Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00016)
| Name |
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 (ATF2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
cAMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2; Activating transcription factor 2; Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 2; CREB-2; cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 2; HB16; cAMP response element-binding protein CRE-BP1; CREB2; CREBP1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ATF2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:175072250-175168382[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MKFKLHVNSARQYKDLWNMSDDKPFLCTAPGCGQRFTNEDHLAVHKHKHEMTLKFGPARN
DSVIVADQTPTPTRFLKNCEEVGLFNELASPFENEFKKASEDDIKKMPLDLSPLATPIIR SKIEEPSVVETTHQDSPLPHPESTTSDEKEVPLAQTAQPTSAIVRPASLQVPNVLLTSSD SSVIIQQAVPSPTSSTVITQAPSSNRPIVPVPGPFPLLLHLPNGQTMPVAIPASITSSNV HVPAAVPLVRPVTMVPSVPGIPGPSSPQPVQSEAKMRLKAALTQQHPPVTNGDTVKGHGS GLVRTQSEESRPQSLQQPATSTTETPASPAHTTPQTQSTSGRRRRAANEDPDEKRRKFLE RNRAAASRCRQKRKVWVQSLEKKAEDLSSLNGQLQSEVTLLRNEVAQLKQLLLAHKDCPV TAMQKKSGYHTADKDDSSEDISVPSSPHTEAIQHSSVSTSNGVSSTSKAEAVATSVLTQM ADQSTEPALSQIVMAPSSQSQPSGS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Transcriptional activator which regulates the transcription of various genes, including those involved in anti-apoptosis, cell growth, and DNA damage response. Dependent on its binding partner, binds to CRE (cAMP response element) consensus sequences (5'-TGACGTCA-3') or to AP-1 (activator protein 1) consensus sequences (5'-TGACTCA-3'). In the nucleus, contributes to global transcription and the DNA damage response, in addition to specific transcriptional activities that are related to cell development, proliferation and death. In the cytoplasm, interacts with and perturbs HK1- and VDAC1-containing complexes at the mitochondrial outer membrane, thereby impairing mitochondrial membrane potential, inducing mitochondrial leakage and promoting cell death. The phosphorylated form (mediated by ATM) plays a role in the DNA damage response and is involved in the