Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01626) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Naquotinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Naquotinib; 1448232-80-1; ASP8273; UNII-47DD4548PB; 2-Pyrazinecarboxamide, 6-ethyl-3-[[4-[4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1-piperidinyl]phenyl]amino]-5-[[(3R)-1-(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]oxy]-; 47DD4548PB; ASP-8273; 6-ethyl-3-[4-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl]anilino]-5-[(3R)-1-prop-2-enoylpyrrolidin-3-yl]oxypyrazine-2-carboxamide; (R)-5-((1-acryloylpyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)-6-ethyl-3-((4-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)phenyl)amino)pyrazine-2-carboxamide; e-2-carboxamide; 2-Pyrazinecarboxamide, 6-ethyl-3-((4-(4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1-piperidinyl)phenyl)amino)-5-(((3R)-1-(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-3-pyrrolidinyl)oxy)-; Naquotinib [USAN]; Naquotinib (USAN/INN); ASP8273 (Naquotinib); Naquotinib; ASP-8273; GTPL9248; CHEMBL3663929; SCHEMBL16196078; BDBM170514; EX-A2669; YHC23280; NSC793322; s8412; ZINC205341959; CCG-270060; CS-5469; DB12036; NSC-793322; AS-75247; HY-19729; J3.496.214F; A14408; C91356; D10958; US9085540, 54; A857977; Q27074546; 5-[[(3R)-1-Acryloylpyrrolidine-3-yl]oxy]-6-ethyl-3-[4-[4-(4-methylpiperazine-1-yl)piperidino]anilino]pyrazine-2-carboxamide; 6-Ethyl-3-((4-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)phenyl)amino)-5-(((3R)-1-(1-oxoprop-2-en-1-yl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)pyrazine-2-carboxamide; 6-ethyl-3-({4-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl]phenyl}amino)-5-{[(3R)-1-(prop-2-enoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxy}pyrazine-2-carboxamide; 6-Ethyl-3-(4-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)anilino)-5-(((3R)-1-(prop-2-enoyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)pyrazine-2-carboxamide; 6-Ethyl-3-[[4-[4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1-piperidinyl]phenyl]amino]-5-[[(3R)-1-(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]oxy]-2-pyrazinecarboxamide; 6-ethyl-3-[[4-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl]phenyl]amino]-5-[(3R)-1-prop-2-enoylpyrrolidin-3-yl]oxy-pyrazin
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
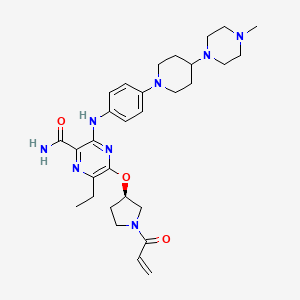
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCC1=C(N=C(C(=N1)C(=O)N)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)N3CCC(CC3)N4CCN(CC4)C)O[C@@H]5CCN(C5)C(=O)C=C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C30H42N8O3/c1-4-25-30(41-24-12-15-38(20-24)26(39)5-2)34-29(27(33-25)28(31)40)32-21-6-8-22(9-7-21)36-13-10-23(11-14-36)37-18-16-35(3)17-19-37/h5-9,23-24H,2,4,10-20H2,1,3H3,(H2,31,40)(H,32,34)/t24-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QKDCLUARMDUUKN-XMMPIXPASA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.Y764_V765insHH (c.2292_2293insCATCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R (c.2573T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Complex-indel | p.L747_P753delinsS (c.2240_2257del18) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A763_Y764insFQEA (c.2290_2291insTTCAAGAGGCAT) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.A767_V769 (c.2299_2307) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.P772_H773insGNP (c.2316_2317insGGTAACCCT) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R (c.2573T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.E746_A750delELREA (c.2236_2250del15) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A763_Y764insFQEA (c.2290_2291insTTCAAGAGGCAT) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
