Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00818) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Gatifloxacin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Gatifloxacin; 112811-59-3; Tequin; Gatiflo; Zymar; AM-1155; Zymaxid; AM 1155; gatifloxacin anhydrous; CG 5501; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; BMS-206584; GTFX; BMS 206584-01; PD 135432; 1-Cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; Gatifloxacin hydrate; CHEMBL31; 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; PD-135432; CHEBI:5280; Gatilox; Gatiquin; Gatispan; 160738-57-8; Gaity; CG5501; MFCD00895399; NSC-758701; gatifloxin; NCGC00068236-02; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; DSSTox_CID_25704; DSSTox_RID_81076; DSSTox_GSID_45704; Gatifloxacin [USAN:INN]; Bonoq; Tymer; Zymer; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro- 8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)- 4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid,1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-; SMR000043336; Gatifloxacin (TN); Gatifloxacin (INN); CAS-112811-59-3; Zymer (TN); 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-; SR-01000610458; (3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-; gatifloxacino; gatifloxacinum; Gatifloxcin; Tequin in dextrose 5% in plastic container; AM-1155 (*Sesquihydrate*); Gatifloxacin & Gamma Interferon; Gatifloxacin,(S); (+-)-1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; CG-5501; Kinome_3137; Spectrum_001909; CPD000043336; PD135432; BMS-206584-01; Spectrum2_000487; Spectrum3_000999; Spectrum4_001127; Spectrum5_001468; Gatifloxacin (sesquihydrate); SCHEMBL22591; BSPBio_002697; KBioGR_001613; KBioSS_002448; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; MLS000040259; MLS000759493; MLS006011836; SPECTRUM1504272; SPBio_000353; Gatifloxacin Sesquihydrate,(S); DTXSID5045704; GTPL10816; KBio2_002442; KBio2_005010; KBio2_007578; KBio3_001917; HMS1922J15; HMS2090K10; HMS2093G06; HMS2233D20; HMS3259P06; HMS3372J10; HMS3372J12; HMS3715N03; Pharmakon1600-01504272; ALBB-028535; AMY17781; BCP13408; RKL10068; Tox21_110984; BBL010485; BDBM50117914; CCG-39529; NSC758701; s1340; STK801620; C19H22FN3O4.1.5H2O; AKOS004119932; AKOS016340697; Tox21_110984_1; AC-1944; CS-1841; DB01044; KS-1066; MCULE-4557972261; NC00702; NSC 758701; NCGC00068236-03; NCGC00068236-04; NCGC00068236-05; NCGC00068236-06; NCGC00068236-07; NCGC00068236-08; NCGC00095126-01; NCGC00095126-02; NCGC00178525-01; BMS-20658401; HY-10581; SBI-0206764.P001; DB-019145; Gatifloxacin 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; FT-0626635; FT-0631189; FT-0668952; G0325; C07661; D08011; G-2380; AB00171654-13; AB00171654-14; AB00171654_16; AB00171654_17; 811G593; A802657; Gatifloxacin, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only; Q2365016; SR-01000610458-2; SR-01000610458-3; BRD-A74980173-001-02-8; BRD-A74980173-001-06-9; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic a; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazino)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
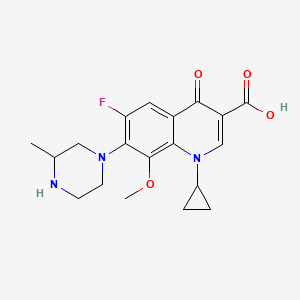
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial DNA gyrase (Bact gyrase) |
GYRA_STAAU
; GYRB_STAAU |
[1] | ||
| Staphylococcus Topoisomerase IV (Stap-coc parC) | PARC_STAAS | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H22FN3O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1CN(CCN1)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2OC)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C4CC4)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H22FN3O4/c1-10-8-22(6-5-21-10)16-14(20)7-12-15(18(16)27-2)23(11-3-4-11)9-13(17(12)24)19(25)26/h7,9-11,21H,3-6,8H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XUBOMFCQGDBHNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit A (GYRA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G280A (c.D94N) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit A (GYRA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A281G (c.D94G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit A (GYRA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G280T (c.D94Y) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit A (GYRA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G262T (c.G88C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit B (GYRB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A1495G (c.N499D) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit B (GYRB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C1497A (c.N499K) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit B (GYRB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C1497G (c.N499K) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit B (GYRB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycolicibacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A1503C (c.E501D) |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes are the main mechanisms of Gatifloxacin (GAT) resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
