Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01554) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Mps1-IN-1
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Mps1-IN-1; 1125593-20-5; 1-(4-(4-(2-(Isopropylsulfonyl)phenylamino)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-ylamino)-3-methoxyphenyl)piperidin-4-ol; 1-[3-methoxy-4-[[4-(2-propan-2-ylsulfonylanilino)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl]amino]phenyl]piperidin-4-ol; 1-(4-((4-((2-(isopropylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl)amino)-3-methoxyphenyl)piperidin-4-ol; 1MPS1-IN-1; 3gfw; MLS003230944; GTPL9271; SCHEMBL4051419; CHEMBL1235786; BDBM36485; CHEBI:91379; DTXSID60649015; AVB59320; BCP27688; 3868AH; ZINC58661129; CS-3776; QC-8177; NCGC00387463-01; NCGC00387463-04; HY-13298; SMR001913509; A925638; J-503190; Q27087728; 1-(3-methoxy-4-{[4-({2-[(1-methylethyl)sulfonyl]phenyl}amino)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl]amino}phenyl)piperidin-4-ol; 1-[3-Methoxy-4-({4-[2-(propane-2-sulfonyl)anilino]-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl}amino)phenyl]piperidin-4-ol; s22
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
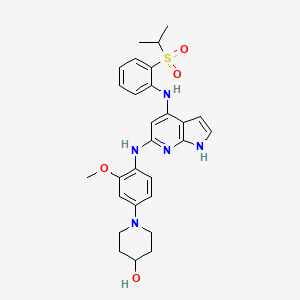
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
8
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1NC2=CC(=NC3=C2C=CN3)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)N5CCC(CC5)O)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H33N5O4S/c1-18(2)38(35,36)26-7-5-4-6-23(26)30-24-17-27(32-28-21(24)10-13-29-28)31-22-9-8-19(16-25(22)37-3)33-14-11-20(34)12-15-33/h4-10,13,16-18,20,34H,11-12,14-15H2,1-3H3,(H3,29,30,31,32)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NMJMRSQTDLRCRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.S45delS (c.133_135delTCT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| SW48 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1724 | |
| TOV-21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | |
| HuTu80 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1301 | |
| TOV-112D cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3612 | |
| LS 174T cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1384 | |
| A427 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1055 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene set analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The if-deletion p.S45delS (c.133_135delTCT) in gene CTNNB1 cause the sensitivity of Mps1-IN-1 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S45F (c.134C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.45 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
T
T
T
T
A
A
P
P
S
F
L
L
S
S
G
G
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| SW48 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1724 | ||||||||||
| TOV-21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | ||||||||||
| HuTu80 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1301 | ||||||||||
| TOV-112D cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3612 | ||||||||||
| LS 174T cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1384 | ||||||||||
| A427 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1055 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene set analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.S45F (c.134C>T) in gene CTNNB1 cause the sensitivity of Mps1-IN-1 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S33Y (c.98C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| SW48 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1724 | ||||||||||
| TOV-21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | ||||||||||
| HuTu80 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1301 | ||||||||||
| TOV-112D cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3612 | ||||||||||
| LS 174T cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1384 | ||||||||||
| A427 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1055 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene set analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.S33Y (c.98C>A) in gene CTNNB1 cause the sensitivity of Mps1-IN-1 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Catenin beta-1 (CTNNB1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T41A (c.121A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| SW48 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1724 | |
| TOV-21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | |
| HuTu80 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1301 | |
| TOV-112D cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3612 | |
| LS 174T cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1384 | |
| A427 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1055 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene set analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.T41A (c.121A>G) in gene CTNNB1 cause the sensitivity of Mps1-IN-1 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
