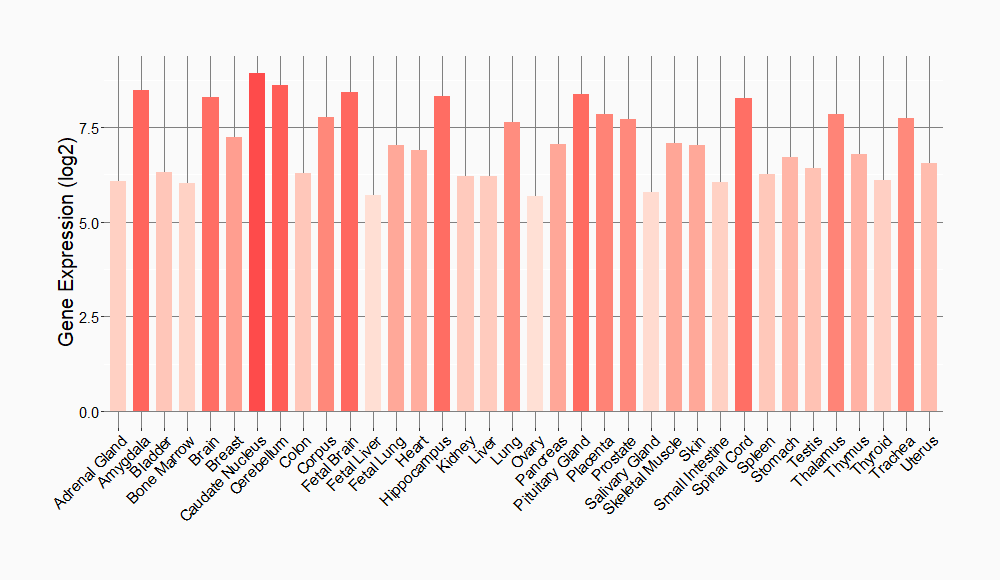
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