ionizing radiation (IR)-induced S phase checkpoint control and in the recruitment of the MRN complex into the IR-induced foci (IRIF). Exhibits histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity which specifically acetylates histones H2B and H4 in vitro. In concert with CUL3 and RBX1, promotes the degradation of KAT5 thereby attenuating its ability to acetylate and activate ATM. Can elicit oncogenic or tumor suppressor activities depending on the tissue or cell type.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Laryngeal cancer [ICD-11: 2C23.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HEp-2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1906 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR26b decreases the cisplatin-resistance in laryngeal cancer by targeting ATF2. miR26b in Hep-2/R decreased the expression of ATF2, and thus inhibiting the phosphorylation of ATF2 and formation of cellular ATF2-c-Jun complex induced by cisplatin. As the results, Hep-2/R cells failed to overexpress the Bcl-xl which is a key anti-apoptotic protein under the cisplatin treatment. Therefore, overexpression of miR26b was found to be able to promote mitochondrial apoptosis induced by cisplatin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ACHN cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1067 |
| GRC-1 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection assay; MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-451 regulates chemoresistance in renal cell carcinoma by targeting ATF-2 gene. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |
| The Specified Disease | Kidney cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.58E-01; Fold-change: 4.87E-01; Z-score: 5.32E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.10E-01; Fold-change: 2.18E-01; Z-score: 3.76E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
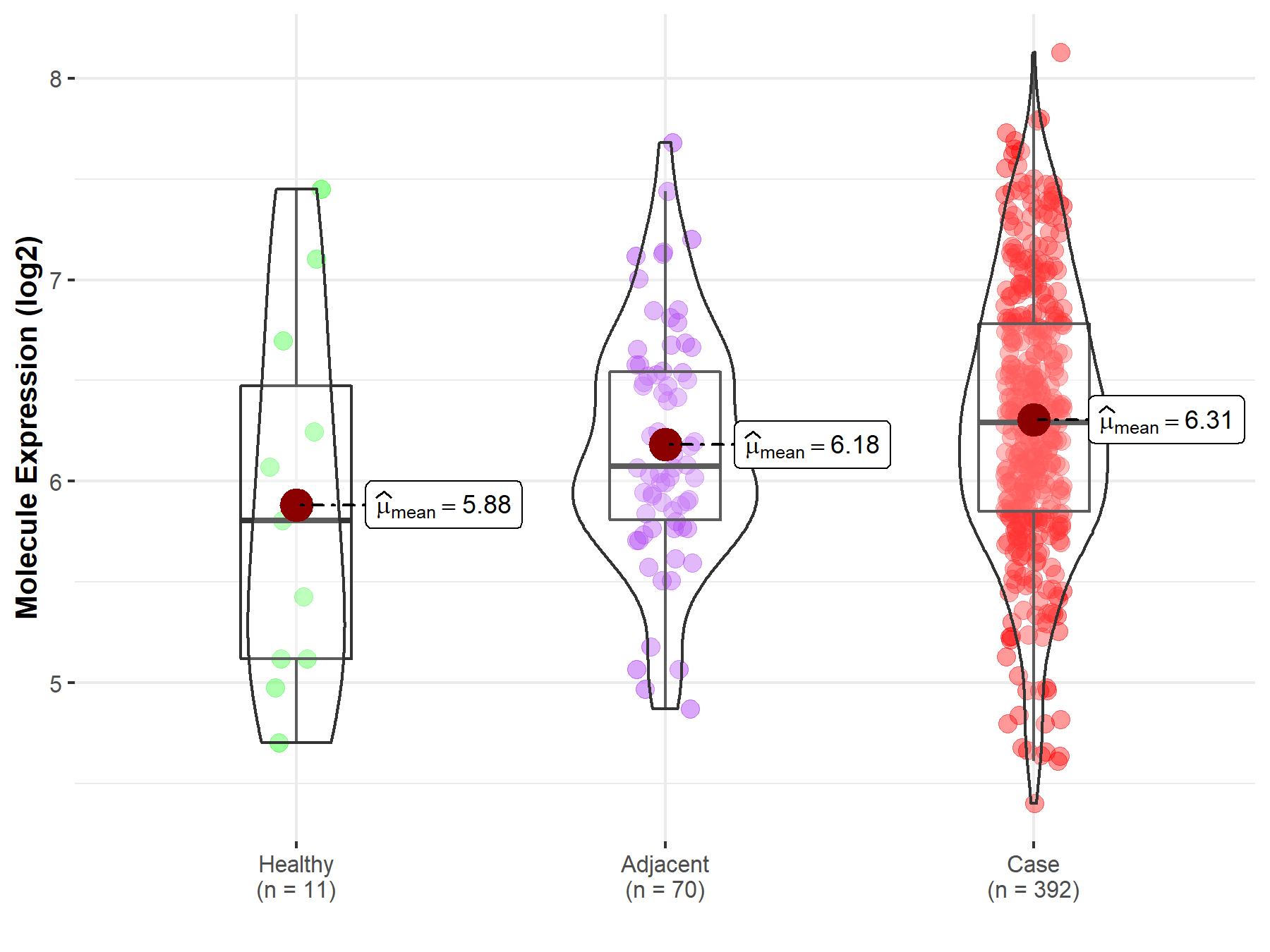
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

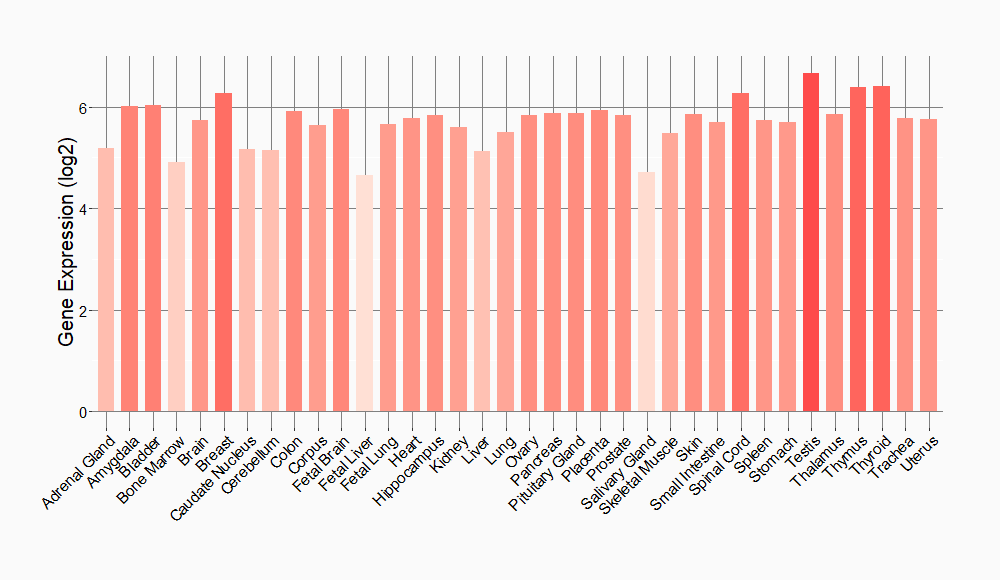
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
