Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01096) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pyrvinium
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PYRVINIUM; Pyrvinum; 7187-62-4; pyrvinium (cation); HSDB 3178; UNII-6B9991FLU3; CHEBI:8687; 6B9991FLU3; 2-[(E)-2-(2,5-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrrol-3-yl)ethenyl]-N,N,1-trimethylquinolin-1-ium-6-amine; Pyrvinium ion; Pyrvinium cation; pyrvinium-pamoate; Pyrvinum (base); 6-(Dimethylamino)-2-(2-(2,5-dimethyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)ethenyl)-1-methylquinolinium; CHEMBL1201303; DTXSID2043795; ZINC3831401; DB06816; Quinolinium, 6-(dimethylamino)-2-(2-(2,5-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrrol-3-yl)vinyl)-1-methyl-; Quinolinium, 6-(dimethylamino)-2-(2-(2,5-dimethyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)ethenyl)-1-methyl-; C07412; AB00053809_02; Q264039; 2-[(E)-2-(2,5-dimethyl-1-phenyl-pyrrol-3-yl)vinyl]-N,N,1-trimethyl-quinolin-1-ium-6-amine; 6-(dimethylamino)-2-[(E)-2-(2,5-dimethyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)ethenyl]-1-methylquinolinium
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
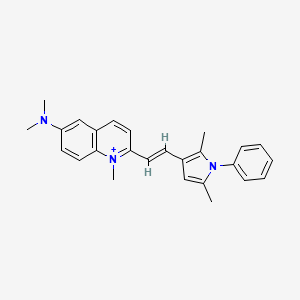
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C26H28N3+
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=CC(=C(N1C2=CC=CC=C2)C)/C=C/C3=[N+](C4=C(C=C3)C=C(C=C4)N(C)C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C26H28N3/c1-19-17-21(20(2)29(19)24-9-7-6-8-10-24)11-13-23-14-12-22-18-25(27(3)4)15-16-26(22)28(23)5/h6-18H,1-5H3/q+1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QMHSXPLYMTVAMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5 (LGR5) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Anaplastic thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Thyroid cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Thyroid | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.08E-05 Fold-change: 8.12E-02 Z-score: 4.47E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; ART sensitivity assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 cell proliferation assay; Flow cytometry | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pyrvinium pamoate can overcome artemisinin's resistance in anaplastic thyroid cancer. The resistance of CAL-62 to ART was related to the upregulation of the WNT signaling pathway. | |||
| Key Molecule: Wnt family member 7B (WNT7B) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Anaplastic thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Thyroid cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Thyroid | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.23E-19 Fold-change: 7.54E-02 Z-score: 9.46E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; ART sensitivity assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 cell proliferation assay; Flow cytometry | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pyrvinium pamoate can overcome artemisinin's resistance in anaplastic thyroid cancer. The resistance of CAL-62 to ART was related to the upregulation of the WNT signaling pathway. | |||
| Key Molecule: Frizzled class receptor 7 (FZD7) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Anaplastic thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; ART sensitivity assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 cell proliferation assay; Flow cytometry | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pyrvinium pamoate can overcome artemisinin's resistance in anaplastic thyroid cancer. The resistance of CAL-62 to ART was related to the upregulation of the WNT signaling pathway. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sclerostin (SOST) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Anaplastic thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; ART sensitivity assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 cell proliferation assay; Flow cytometry | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pyrvinium pamoate can overcome artemisinin's resistance in anaplastic thyroid cancer. The resistance of CAL-62 to ART was related to the upregulation of the WNT signaling pathway. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
