Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00577) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ritonavir
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ritonavir; 155213-67-5; Norvir; ABT-538; Abbott 84538; A-84538; ABBOTT-84538; ABT 538; RTV; UNII-O3J8G9O825; CHEBI:45409; 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[methyl-[(2-propan-2-yl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]carbamoyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl]carbamate; O3J8G9O825; MFCD00927142; NSC693184; NSC-693184; 2,7,10,12-Tetraazatridecanoic acid, 4-hydroxy-12-methyl-9-(1-methylethyl)-13-[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]-8,11-dioxo-3,6-bis(phenylmethyl)-, 5-thiazolylmethyl ester, (3S,4S,6S,9S)-; thiazol-5-ylmethyl ((2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-((S)-2-(3-((2-isopropylthiazol-4-yl)methyl)-3-methylureido)-3-methylbutanamido)-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl)carbamate; NCGC00159462-02; NCGC00183130-01; Norvir Softgel; DSSTox_CID_28553; DSSTox_RID_82825; DSSTox_GSID_48627; N-[(2S,4S,5S)-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenyl-5-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}hexan-2-yl]-N~2~-(methyl{[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)-L-valinamide; RIT; ABT538; DRG-0244; 2,4,7,12-Tetraazatridecan-13-oic acid, 10-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-1-(2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl)-3,6-dioxo-8,11-bis(phenylmethyl)-, 5-thiazolylmethyl ester, (5S-(5R*,8R*,10R*,11R*))-; SMR000466395; thiazol-5-ylmethyl (2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-((S)-2-(3-((2-isopropylthiazol-4-yl)methyl)-3-methylureido)-3-methylbutanamido)-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-ylcarbamate; thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(1S,2S,4S)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-[[(2S)-2-[[(2-isopropylthiazol-4-yl)methyl-methyl-carbamoyl]amino]-3-methyl-butanoyl]amino]-5-phenyl-pentyl]carbamate; Norvir (TM); Norvir (TN); CAS-155213-67-5; HSDB 7160; 1,3-Thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(2S,3S,5R)-3-hydroxy-5-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[methyl-[(2-propan-2-yl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]carbamoyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]-1,6-diphenyl-hexan-2-yl]carbamate; Ritonavirum; TMC 114r; Empetus; Ritomune; Ritovir; Viekirax; Viriton; 1hxw; 3prs; 3tne; 4eyr; Ritonavir [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; Ritonavir- Bio-X; 2,4,7,12-Tetraazatridecan-13-oic acid, 10-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-1-[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]-3,6-dioxo-8,11-bis(phenylmethyl)-, 5-thiazolylmethyl ester, [5S-(5R*,8R*,10R*,11R*)]-; Ritonavir & PLGA; 5-Thiazolylmethyl ((alphaS)-alpha-((1S,3S-1-hydroxy-3-((2S)-2-(3-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)-3-methylureido)-3-methylbutyramido)-4-phenylbutyl)phenethyl)carbamate; 1sh9; Abbot 84538; CHEMBL163; SCHEMBL6679; Ritonavir (JAN/USP/INN); BIDD:PXR0023; 5-Thiazolylmethyl ((alphaS)-alpha-((1S,3S)-1-hydroxy-3-((2S)-2-(3-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)-3-methylureido)-3-methylbutyramido)-4-phenylbutyl)phenethyl)carbamate; MLS000759541; MLS001424063; MLS006011764; BIDD:GT0387; GTPL8804; DTXSID1048627; Ritonavir, >=98% (HPLC); AOB1044; HMS2051B08; HMS2235O10; HMS3715L22; Pharmakon1600-01502391; Ritonavir related compounds mixture; ZINC3944422; Tox21_112969; Tox21_113431; AC-733; BDBM50088504; NSC760369; s1185; STK634209; AKOS000280930; Ritonavir & Poly-lactide-co-glycolide; Tox21_112969_1; CCG-101007; CS-0432; DB00503; KS-5017; MCULE-9029064305; NC00257; NSC 693184; NSC 760369; NSC-760369; MRF-0000287; NCGC00159462-03; NCGC00159462-04; NCGC00159462-07; NCGC00159462-20; Ritonavir 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; BR164353; HY-90001; MLS000759541-02; R0116; SW197637-2; C07240; D00427; AB00639991-06; AB00639991-08; AB00639991_09; AB00639991_10; 213R675; A 84538; A904691; Q422618; J-009178; BRD-K51485625-001-07-6; Ritonavir solution, 1.0 mg/mL in acetonitrile, certified reference material; (2S, 3S, 5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinvl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S )-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl) methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl) methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-MethyI-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1.6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl) methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino )-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1 .6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1,6-diphenyl-3hydroxyhexane; (2S,3S,5S)-5-(N-(N-((N-Methyl-N-((2-isopropyl-4-thiazolyl)methyl)amino)carbonyl)valinyl)amino)-2-(N-((5-thiazolyl)methoxycarbonyl)amino)-1.6-diphenyl-3-hydroxyhexane; 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-[(2S)-3-methyl-2-{[methyl({[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl})carbamoyl]amino}butanamido]-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl]carbamate; 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[methyl-[(2-propan-2-yl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]carbamoyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]-1,6-di(phenyl)hexan-2-yl]carbamate; 5-Thiazolylmethyl (3S,4S,6S,9S)-4-hydroxy-12-methyl-9-(1-methylethyl)-13-[2-(1-methylethyl)-4-thiazolyl]-8,11-dioxo-3,6-bis(phenylmethyl)-2,7,10,12-tetraazatridecanoate; N-[(2S,4S,5S)-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenyl-5-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}hexan-2-yl]-N(2)-(methyl{[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)-L-valinamide; N1-((1S,3S,4S)-1-benzyl-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-4-{[(1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}pentyl)-N2-{[[(2-isopropyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl](methyl)amino]carbonyl}-L-valinamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
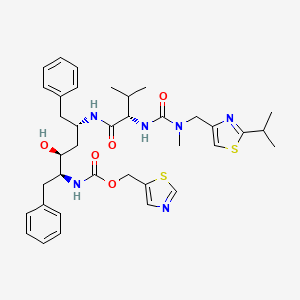
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Human immunodeficiency virus Protease (HIV PR) | POL_HV1B1 | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C37H48N6O5S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)C1=NC(=CS1)CN(C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)C[C@@H]([C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)OCC4=CN=CS4)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C37H48N6O5S2/c1-24(2)33(42-36(46)43(5)20-29-22-49-35(40-29)25(3)4)34(45)39-28(16-26-12-8-6-9-13-26)18-32(44)31(17-27-14-10-7-11-15-27)41-37(47)48-21-30-19-38-23-50-30/h6-15,19,22-25,28,31-33,44H,16-18,20-21H2,1-5H3,(H,39,45)(H,41,47)(H,42,46)/t28-,31-,32-,33-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NCDNCNXCDXHOMX-XGKFQTDJSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: HIV1 Reverse transcriptase (HIV1 RT) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.G48T+p.L89M |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Molecular dynamics simulation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The decrease in van der Waals interactions of inhibitors with the mutated PR relative to the wild-type (WT) PR mostly drives the drug resistance of mutations toward these four inhibitors. The energy decomposition analysis further indicates that the drug resistance of mutations can be mainly attributed to the change in van der Waals and electrostatic energy of some key residues (around Ala28/Ala28' and Ile50/Ile50'). Our work can give significant guidance to design a new generation of anti-AIDS inhibitors targeting PR in the therapy of patients with HIV-1 infection. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
