Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01651) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
TAS6417
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
TAS6417; 1661854-97-2; Zipalertinib; TAS-6417; UNII-T4YMU8TW9H; T4YMU8TW9H; (S)-N-(4-amino-6-methyl-5-(quinolin-3-yl)-8,9-dihydropyrimido[5,4-b]indolizin-8-yl)acrylamide; CLN-081; N-[(8S)-4-Amino-6-methyl-5-quinolin-3-yl-8,9-dihydropyrimido[5,4-b]indolizin-8-yl]prop-2-enamide; Zipalertinib [INN]; CLN081; CHEMBL4650281; SCHEMBL16525948; GTPL11889; EX-A3391; NSC812926; s8814; NSC-812926; AS-79368; HY-112299; CS-0044757; D93895; A937514; 2-Propenamide, N-((8S)-4-amino-8,9-dihydro-6-methyl-5-(3-quinolinyl)pyrimido(5,4-b)indolizin-8-yl)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
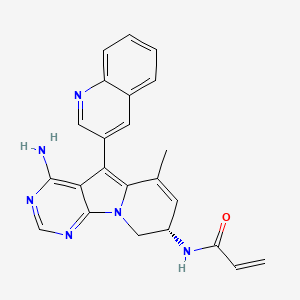
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
3
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C[C@@H](CN2C1=C(C3=C(N=CN=C32)N)C4=CC5=CC=CC=C5N=C4)NC(=O)C=C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H20N6O/c1-3-18(30)28-16-8-13(2)21-19(15-9-14-6-4-5-7-17(14)25-10-15)20-22(24)26-12-27-23(20)29(21)11-16/h3-10,12,16H,1,11H2,2H3,(H,28,30)(H2,24,26,27)/t16-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MKCYPWYURWOKST-INIZCTEOSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A763_Y764insFQEA (c.2290_2291insTTCAAGAGGCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.A767_V769 (c.2299_2307) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S768_D770 (c.2302_2310) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.D770_N771insG (c.2310_2311insGGT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.N771_H773 (c.2311_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.P772_H773 (c.2314_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.E746_A750delELREA (c.2236_2250del15) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.A767_V769 (c.2299_2307) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S768_D770 (c.2302_2310) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.N771_H773 (c.2311_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| NCI-H1875 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| LXF 2378L cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAS6417 is a novel EGFR inhibitor that targets EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations while sparing wild-type (WT) EGFR. In cell viability assays using Ba/F3 cells engineered to express human EGFR, TAS6417 inhibited EGFR with various exon 20 insertion mutations more potently than it inhibited the WT. Western blot analysis revealed that TAS6417 inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and downstream molecules in NSCLC cell lines expressing EGFR exon 20 insertions, resulting in caspase activation. These characteristics led to marked tumor regression in vivo in both a genetically engineered model and in a patient-derived xenograft model. Furthermore, TAS6417 provided a survival benefit with good tolerability in a lung orthotopic implantation mouse model. These findings support the clinical evaluation of TAS6417 as an efficacious drug candidate for patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
