Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01482) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
NAV-2729
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
NAV-2729; 419547-11-8; 2-benzyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-(4-nitrophenyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-one; CHEMBL3716578; NAV 2729; 2-benzyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-one; 3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-5-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-(phenylmethyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-one; NAV-2729Grassofermata; Oprea1_305395; SCHEMBL13516218; NAV2729; CHEBI:132811; AMY23749; EX-A2011; BDBM50168142; AKOS030211129; ZINC106616565; BS-16805; HY-112473; CS-0046101; D80454; 2-benzyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-(4-nitrophenyl)-4H-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
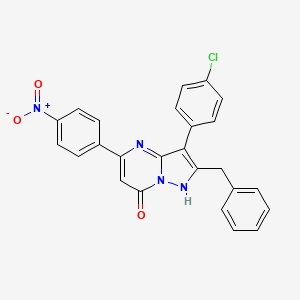
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C3=NC(=CC(=O)N3N2)C4=CC=C(C=C4)[N+](=O)[O-])C5=CC=C(C=C5)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H17ClN4O3/c26-19-10-6-18(7-11-19)24-22(14-16-4-2-1-3-5-16)28-29-23(31)15-21(27-25(24)29)17-8-12-20(13-9-17)30(32)33/h1-13,15,28H,14H2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WHYGBVWGARJOCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-q (GNAQ) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Uveal melanoma [ICD-11: 2D0Y.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q209L (c.626A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 3.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 2.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
0
|
-
H
M
H
T
T
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
M
M
A
A
C
C
10
|
C
C
L
L
S
S
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
E
E
A
A
R
R
20
|
R
R
I
I
N
N
D
D
E
E
I
I
E
E
R
R
Q
Q
L
L
30
|
R
R
R
R
D
D
K
K
R
R
D
D
A
A
R
R
R
R
E
E
40
|
L
L
K
K
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
G
G
T
T
G
G
E
E
50
|
S
S
G
G
K
K
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
60
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
H
H
G
G
S
S
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
D
D
70
|
E
E
D
D
K
K
R
R
G
G
F
F
T
T
K
K
L
L
V
V
80
|
Y
Y
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
F
F
T
T
A
A
M
M
Q
Q
A
A
90
|
M
M
I
I
R
R
A
A
M
M
D
D
T
T
L
L
K
K
I
I
100
|
P
P
Y
Y
K
K
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
N
N
K
K
A
A
H
H
110
|
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
R
R
E
E
V
V
D
D
V
V
E
E
120
|
K
K
V
V
S
S
A
A
F
F
E
E
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
V
V
130
|
D
D
A
A
I
I
K
K
S
S
L
L
W
W
N
N
D
D
P
P
140
|
G
G
I
I
Q
Q
E
E
C
C
Y
Y
D
D
R
R
R
R
R
R
150
|
E
E
Y
Y
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
D
D
S
S
T
T
K
K
Y
Y
160
|
Y
Y
L
L
N
N
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
V
V
A
A
D
D
170
|
P
P
A
A
Y
Y
L
L
P
P
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
180
|
L
L
R
R
V
V
R
Q
V
V
P
P
T
T
T
T
G
G
I
I
190
|
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
P
P
F
F
D
D
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
V
V
200
|
I
I
F
F
R
R
M
M
V
V
D
D
V
V
G
G
G
G
Q
L
210
|
R
R
S
S
E
E
R
R
R
R
K
K
W
W
I
I
H
H
C
C
220
|
F
F
E
E
N
N
V
V
T
T
S
S
I
I
M
M
F
F
L
L
230
|
V
V
A
A
L
L
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
240
|
V
V
E
E
S
S
D
D
N
N
E
E
N
N
R
R
M
M
E
E
250
|
E
E
S
S
K
K
A
A
L
L
F
F
R
R
T
T
I
I
I
I
260
|
T
T
Y
Y
P
P
W
W
F
F
Q
Q
N
N
S
S
S
S
V
V
270
|
I
I
L
L
F
F
L
L
N
N
K
K
K
K
D
D
L
L
L
L
280
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
I
I
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
H
H
L
L
V
V
290
|
D
D
Y
Y
F
F
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
P
P
Q
Q
300
|
R
R
D
D
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
A
A
R
R
E
E
F
F
I
I
310
|
L
L
K
K
M
M
F
F
V
V
D
D
L
L
N
N
P
P
D
D
320
|
S
S
D
D
K
K
I
I
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
H
H
F
F
T
T
330
|
C
C
A
A
T
T
D
D
T
T
E
E
N
N
I
I
R
R
F
F
340
|
V
V
F
F
A
A
A
A
V
V
K
K
D
D
T
T
I
I
L
L
350
|
Q
Q
L
L
N
N
L
L
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
N
N
L
L
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Mel921 cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| Mel202 cells | Eye | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C301 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Activating mutations in Galphaq proteins, which form the a subunit of certain heterotrimeric G proteins, drive uveal melanoma oncogenesis by triggering multiple downstream signaling pathways, including PLC/PKC, Rho/Rac, and YAP. Here we show that the small GTPase ARF6 acts as a proximal node of oncogenic Galphaq signaling to induce all of these downstream pathways as well as beta-catenin signaling. ARF6 activates these diverse pathways through a common mechanism-the trafficking of GNAQ and beta-catenin from the plasma membrane to cytoplasmic vesicles and the nucleus, respectively. Blocking ARF6 with a small molecule reduces uveal melanoma cell proliferation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model, confirming the functional relevance of this pathway. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
