Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00069)
| Name |
F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 7 (FBXW7)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Archipelago homolog; hAgo; F-box and WD-40 domain-containing protein 7; F-box protein FBX30; SEL-10; hCdc4; FBW7; FBX30; SEL10
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
FBXW7
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr4:152320544-152536092[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MNQELLSVGSKRRRTGGSLRGNPSSSQVDEEQMNRVVEEEQQQQLRQQEEEHTARNGEVV
GVEPRPGGQNDSQQGQLEENNNRFISVDEDSSGNQEEQEEDEEHAGEQDEEDEEEEEMDQ ESDDFDQSDDSSREDEHTHTNSVTNSSSIVDLPVHQLSSPFYTKTTKMKRKLDHGSEVRS FSLGKKPCKVSEYTSTTGLVPCSATPTTFGDLRAANGQGQQRRRITSVQPPTGLQEWLKM FQSWSGPEKLLALDELIDSCEPTQVKHMMQVIEPQFQRDFISLLPKELALYVLSFLEPKD LLQAAQTCRYWRILAEDNLLWREKCKEEGIDEPLHIKRRKVIKPGFIHSPWKSAYIRQHR IDTNWRRGELKSPKVLKGHDDHVITCLQFCGNRIVSGSDDNTLKVWSAVTGKCLRTLVGH TGGVWSSQMRDNIIISGSTDRTLKVWNAETGECIHTLYGHTSTVRCMHLHEKRVVSGSRD ATLRVWDIETGQCLHVLMGHVAAVRCVQYDGRRVVSGAYDFMVKVWDPETETCLHTLQGH TNRVYSLQFDGIHVVSGSLDTSIRVWDVETGNCIHTLTGHQSLTSGMELKDNILVSGNAD STVKIWDIKTGQCLQTLQGPNKHQSAVTCLQFNKNFVITSSDDGTVKLWDLKTGEFIRNL VTLESGGSGGVVWRIRASNTKLVCAVGSRNGTEETKLLVLDFDVDMK Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Substrate recognition component of a SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Recognizes and binds phosphorylated sites/phosphodegrons within target proteins and thereafter bring them to the SCF complex for ubiquitination. Identified substrates include cyclin-E (CCNE1 or CCNE2), DISC1, JUN, MYC, NOTCH1 released notch intracellular domain (NICD), NFE2L1, NOTCH2, MCL1, and probably PSEN1. Acts as a negative regulator of JNK signaling by binding to phosphorylated JUN and promoting its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Involved in bone homeostasis and negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation. Regulates the amplitude of the cyclic expression of hepatic core clock genes and genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism via ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of their transcriptional repressor NR1D1; CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of NR1D1 is necessary for SCF(FBXW7)-mediated ubiquitination. Also able to promote 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination in response to DNA damage. The SCF(FBXW7) complex facilitates double-strand break repair following phosphorylation by ATM: phosphorylation promotes localization to sites of double-strand breaks and 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of phosphorylated XRCC4, enhancing DNA non-homologous end joining.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
8 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.75E-01 Fold-change: 8.49E-04 Z-score: 3.18E-02 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | PANC-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0480 |
