Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00630) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
AP26113
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AP26113; 1197958-12-5; ALK-IN-1; Brigatinib-analog; (2-((5-chloro-2-((4-(4-(dimethylamino)piperidin-1-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)phenyl)dimethylphosphine oxide; UNII-3DGD69C6PV; AP26113-analog; 5-chloro-2-N-[4-[4-(dimethylamino)piperidin-1-yl]-2-methoxyphenyl]-4-N-(2-dimethylphosphorylphenyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; 3DGD69C6PV; CHEMBL3397300; 1197958-12-5 (analog); 5-Chloro-N~2~-{4-[4-(dimethylamino)piperidin-1-yl]-2-methoxyphenyl}-N~4~-[2-(dimethylphosphoryl)phenyl]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; 2,4-Pyrimidinediamine, 5-chloro-N2-(4-(4-(dimethylamino)-1-piperidinyl)-2-methoxyphenyl)-N4-(2-(dimethylphosphinyl)phenyl)-; 2,4-Pyrimidinediamine, 5-chloro-N2-[4-[4-(dimethylamino)-1-piperidinyl]-2-methoxyphenyl]-N4-[2-(dimethylphosphinyl)phenyl]-; Brigatinib analog; 5-Chloro-N2-(4-(4-(dimethylamino)piperidin-1-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl)-N4-(2-(dimethylphosphoryl)phenyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; 5-CHLORO-N2-{4-[4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)PIPERIDIN-1-YL]-2-METHOXYPHENYL}-N4-[2-(DIMETHYLPHOSPHORYL)PHENYL]PYRIMIDINE-2,4-DIAMINE; Brigatinib(AP26113); C26H34ClN6O2P; SCHEMBL11916416; DTXSID30725416; EX-A770; AP26113;ALK-IN-1; HMS3652H14; HMS3673I09; BCP06648; 2218AH; BDBM50062357; MFCD23704187; NSC776763; NSC800977; s7000; ZINC89630357; AKOS025401944; AKOS032949980; AP 26113-analog, Brigatinib-analog; CCG-264698; CS-1368; NSC-776763; NSC-800977; SB16487; NCGC00351602-02; NCGC00351602-05; NCGC00351602-09; 5-Chloro-N2-(4-(4-(dimethylamino)-1-piperidinyl)-2-methoxyphenyl)-N4-(2-(dimethylphosphinyl)phenyl)-2,4-pyrimidinediamine; AC-27470; AS-75104; DA-35325; HY-13464; QC-11659; FT-0696829; SW219566-1; Q4653190; E5J
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
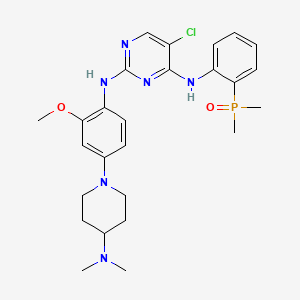
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | ALK_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C26H34ClN6O2P
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN(C)C1CCN(CC1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)NC3=NC=C(C(=N3)NC4=CC=CC=C4P(=O)(C)C)Cl)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C26H34ClN6O2P/c1-32(2)18-12-14-33(15-13-18)19-10-11-21(23(16-19)35-3)30-26-28-17-20(27)25(31-26)29-22-8-6-7-9-24(22)36(4,5)34/h6-11,16-18H,12-15H2,1-5H3,(H2,28,29,30,31)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
OVDSPTSBIQCAIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger C3HC-type containing 1 (ZC3HC1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | NPM-ALK-Positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.8] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 |
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For KARPAS-299-derived cell lines, we observed oncogene overexpression as the main resistance mechanism, whereas in SUP-M2-derived cell lines, we identified several point mutations located within the NPM-ALK kinase domain, which could explain drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger C3HC-type containing 1 (ZC3HC1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | NPM-ALK-Positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.8] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.L1122V+p.139S+p.F1174V+p.L1196M+p.L1198F+p.S1206C+p.L1122V+p.L1196M+p.F1174V+p.L1198F+p.L1196M+p.D1203N |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 |
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For KARPAS-299-derived cell lines, we observed oncogene overexpression as the main resistance mechanism, whereas in SUP-M2-derived cell lines, we identified several point mutations located within the NPM-ALK kinase domain, which could explain drug resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