| AsPC-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0152 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Transwell migration and invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-223 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells due to down-regulation of its target Fbw7 and subsequent upregulation of Notch-1, which enhances GR cells to gemcitabine sensitivity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.37E-01 Fold-change: -1.86E-02 Z-score: -2.10E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| miR223/FBXW7 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-N87 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1603 |
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | |
| KATO-3 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0371 | |
| NUGC3 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1612 | |
| NUGC4 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3082 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-223 decreased FBXW7 expression and the sensitivity of GC cells to trastuzumab, while suppression of miR-223 restored FBXW7 expression and the sensitivity of GC cells to trastuzumab. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| HGC27 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-363 promotes gastric cancer cells proliferation by inhibiting FBW7 expression and was associated with chemo-resistance of gastric cancer cells. Silencing FBW7 largely phenocopied miR-363-induced resistance to chemotherapy agents and promoted proliferation in gastric cancer cells. In addition, an inverse correlation between miR-363 and FBW7 mRNA expression was observed in gastric cancer tissues. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| HGC27 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-363 promotes gastric cancer cells proliferation by inhibiting FBW7 expression and was associated with chemo-resistance of gastric cancer cells. Silencing FBW7 largely phenocopied miR-363-induced resistance to chemotherapy agents and promoted proliferation in gastric cancer cells. In addition, an inverse correlation between miR-363 and FBW7 mRNA expression was observed in gastric cancer tissues. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| miR223/FBXW7 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |
| HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-223 decreased FBXW7 expression and the sensitivity of CRC cells to doxorubicin, while suppression of miR-223 had the opposite effect. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Notch/miR223/FBXW7 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |
| HCC827/ER cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EJ07 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay; Flow cytometric apoptosis assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to erlotinib is regulated by the Notch/miR223/FBXW7 pathway. Blocking either the Akt or Notch signaling pathway and reducing miR223 expression resulted in decreased resistance in HCC827/ER cells, miR223 enhanced resistance to erlotinib by down-regulating FBXW7 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| HGC27 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1279 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-363 promotes gastric cancer cells proliferation by inhibiting FBW7 expression and was associated with chemo-resistance of gastric cancer cells. Silencing FBW7 largely phenocopied miR-363-induced resistance to chemotherapy agents and promoted proliferation in gastric cancer cells. In addition, an inverse correlation between miR-363 and FBW7 mRNA expression was observed in gastric cancer tissues. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R505C (c.1513C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | DLD1 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0248 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| RkO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0504 | |
| NCI-H508 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1564 | |
| DiFi cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6895 | |
| VACO432 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5402 | |
| PIK3CA-KO cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| CCK-81 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2873 | |
| BRAF-KO cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | FBW7, an E3 ubiquitin ligase and a tumor suppressor frequently mutated in CRCs, contribute to resistance to targeted therapies. CRC cells containing FBW7 inactivating mutations are insensitive to clinically used multi-kinase inhibitors of RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling, including regorafenib and sorafenib. In contrast, sensitivity to these agents is not affected by oncogenic mutations in KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, or p53. These cells are defective in apoptosis due to blocked degradation of Mcl-1, a pro-survival Bcl-2 family protein. Deleting FBW7 in FBW7-wild-type CRC cells abolishes Mcl-1 degradation and recapitulates the in vitro and in vivo drug resistance phenotypes of FBW7-mutant cells. CRC cells selected for regorafenib resistance have progressive enrichment of pre-existing FBW7 hotspot mutations, and are cross-resistant to other targeted drugs that induce Mcl-1 degradation. Furthermore, a selective Mcl-1 inhibitor restores regorafenib sensitivity in CRC cells with intrinsic or acquired resistance. | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | MRK-003 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R505C (c.1513C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | T-ALL cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1736 |
| 293a cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6910 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
V-FITC apoptosis detection kit I assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R505C (c.1513C>T) in gene FBXW7 cause the resistance of MRK-003 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Disease Class: T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | MRK-003 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R465C (c.1393C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | T-ALL cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1736 |
| 293a cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6910 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
V-FITC apoptosis detection kit I assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R465C (c.1393C>T) in gene FBXW7 cause the resistance of MRK-003 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Disease Class: T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | MRK-003 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R465H (c.1394G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | T-ALL cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1736 |
| 293a cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6910 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
V-FITC apoptosis detection kit I assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R465H (c.1394G>A) in gene FBXW7 cause the resistance of MRK-003 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Disease Class: T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | MRK-003 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R479Q (c.1436G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | T-ALL cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1736 |
| 293a cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6910 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
V-FITC apoptosis detection kit I assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R479Q (c.1436G>A) in gene FBXW7 cause the resistance of MRK-003 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute T-cell lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A90.5] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute T-cell lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A90.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dapt (Gsi IX) | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Notch/NF-kB signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Jurkat cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0065 |
| DND41 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2022 | |
| Jurkat IkkGamma -/- cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0065 | |
| Molt3 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0624 | |
| TALL-1 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1736 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue staining; MTT assay; Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Specific inhibition of miR-223 restores GSI sensitivity in GSI-resistant Molt3 cells carrying wt FBXW7. Therefore, upregulation of FBXW7 through the specific inhibition of miR-223 could offer an attractive targeted therapy for GSI-resistant T-ALLs harboring wt FBXW7 and overexpressing miR-223. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.37E-01; Fold-change: -1.24E-01; Z-score: -1.83E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.29E-06; Fold-change: -8.11E-01; Z-score: -1.87E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
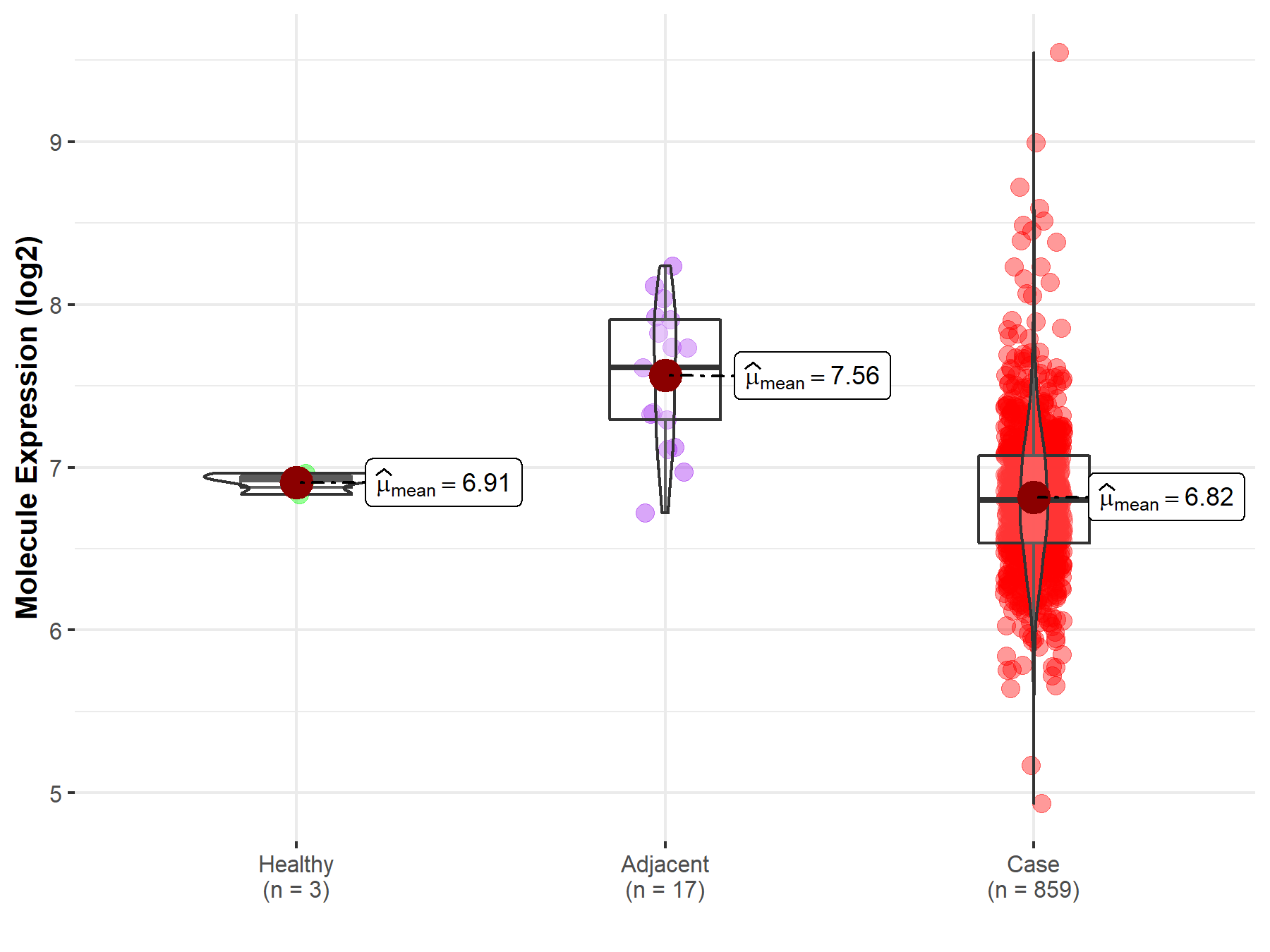
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.75E-01; Fold-change: 6.70E-03; Z-score: 1.30E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.03E-03; Fold-change: 2.40E-01; Z-score: 6.15E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
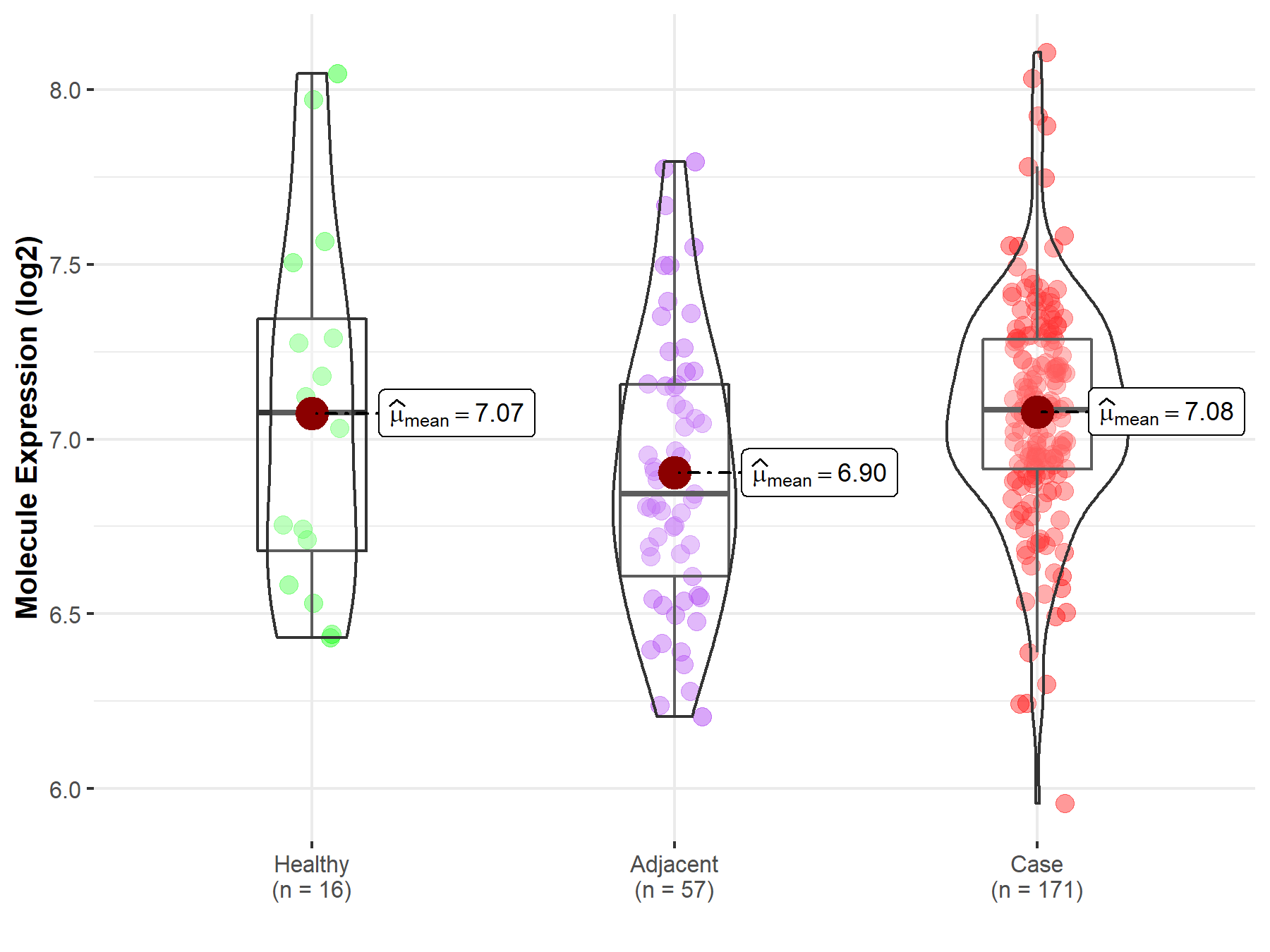
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.12E-45; Fold-change: 3.27E-01; Z-score: 1.38E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.57E-22; Fold-change: 2.51E-01; Z-score: 9.31E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

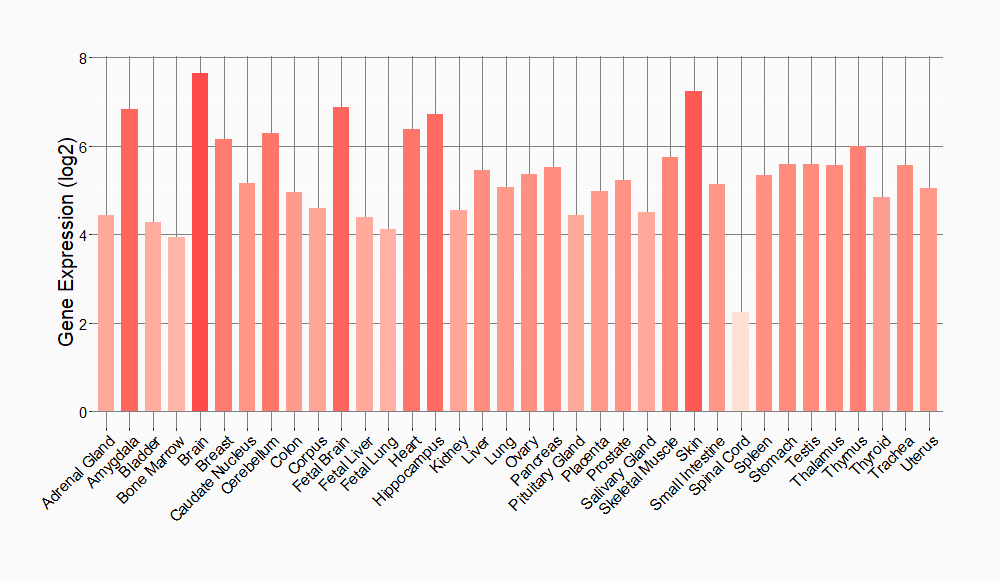
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
